All my walks have sold out, however I have had a request to run the “South Bank – Marsh, Industry, Culture and the Festival of Britain” walk on a weekday, so have added a walk on Thursday, the 9th of November, which can be booked here.
For this week’s post, I am in Watney Market and Watney Street in Shadwell. A street that runs between Cable Street and Commercial Road.
It is a rather long post, however the post does what I really love about writing the blog. It takes one of my father’s photos and with some digging discovers so much about life in the area of a single street.
East London poverty, the relationship with the River Thames, a market that has traded for many years, a lost pub, Blackshirts, post-war Germany and post-war redevelopment which erased a long familiar street.
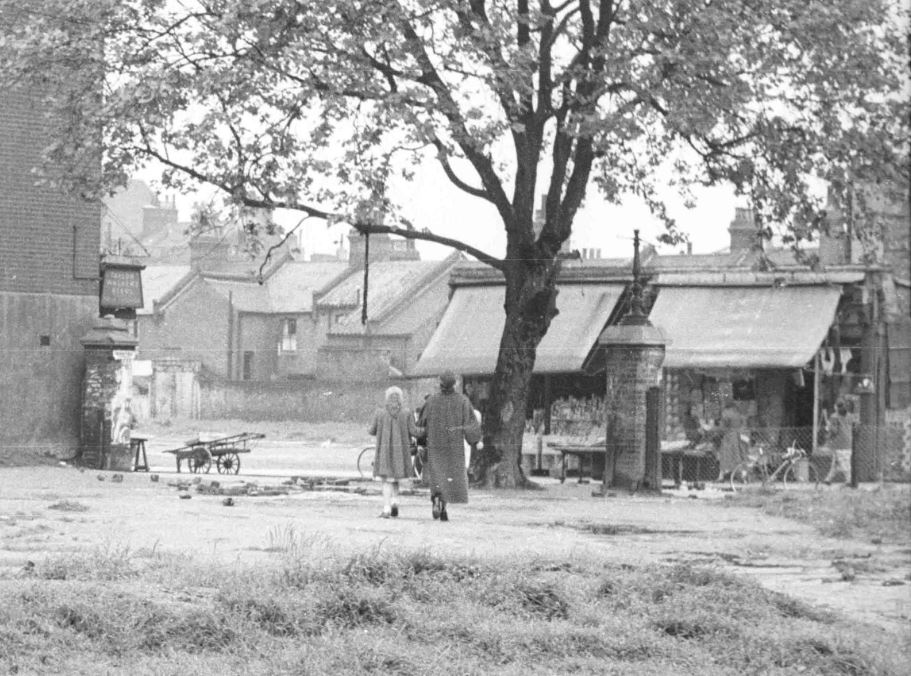
This is the photo, taken by my father in 1952:

As c;lose as I could get to the same view today:
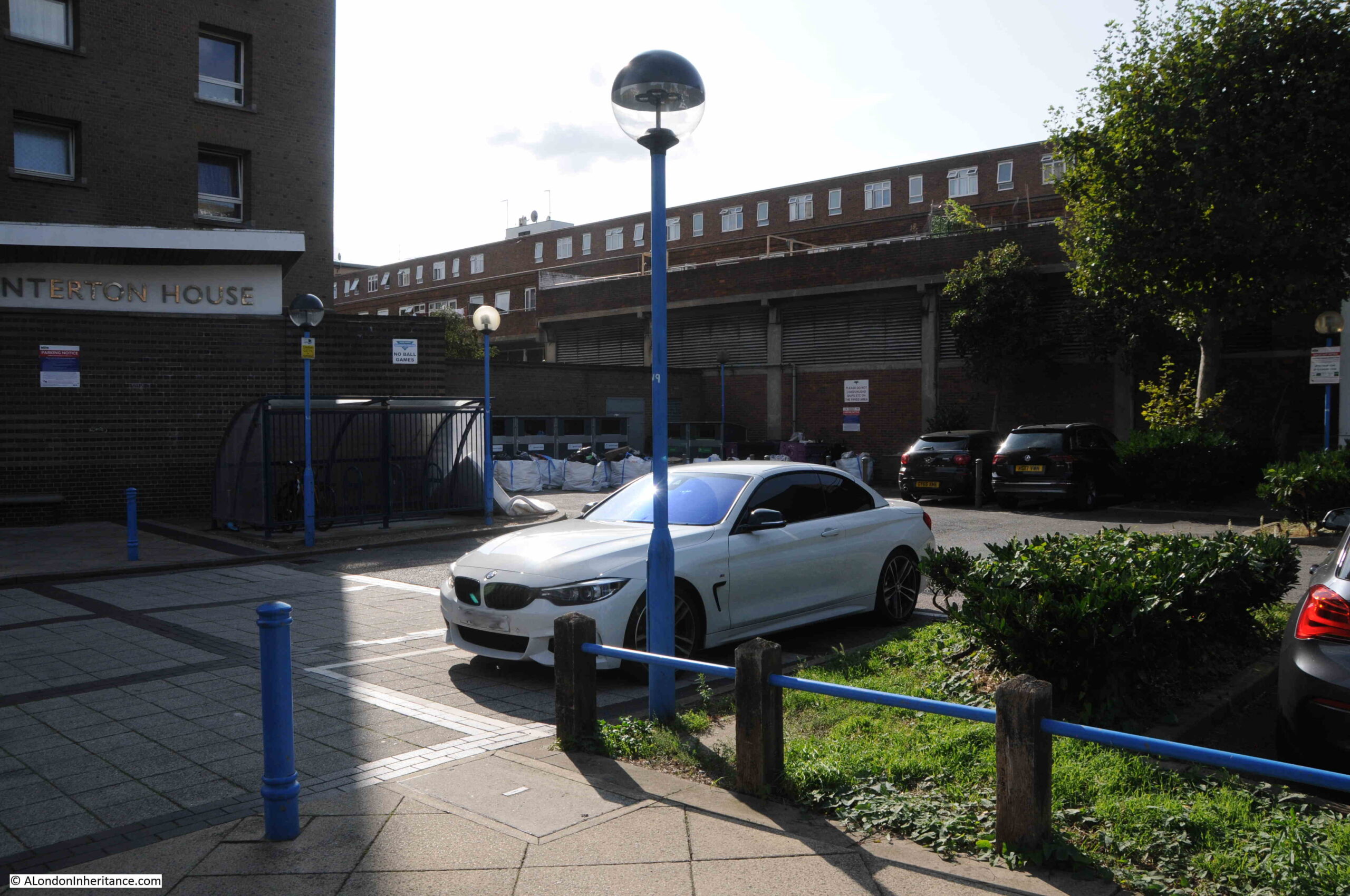

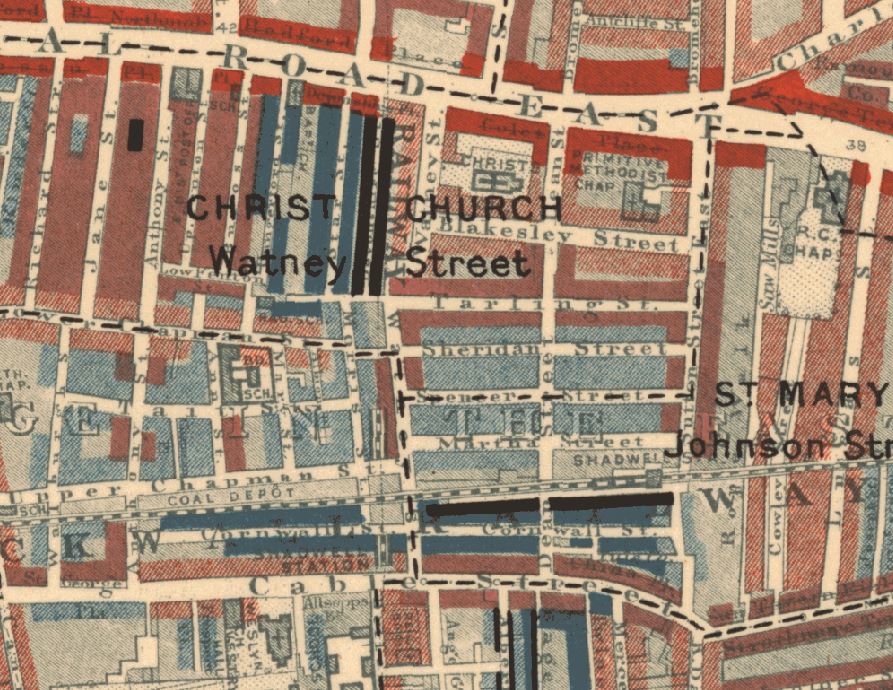
My father’s photo was taken from the bombed space once occupied by a church, and it was looking southwest towards a pub, the Masons Arms, which faced onto Watney Street and Watney Market.
The following extract from the 1952 photo shows on the left, the large sign or perhaps a lantern on the front of the pub and two of the remaining shops which seem to have part survived the bombing which destroyed the area around them.

I have marked the spot with the red circle in the following map of the area today ( © OpenStreetMap contributors):
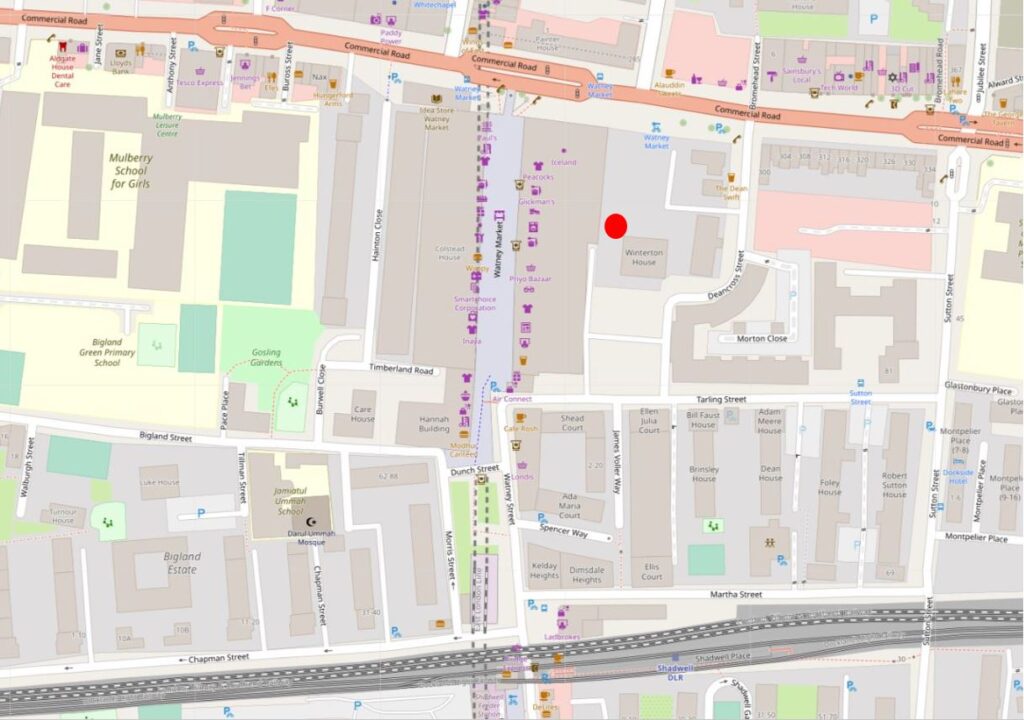
Commercial Road is the road running left to right at the top of the map. The train tracks at the bottom of the map is the Docklands Light Railway. Watney Street is running from the junction with Commercial Road at the top centre of the map, down to the DLR where it heads under the railway, down to Cable Street which is just below the bottom of the map
The following map is from the 1948 revision of the OS map, and shows the area much as it was when my father took the photo, from the location of the red dot (‘Reproduced with the permission of the National Library of Scotland“).:
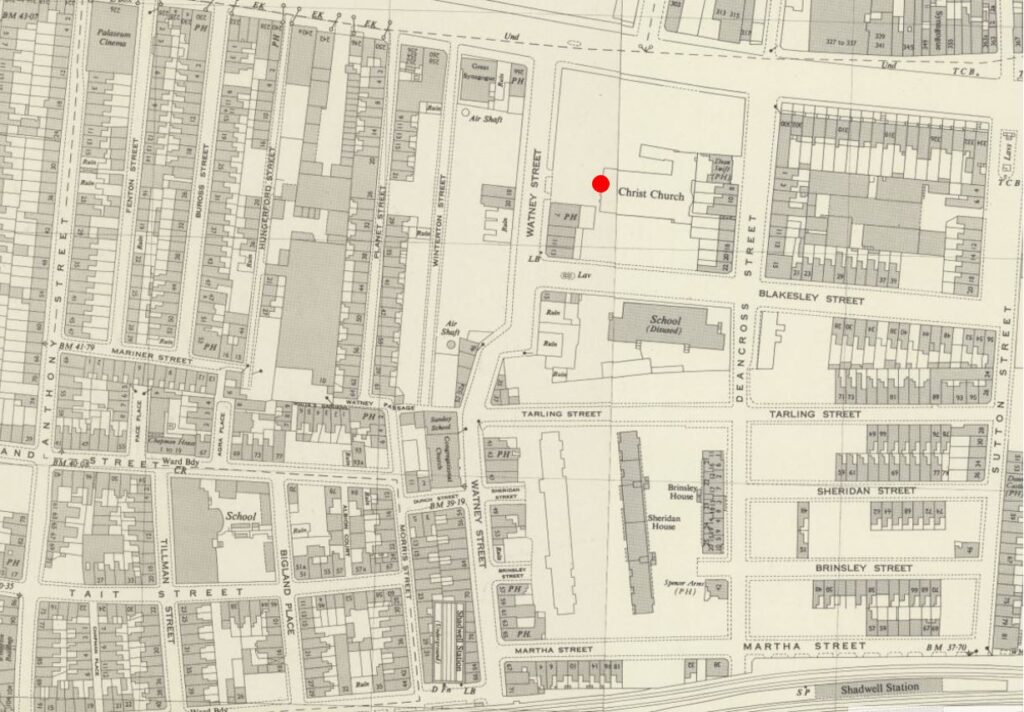
I have mapped some of the key features in the photo onto the map below.
- The red line and arrow points from the Masons Arms pub in the photo to the pub in the map
- The blue line and arrow points from the two remaining shops in this section of Watney Street to their location on the map
- The yellow oval is around one of the pillars that originally stood either side of the main entrance into the open space in front of the church
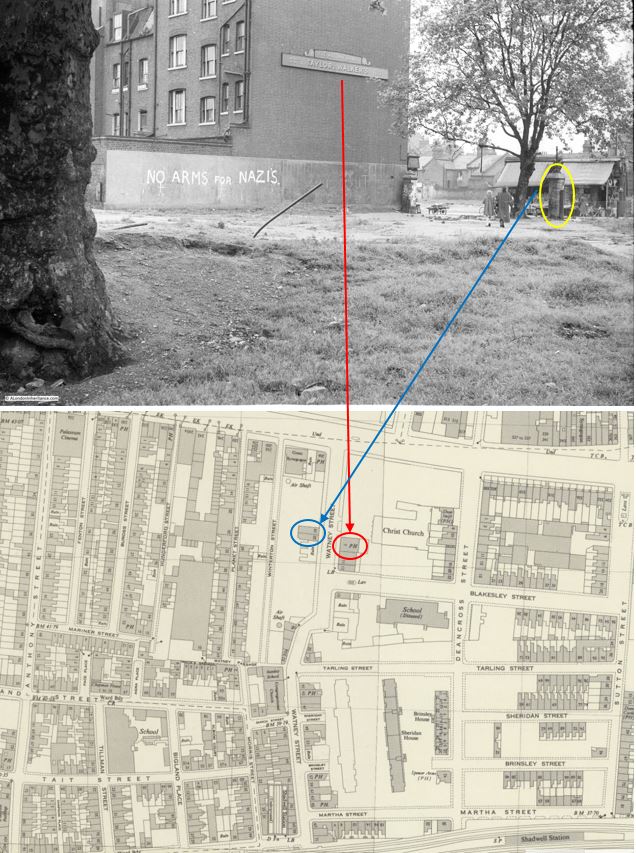
In the above maps, you will see that my father was standing in front of the outline of Christ Church.
These were the ruins of a church that had been very badly damaged by bombing in 1941, and had then been demolished. It was not rebuilt, and the land was integrated into the post war redevelopment.
The church was not that old. The foundation stone was laid on the 11th of March, 1840, with the land being the site of three former houses on land owned by the Mercers Company, who conveyed the land to the church.
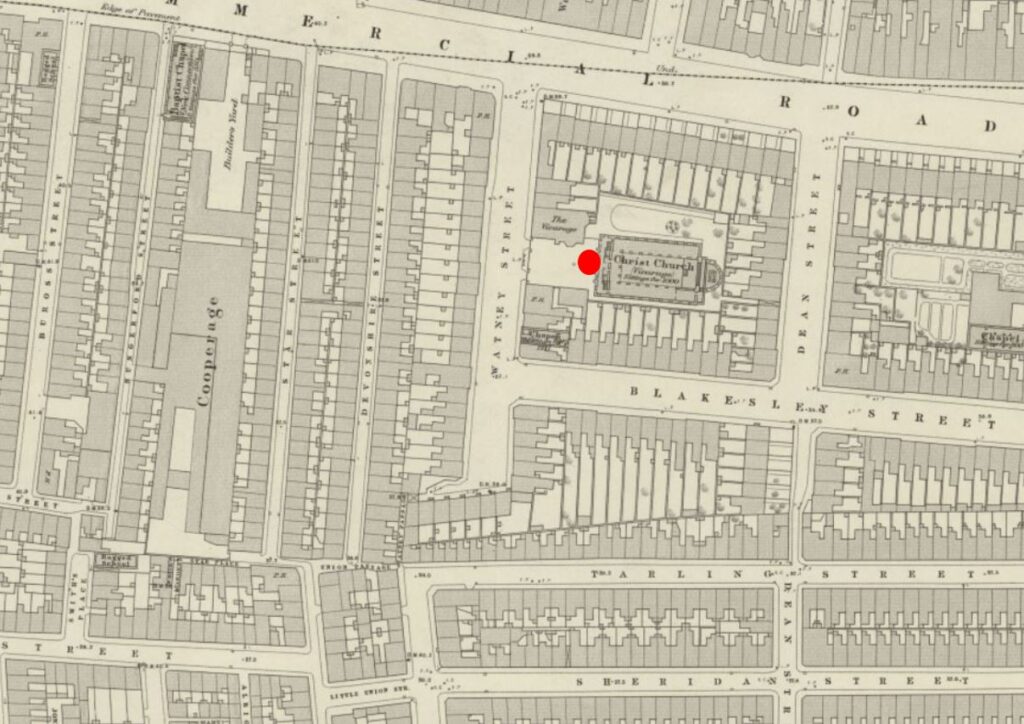
The site of the church, and the surrounding housing, before wartime bombing and post war redevelopment obliterated the area is shown in the following extract from the 1914 revision of the OS map (again the red circle indicates where my father was standing to take the photo) (‘Reproduced with the permission of the National Library of Scotland“).:
In my father’s photo, the slogan “No arms for Nazis” is painted on the wall running alongside the pub. This slogan represented a concern about the level of Nazi sympathies still remaining in Germany, rearming Germany, and the need to integrate Germany into the wider European community.
In 1953, British security services had made several arrests, and the US had undertaken a survey which revealed that the undercurrents of Nazi-ism in Germany should be taken seriously. It was claimed that the growth of “nationalistic discontent among young men is ominous”.
There was unemployment in Germany and economic grievances were being intensified by the numbers of refuges from the Eastern Zone.
At the time, Germany was not considered an equal partner with other countries in western Europe, and, to quote papers of the time “And the vagueness of British policy, the passive attitude of the Tories towards European co-operation – which they encouraged with words when not in power – has done nothing to speed things up”.
This had already been going on for some years, and when the German Chancellor, Konrad Adenauer was in London in December 1951, he was met by a demonstration when he arrived in Downing Street for a lunch with Churchill.
He was met with cries of “Adenauer go home”, “Sieg heil” and “Heil Hitler”.
Adenaur had been an opponent of the Nazis and had only just survived the war as he had lost all his property, money and position in the 1930s.
He was strongly anti-communist, wanted cooperation within Europe and the US, wanted to start the rearming of Germany, and he had earlier ended the de-Nazification process.
He was part of the negotiations that led to the Treaty of Paris in 1951, which established the European Coal and Steel Community (the predecessor of the European Union), not a popular move in Germany as it was seen to give France too much influence over German industry.
Adenaur also ensured that West Germany joined NATO in May 1955, and secured agreement for Germany to rearm (although agreeing that Germany would not have nuclear weapons).
When Adenaur visited Downing Street in 1951, leaflets were handed out to the crowd with the words “No arms for Nazis”. These leaflets, and the slogan were part of a campaign by the London Peace Council, based at New Compton Street, W.C.2.
The slogan appeared at many sites across London, and also across the country, for example an article in the East Kent Times reported that in Ramsgate “Motorists and residents were startled to see on the parapet of the viaduct, high above the main Margate Road, the words ‘No arms for Nazis’ painted in large white capitals.”
The use of white paint and capital letters seems to have been standard for where the slogan was found.
The slogan was on the wall that ran alongside the Masons Arms pub. The pub seems to date from the mid 19th century and features in numerous newspaper reports. All the usual issues of crime, drunkenness, change in licensee, meetings etc.
There were a couple of reports which gave an insight into life in 19th century London and the River Thames.
From the Kentish Gazette on the 17th of May, 1859:
“ENROLMENT OF NAVAL WOLUNTEERS – The recruiting officers of the Royal Navy had quite a field-day on the river of Tuesday. A steam boat, profusely decorated with union jacks, ensigns and other national colours, and manned by a dashing crew of blue jackets, with a powerful band on board, left the London-bridge-wharf shortly after eleven o’clock for a cruise down the river. The steamer on her paddle-box bore the words ‘Queen’s bounty’ and on her sides fore and aft, ‘£10 able seamen, £5 ordinary seamen’.
On leaving the band struck up ‘Hearts of Oak’. The sailors gave a most deafening cheer, which was taken up by the vast multitude which lined London-bridge and crowded the water side. The trip was continued to Gravesend, where the blue jackets landed and paraded through the principle thoroughfares, and the proclamation being frequently read. A vast crowd followed the recruiting party, and during their stay the town was kept in a most lively state of excitement. many volunteers were received and numbers promised to present themselves at the rendezvous on Tower-hill. Owing, however to the long prevalence of easterly winds there were not so many first class seamen in port, a large fleet of homeward-bounders being detained in the Channel.
As far as it has gone, however this new popular mode of beating up naval recruits has answered admirably; and the Masons Arms, Watney Street, Commercial Road (situated in a locality crowded with sailors), has been opened as a rendezvous. A change in wind must bring in large numbers of first-class men, who will doubtless avail themselves of the £10 bounty.”
There is so much in the above article. It tells us that in the mid 19th century:
- Large numbers of sailors lived around Watney Street
- Ships still being mainly powered by the wind could be stuck in the channel with an easterly wind as they could not round the eastern edge of Kent to access the Thames Estuary
- That the Thames and the London Docks were a very important part in the life of London
As with most other East London pubs, inquests into unexpected and accidental deaths would be held in the Masons Arms. A newspaper report from October 1841 tells the story of 34 year old James Holland who worked as a coal-whipper (a coal-whipper brought up the coal from below decks using baskets attached to a pulley system).
He was working on the “Three Sons”, a collier from Sunderland which was moored in the river off Rotherhithe and whilst filling a basket with coal, he collapsed with blood pouring from his mouth and nose, and died almost immediately.
At the inquest in the Masons Arms, the verdict was “Died by a visitation of God”. No reference to his working conditions, long exposure to coal dust etc.
Time to have a look at Watney Street. The street has almost completely been rebuilt, with only a couple of pre-war buildings remaining at the very southern part of the street.
The alignment of the northern half of the street changed, and it has been rebuilt with new tiered housing on either side of a central raised section where the market is now located.
Walking along Commercial Road, this is the first view of Watney Street and Market:
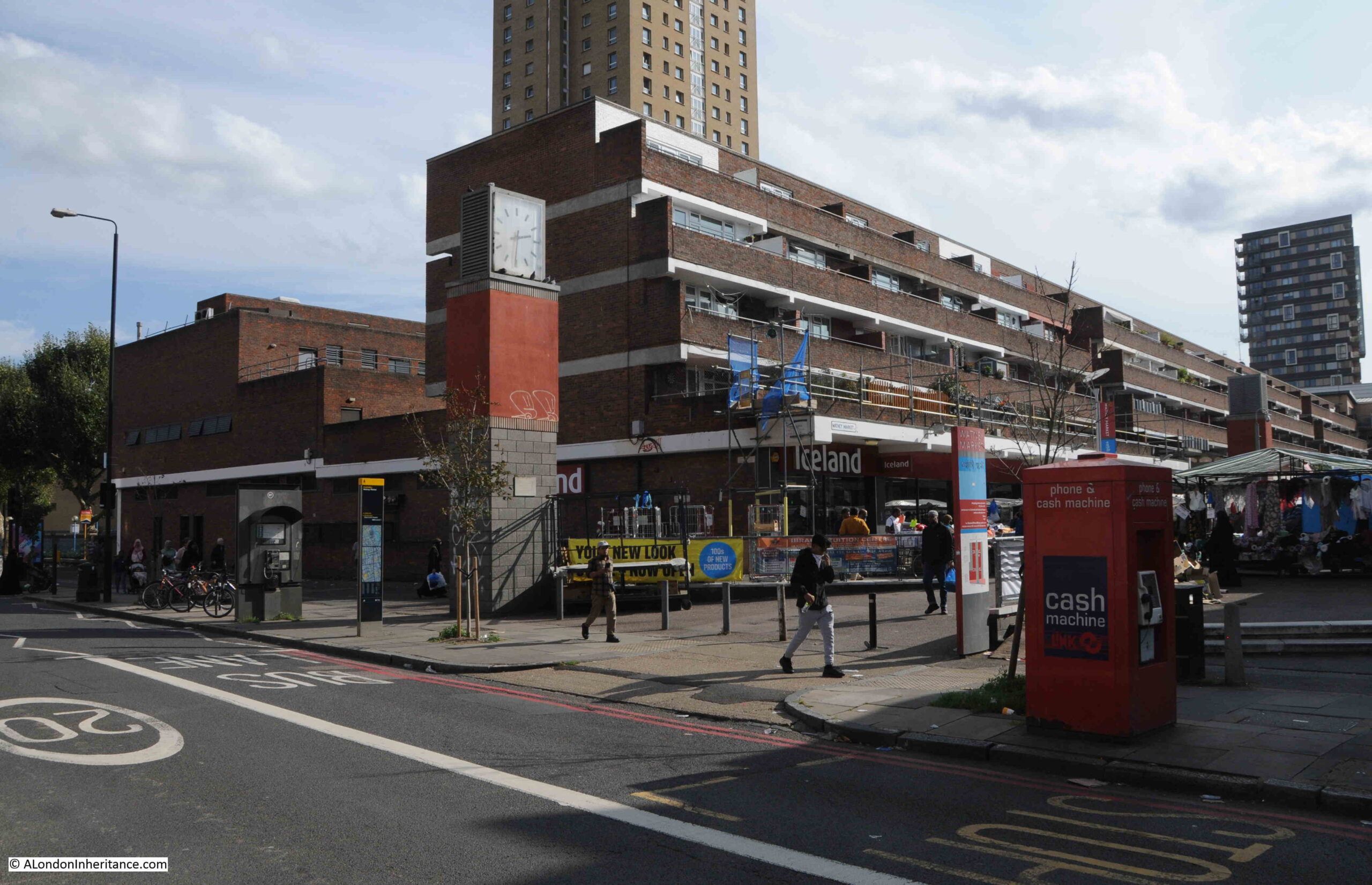

To the east of the entrance to the market is a clock tower:
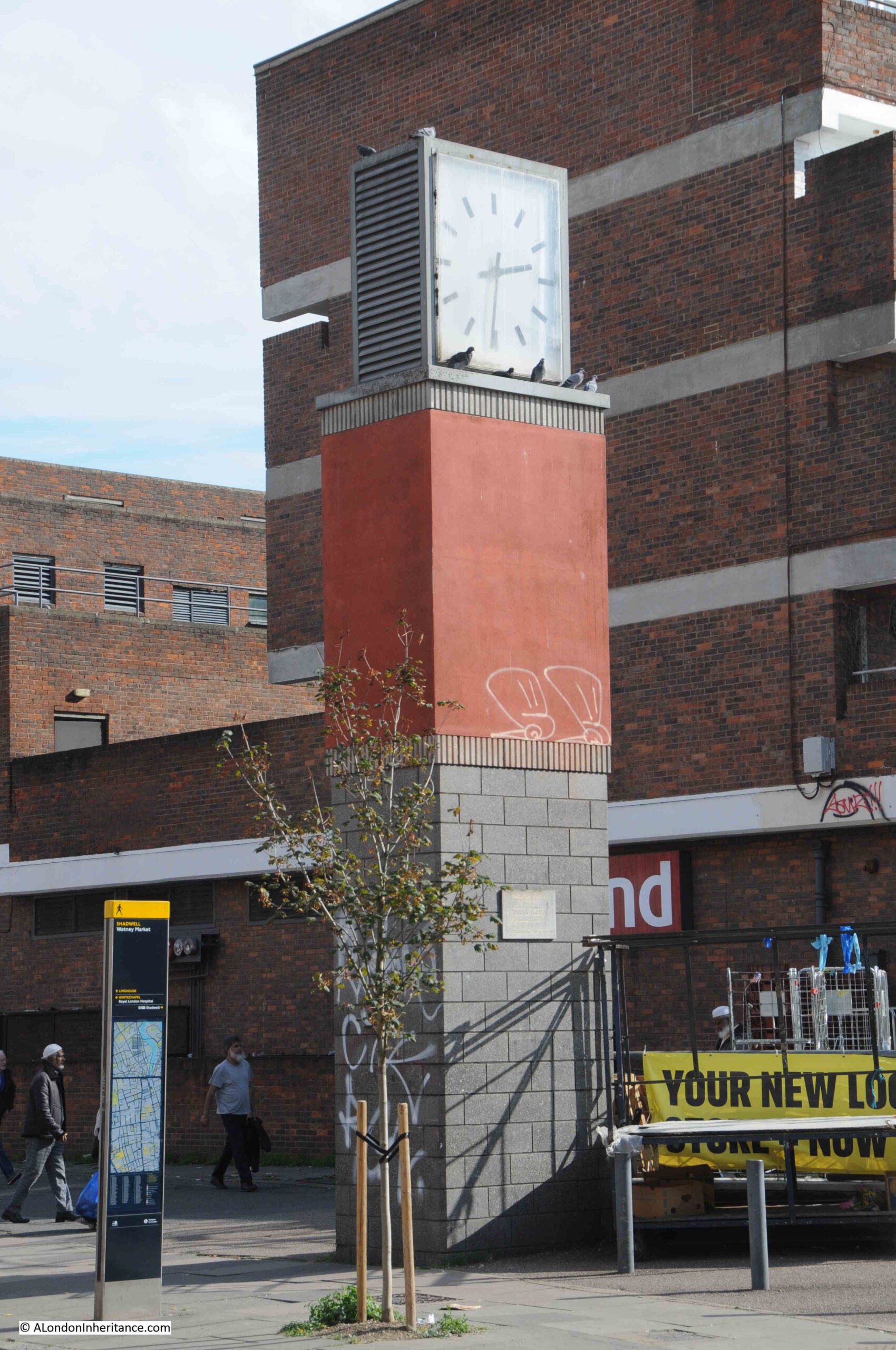

Which has a plaque mounted on the side:

The plaque recalls a dreadful tragedy when three workers died on the 22nd of September, 1990. At the time, they were investigating a blockage in a drain. There were four workers involved. One of them had descended into the drain which was at the bottom of a 9ft shaft. He was overcome by fumes, and in an attempt to rescue him, two other descended the shaft, but were in turn overcome by fumes.
The Fire Brigade was called, and firemen wearing breathing apparatus descended the shaft and pulled the three men out. The man who remained at the top of the shaft was also affected by fumes from the sewer.
It turned out they they have been overcome by hydrogen sulphide gas, and the three who descended all died.
They were not provided with any safety equipment, gas monitoring or breathing equipment, ropes and harnesses etc. and had received no training to undertake such work. It was the type of accident that would have happened in 1890 rather than 1990.
The three who died were trainee electrician Paul Richardson (aged 17), his brother trainee plumber David Richardson (aged 19) and electrician Steven Hammond (aged 32).
Their employer was fined £50,000 which even at the time seemed a ridiculously low amount for the loss of three lives in such avoidable circumstances.
A dreadfully sad loss of life which so easily could have been prevented if they had been provided with the correct equipment and training.
This is the view looking down into Watney Market from Commercial Road:
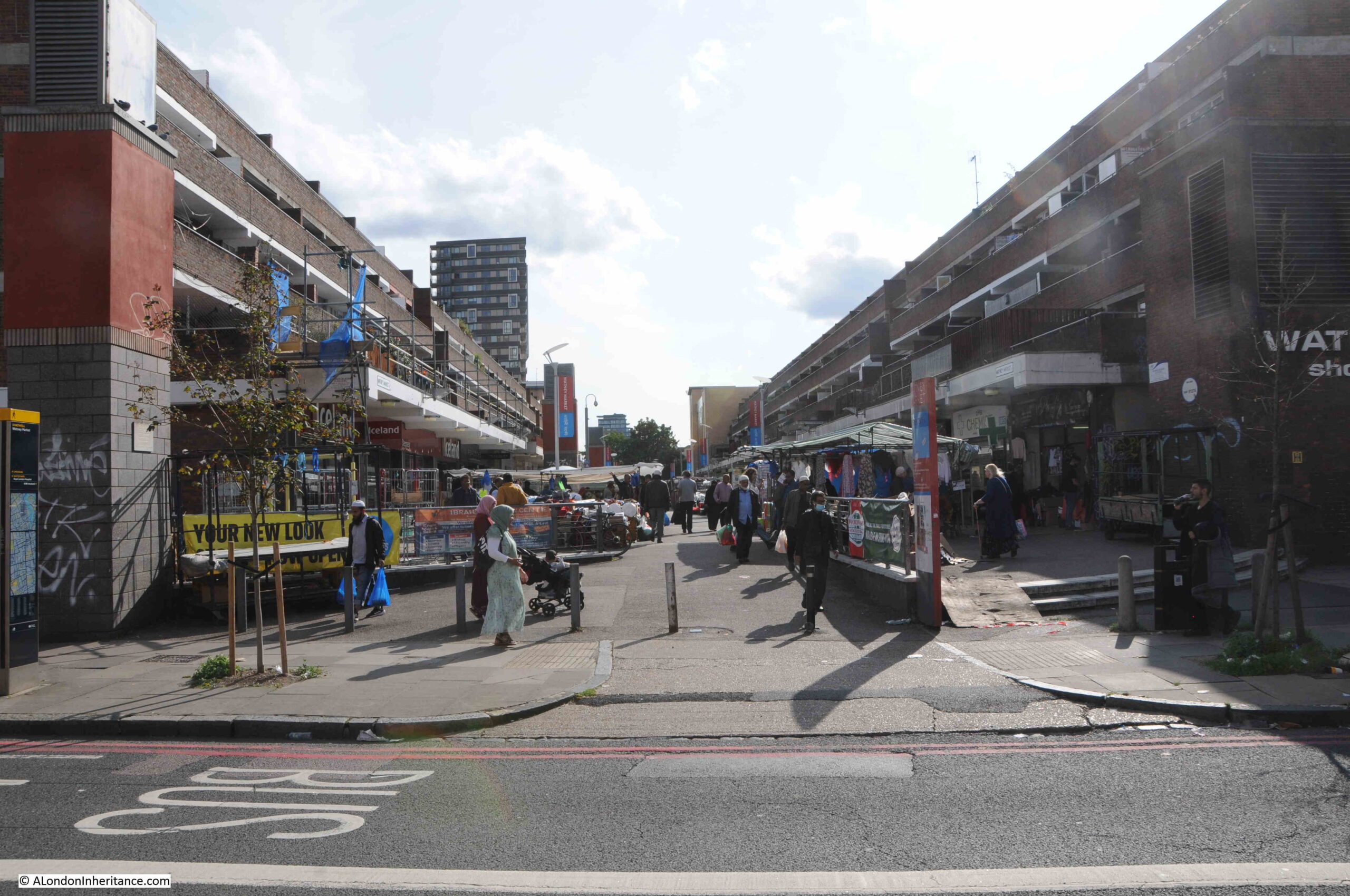

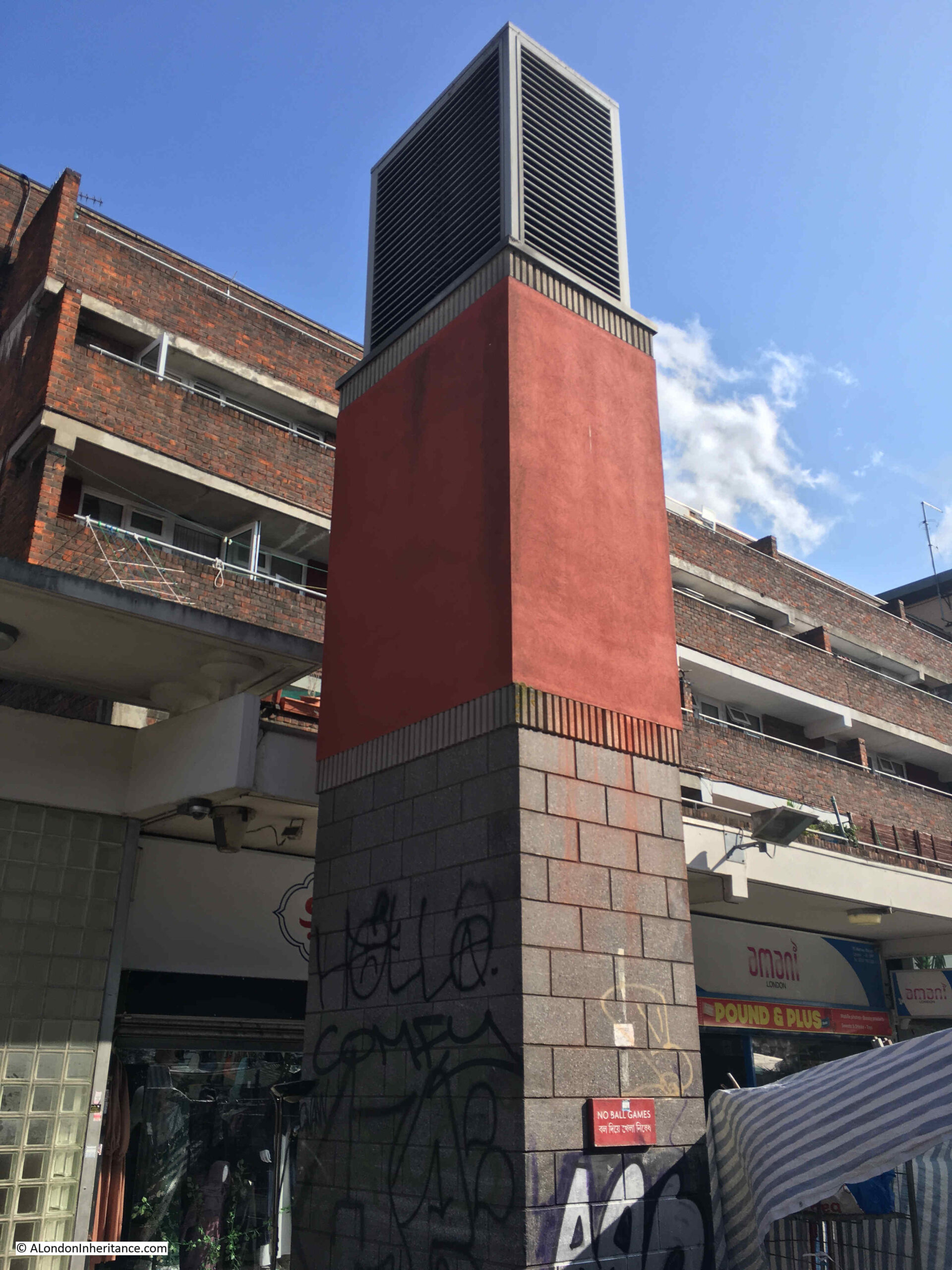
The London Overground between Shadwell and Whitechapel runs beneath Watney Market. If you go back to the 1952 OS map of the area, to the upper left of the original routing of Watney Street, just below Commercial Road, there is a circle with the words “Air Shaft”.
This was a ventilation shaft for the railway which runs just below the surface. In the rebuilt market, the above ground infrastructure of the airshaft can be seen, which is also used to advertise Watney Market:

View looking through the market back up to Commercial Road:
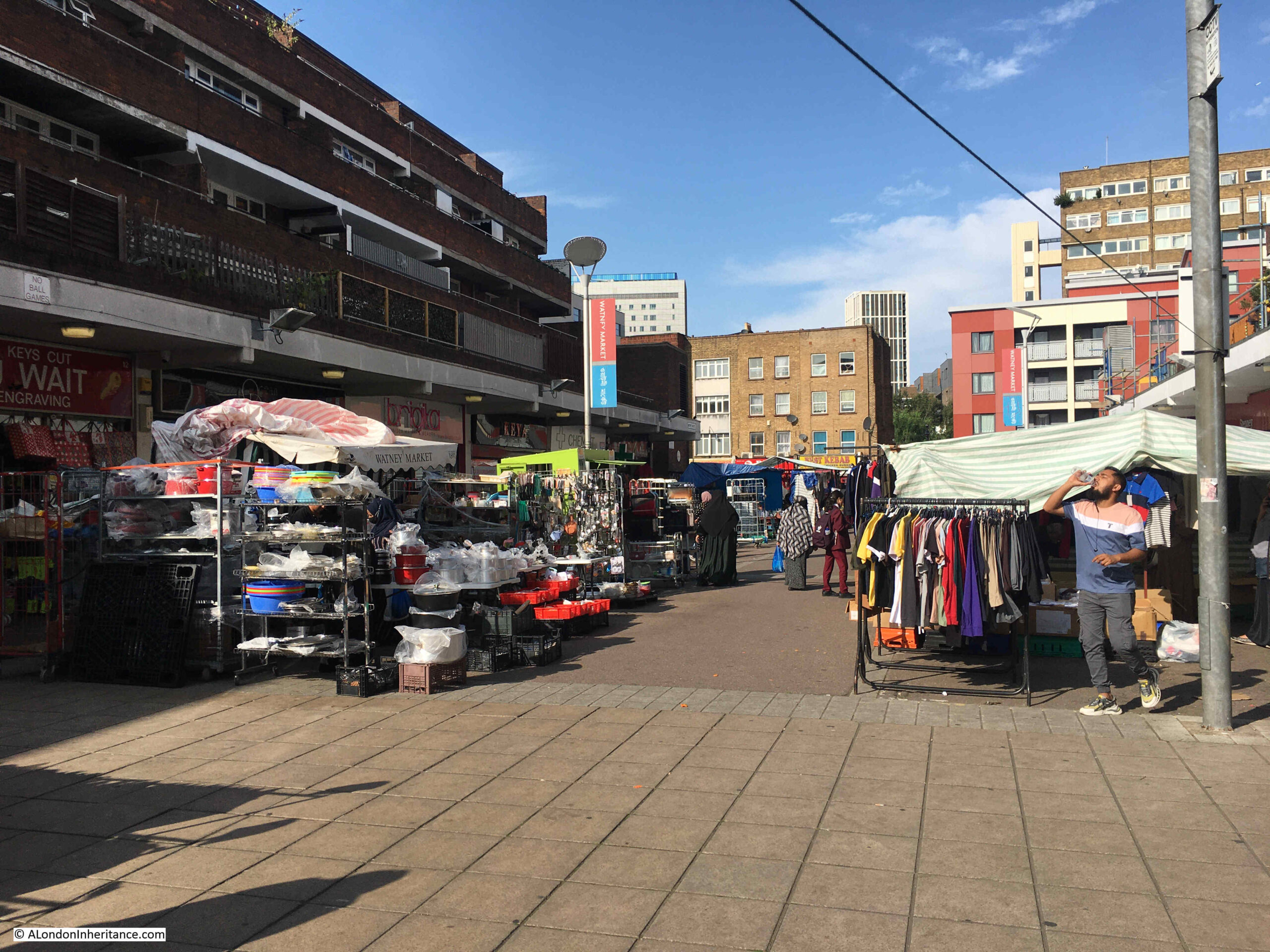

There was an article in the East London Advertiser on Saturday the 21st of August, 1886 about Watney Market. It was a rather long article, however it does provide a really good view of the market, those who shopped there, and the conditions of many of those who lived in the area. The core of the article follows:
“WATNEY STREET MARKET – How, when, or by whom this market was commenced no one seems to know. It has no charter, nor any legal status but that of usage, and like Topsy, it seems to have ‘growed’. Nevertheless it has become an important market, and to the poor inhabitants of St. George’s and Shadwell it is a most useful institution.
At first the market seems to have been confined mostly to the Cable-street end of Watney-street, the busiest being in the neighbourhood of the railway arch; but now, on some days, and particularly on Saturdays, it extends the whole length of the curved street, from Cable-street to Commercial-road and in it can be purchased almost everything needed in a household, from a pennyworth of pins to a suite of furniture, with bedding, bolsters, curtain lace, baby-linen, suits of clothing. washing machines, pianos and perambulators; whilst in the edible department it is always well stocked.
There is fish in every variety, from the lordly salmon down to a fresh herring, whilst the butchers cater for all classes, and in a manner suitable to the means of their numerous customers. Thus, on a Saturday, from morning till late at night, and particularly in the latter portion of the day, this market is crowded. in addition to the shops on both sides of the street, which are numerous, stalls are erected on and outside the footpath, leaving only a sufficient space for a limited amount of vehicular traffic.
A very large proportion of the purchasers in this market are women, and these mostly of the very poorest class, whose families live from hand to mouth. They can afford little at once, but they want that little every day when they can find the money to buy it; and hence the individual amounts spent at any one time are small, whilst their aggregate for a year must represent a very large sum. here the ‘ladies’ saunter about the market in dozens, in the most careless of deshabille, with hair unkempt, faces unwashed, and a general appearance of not having been dressed or undressed for a very considerable period. Each of them is accompanied by two, three or four children, equally elegantly attired. Whilst the mothers are looking out the cheapest bargains, these youngsters dive in, under and around the stalls, picking up rotten fruit, and anything else from the stalls on which the vendor does not keep a sharp eye.
And yet, notwithstanding all this squalor in dress and cleanliness, there is a general air of cheerfulness, frequently arising to hilarity, amongst the habitués of the market, and the general tone is one of careless happiness, especially when the weather is fine, when the women seem in no hurry about their business, but enjoy a thorough good gossip in the market place. Very few bags or baskets are brought by the buyers, they are not needed. A pound of bits of meat for about four pence, a couple of pounds of potatoes for two pence, and a cabbage for a penny, with perhaps a pennyworth of onions, and there is a dinner which has frequently to be eked out, with the aid of bread, for a family of six. An apron or the skirt of a dress will hold much more than this, and so the ladies who attend here will not encumber themselves with a basket, even if they have one, which in most cases is doubtful.
The women who purchase on Saturdays, are for the most part, wives of working men who are paid their wages on Friday; but there is a large class of men who are not paid until Saturday, and sometimes late even on that day. The bulk of these do not go straight home when they have received their wages, but remain about in public houses, where they are joined by their wives in very many instances, until it is too late, or they are too much overcome, to go shopping. What becomes of the children in the interval nobody knows and nobody seems to care. They play out on the street until they are all thoroughly tired out, and then made their way supperless and unwashed to such beds as they have, whilst their parents, with drunken recklessness, are wasting the food supplies on that which makes them utterly oblivious of the morrow and its responsibilities.”
The London Poverty Maps created by Charles Booth date from around the same time as the above report. Watney Street is in the centre of the following extract, and the streets around the street appear to have almost every category from Middle Class, Well-to-do (along Commercial Road), down to Lowest class. Vicious, semi-criminal (area in black).
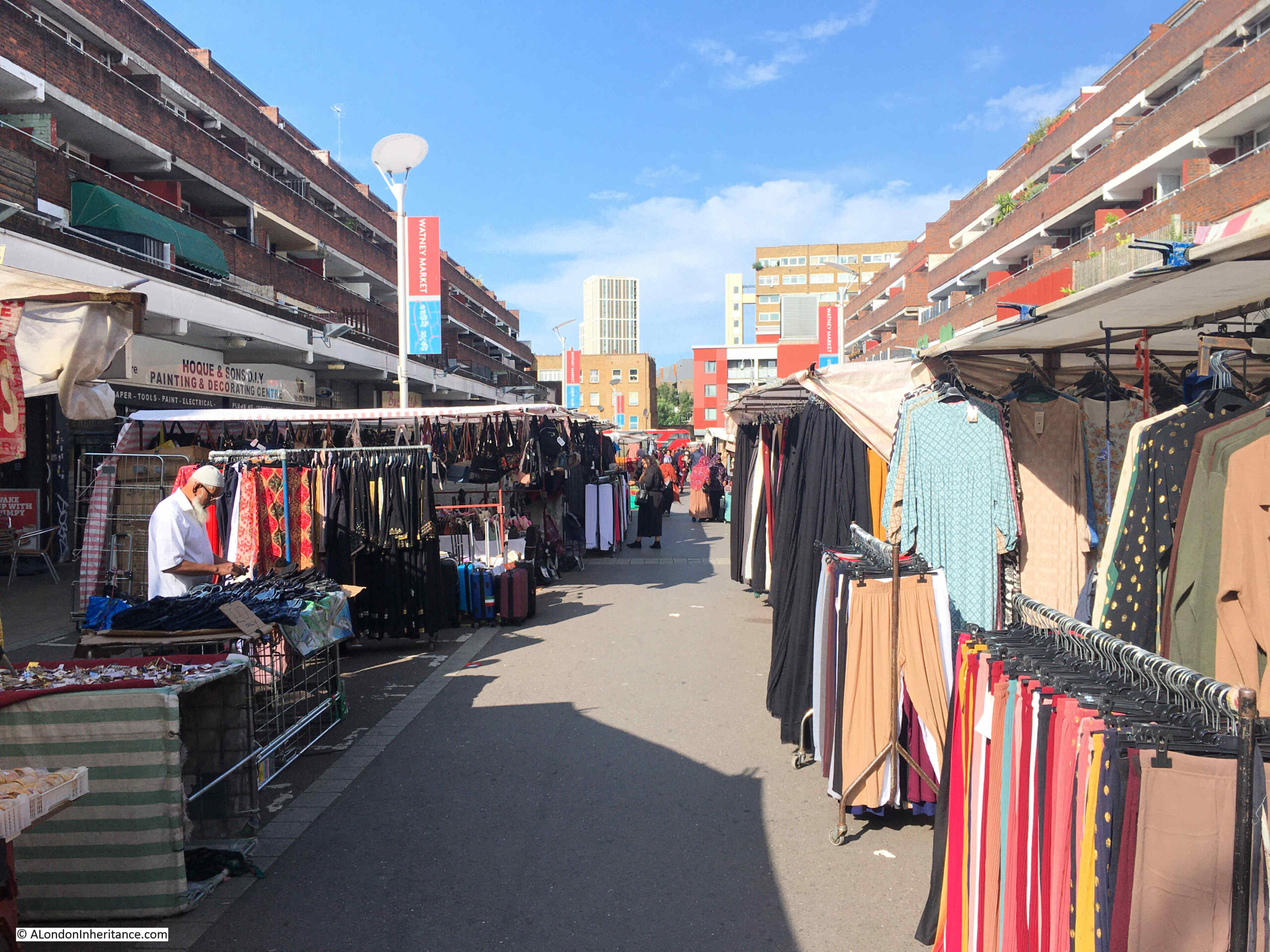
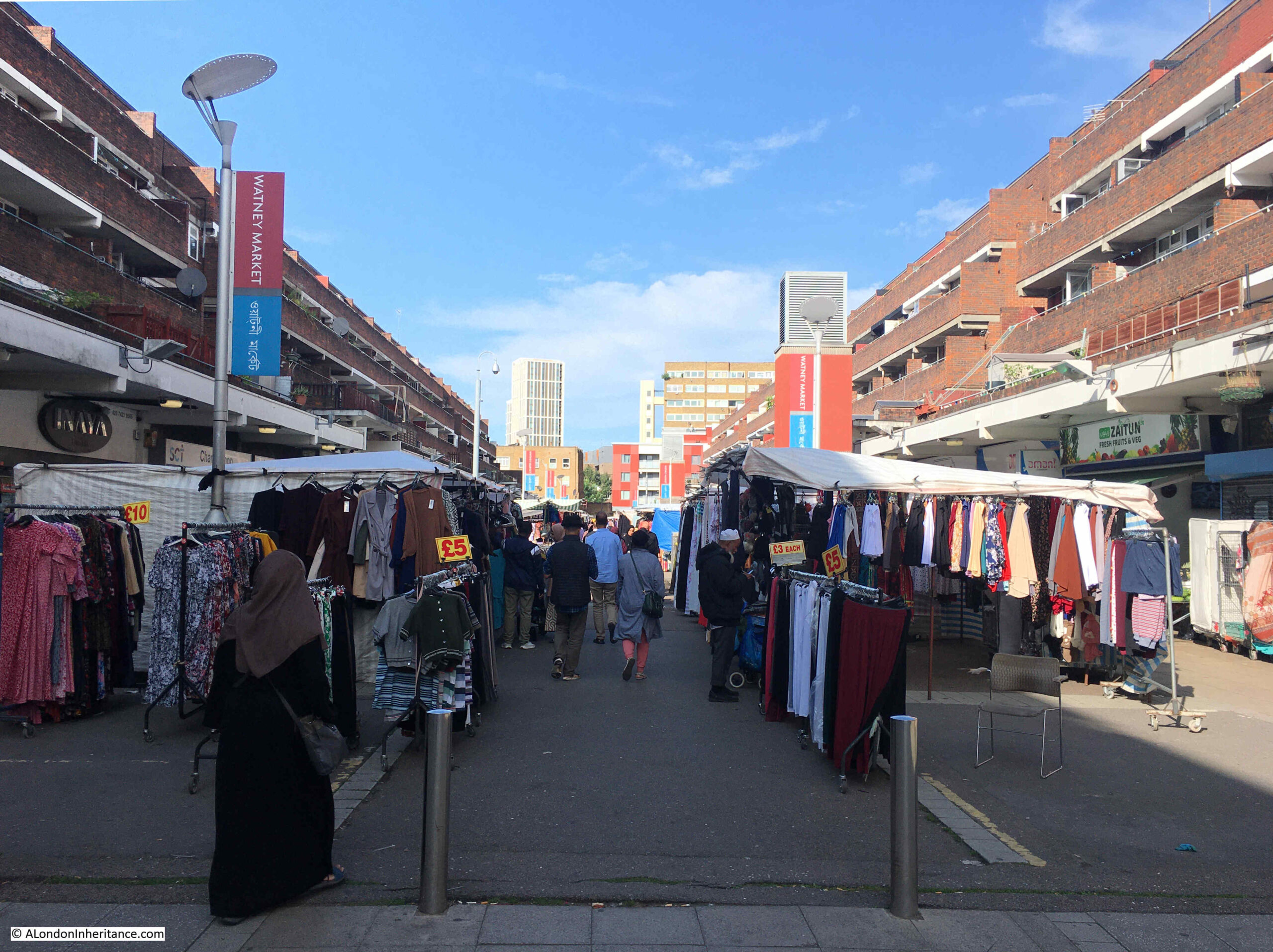
There has been a constant battle regarding space in Watney Market which has been going on for over 100 years, both in the original market, and the post-war rebuild.
The market stalls operate in the central space, with shops in the ground floors of the buildings on either side. These shop owners have long complained about the market stalls hiding their shops. They have complained about the size of the market stalls, the volume of product on display, how close the stalls are to their shops, the amount of traders products also displayed on the floor, and all the problems which the shop owners believe prevent shoppers from seeing, and getting to their shops.
This has been a recurring issue in newspaper reports back to the mid 19th century, and the market today remains a busy place, with market traders using as much space as is possible for the stalls, and to display their goods.
There is only a narrow walkway through the centre of the market, and the shops that line the ground floors of the buildings on either side are quite hard to see:

The southern end of Watney Street is at Cable Street, a street that is well known as the scene of the “Battle of Cable Street”, when on the 4th of October 1936, there were clashes between the Police, ant-fascist demonstrators, and the British Union of Fascists, led by Oswald Mosley, who were attempting to march through the area.
Whilst Cable Street is remembered as the scene of the attempted march, and anti-march demonstrators, in the 1930s, this area of east London was the scene pf regular provocation of the mainly Jewish community who lived in the area, by members of fascist organistions.
Watney Street and Watney Market frequently appeared in newspaper reports of these events. For example, on the 30th of May 1936, the City and East London Observer carried a report titled “Fascists in Watney Street”:
“There was great excitement among the many shoppers and stallholders in Watney Street on Sunday morning when about a dozen Blackshirts paraded up and down the market selling Fascist newspapers amid cries of ‘More Stalls for Englishmen’, ‘Foreigners Last and Nowhere’, while from another section of the crowd there were cries of ‘Blackshirt Thugs’, ‘Rats’, etc.
A great crowd gathered, and a Jewish girl, going up to one of the Blackshirts, bought a paper, tore it to pieces and stamped on the fragments. After this the police took a hand but they found it very difficult to keep the crowd on the move owing to the barrows in the market. Somebody picked up a cucumber from one of the stalls, but was prevented from throwing it at a Blackshirt.
A surprising number of the people present appeared to be in sympathy with the Blackshirts. The Blackshirts are, it is believed, about to open a branch in Stepney.”
A few months later in July 1936 is was reported that the market place in Watney Street “seems to be the chief hunting ground for Blackshirts selling their propaganda, who, according to reports, do their best to encourage hatred of the Jewish community.”
Many of the traders in the market were concerned about the lack of action from the authorities, and “rightly or wrongly, are of the opinion that the police are pro-Fascist”.
The traders were concerned that the Blackshirts were having a negative impact on their trade. Their actions and language put off many of the customers of the market, and when they arrived many of the traders packed up and left.
This all came to a head with the Battle of Cable Street, which greatly diminished the impact of the Blackshirts in Watney Street.
Another air vent, half way along the market. Possibly another air vent to the railway below:

Post war redevelopment of Watney Street and surroundings took some time. It was being planned in the 1950s, however nothing happened on the ground until the 1960s when the market was relocated in 1965, the surviving buildings demolished and the area flattened.
Tiered sets of new flats were built on either side of the new routing of Watney Street and a raised area along the new alignment was created for the market.
This took a long time to complete, with work not being substantially finished until 1977.
The flats were not popular with the original inhabitants of the street. Flats had been planned in the last days of the war, and in 1944 there were protests against the plan for flats, with residents of the Watney Street area telling the Borough Council that “Working people with families must have decent houses in which they can rear them properly”.
The wholesale demolition of many streets of terrace housing across east London, and the construction of flats is one of the themes of post war redevelopment of the area.
Whilst the demolished houses were in very poor condition, often badly maintained by uninterested landlords, lacking basic facilities, and suffering from general war damage and lack of attention, very many could have been refurbished, and would have provided housing, at street level, suitable for a wide range of occupants.
The following photo is looking through the market showing the tiered flats on either side:

The whole scheme, including the tiered flats was designed by the Architect’s Department of the Greater London Council.
The redevelopment work took over ten years, and in 1977 graffiti was appearing in the area complaining that the market has been murdered.
Redevelopment and relocation resulted in a reduction of trade for those running stalls, and the number of market stalls was gradually declining so by the end of the 1970s there were only about 19 market stalls remaining.
It would take the 1980s and most of the 1990s for the market to recover, and to make use of the full space provided by the redevelopment work.
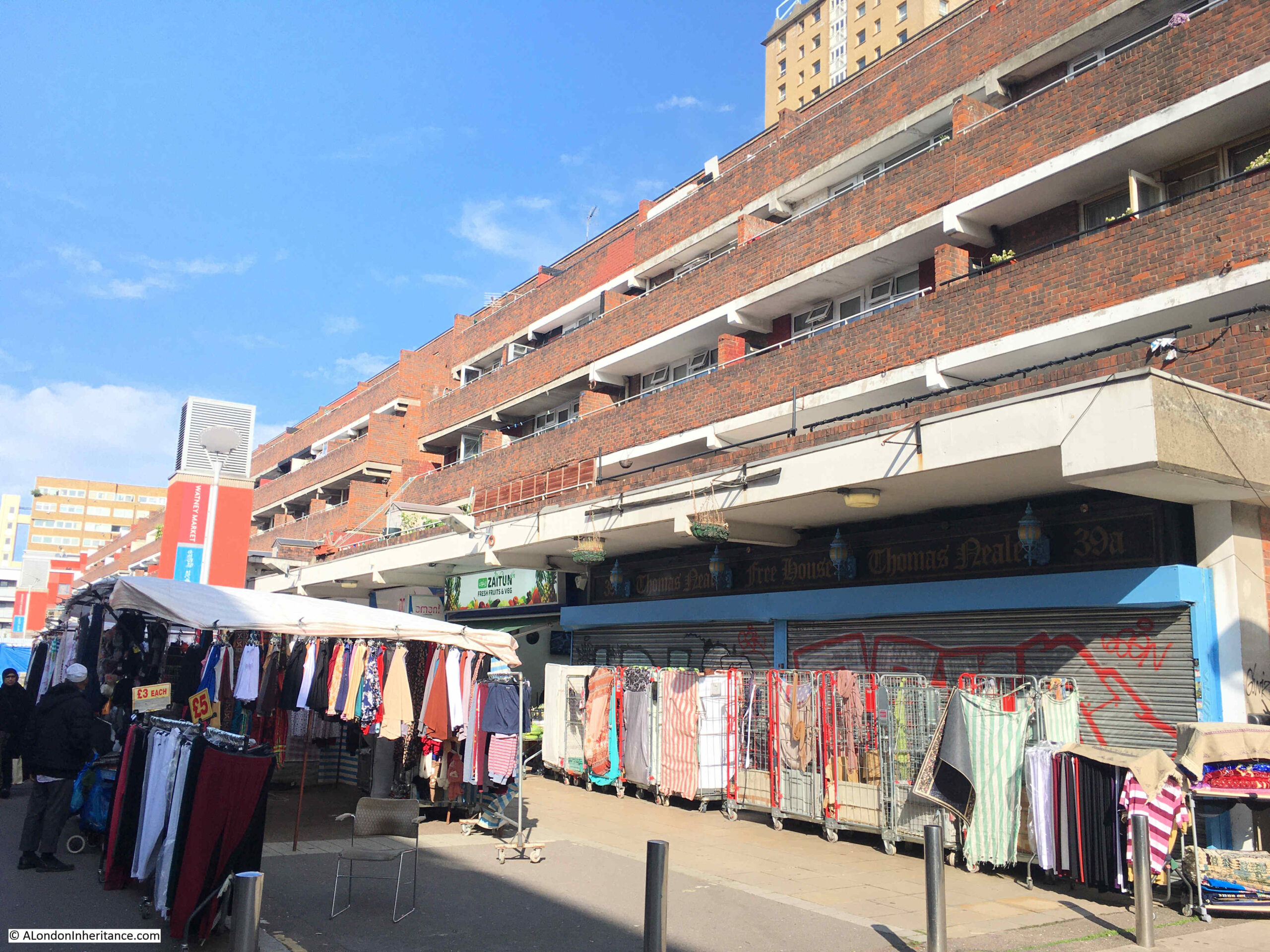
As well as the central market stalls, a large number and range of shops have occupied the buildings along the side. The supermarket Sainsbury’s was a long time resident of Watney Street, opening their first store in the street in 1881, expanding into a second building 13 years later.
Sainsbury’s were in Watney Street for over 100 years, finally moving to Whitechapel in 1994. Iceland then took over the store and are still in Watney Street, at the north-eastern corner, just behind the clock tower.
A couple of the shops are unoccupied, and the space directly in front is quickly occupied by the Watney Market traders:

As can be seen in the 1949 OS map earlier in the post, Watney Street had a rather strange routing. A short distance north along the street, it angled to the east before resuming a northerly route up to Commercial Road.
The point where this swerve to the east happened was at the junction with Tarling Street.
In the photo below, Watney Street is to the right, and where the road does a sharp turn to the right, that is Tarling Street. At this point, Watney Street angled to the right, under where the flats have been built, and continued north, under the flats.
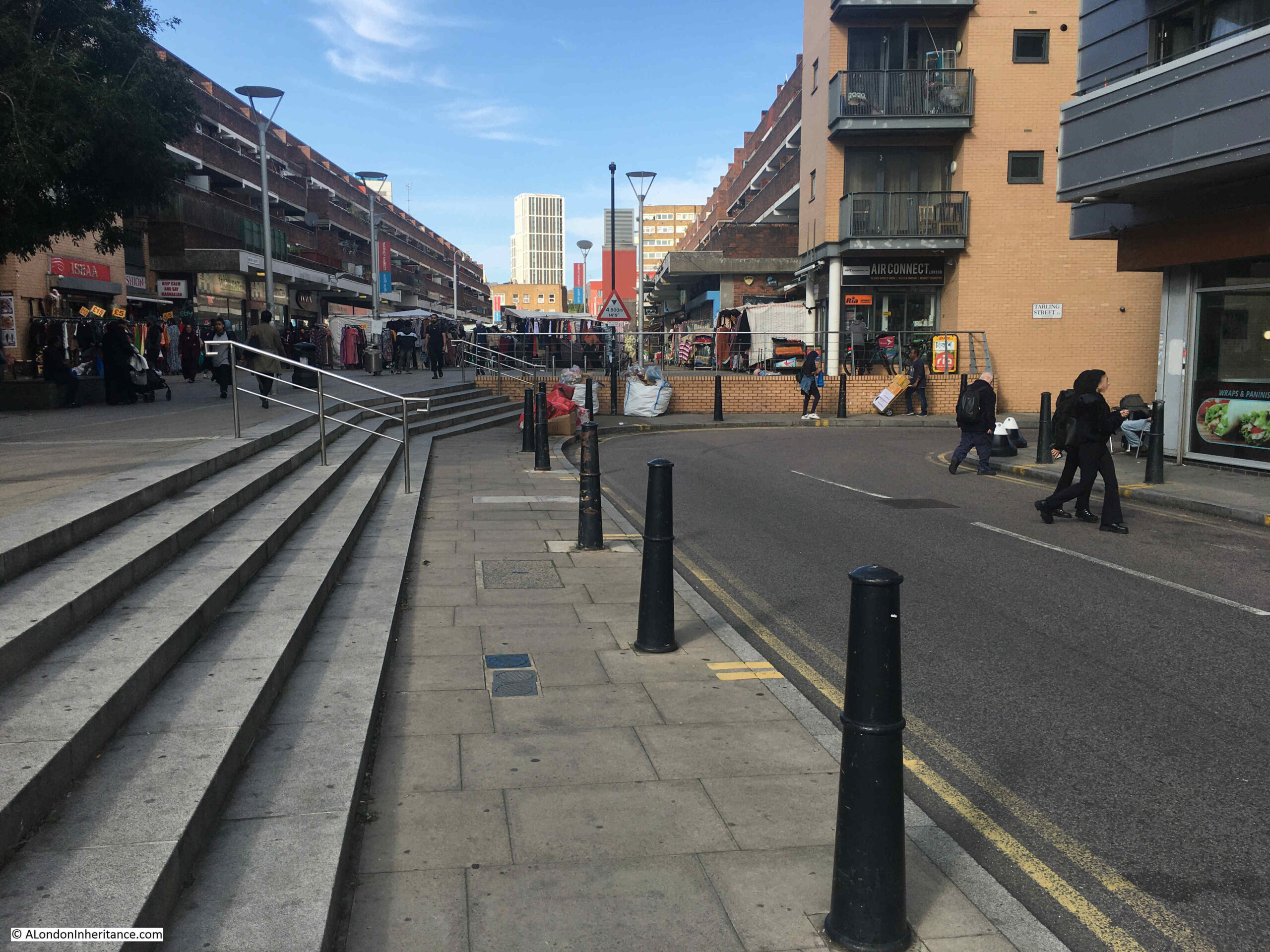

It would seem that when the area was first developed in the early decades of the 19th century, Tarling Street ran left to right across the above photo, and the southern section of what is now Watney Street between Cable Street and Tarling Street was originally Charles Street.
After the junction with Tarling Street, Charles Street changed to Watney Street and was reached through a narrow street or alley, around a larger building to the main section of Watney Street.
This larger building was demolished at some point, replaced by terrace houses, which were also later demolished, and the angle to the right then went through where these buildings was located.
I suspect the name Watney Street displaced Charles Street as the market grew in size and popularity.
I cannot find a firm source for the origin of the name. The general consensus seems to be it comes from the Watney Brewery in Whitechapel, although this was a little distance to the north west so there is no obvious connection.
Watney Market and Watney Street. A working market for well over 150 years. A place once occupied by those working on the river and by the poor of east London, a large Jewish community, and an area targeted by the Blackshirts of the 1930s. Badly bombed during the 1940s then with a lengthy redevelopment that would not see the market busy again until the 1990s.
A fascinating place of east London history.
