All my walks have sold out, however I have had a request to run the “South Bank – Marsh, Industry, Culture and the Festival of Britain” walk on a weekday, so have added a walk on Thursday, the 9th of November, which can be booked here.
I have now been writing the blog for nine and a half years, and it has changed the way I look at things when walking the streets of the city. I now take far more notice of all the little indicators to the history of an area, a street or a building.
Whether it is the way that streets dip and rise, and the sound of running water rising from below a drain cover, both hinting at a lost river, the way the shape of a building hints at an early street pattern before a Victorian road improvement, or the numerous plaques and architectural features telling of a building’s former use.
A typical example of this was when I walked along Cloak Lane in the City a couple of weeks ago. Although I have walked through the street numerous times over the years, I had not noticed this foundation stone on a building on the corner of Cloak Lane and College Hill:

What caught my attention with this foundation stone is that it was laid by a Deputy Chairman of the Police Committee.
The building does not seem to have any current connection with the Police service and is now an office block, and appears to be on sale for offers in excess of £14.7 million.
The building looks as if it was once home to an institution of some form. Plainly decorated and mainly brick with stone cladding on the ground floor, the building still projects a strong, functional image onto Cloak Lane.
The foundation stone on the building is now the only reminder that this was built for the City of London Police and opened as Cloak Lane Police Station:
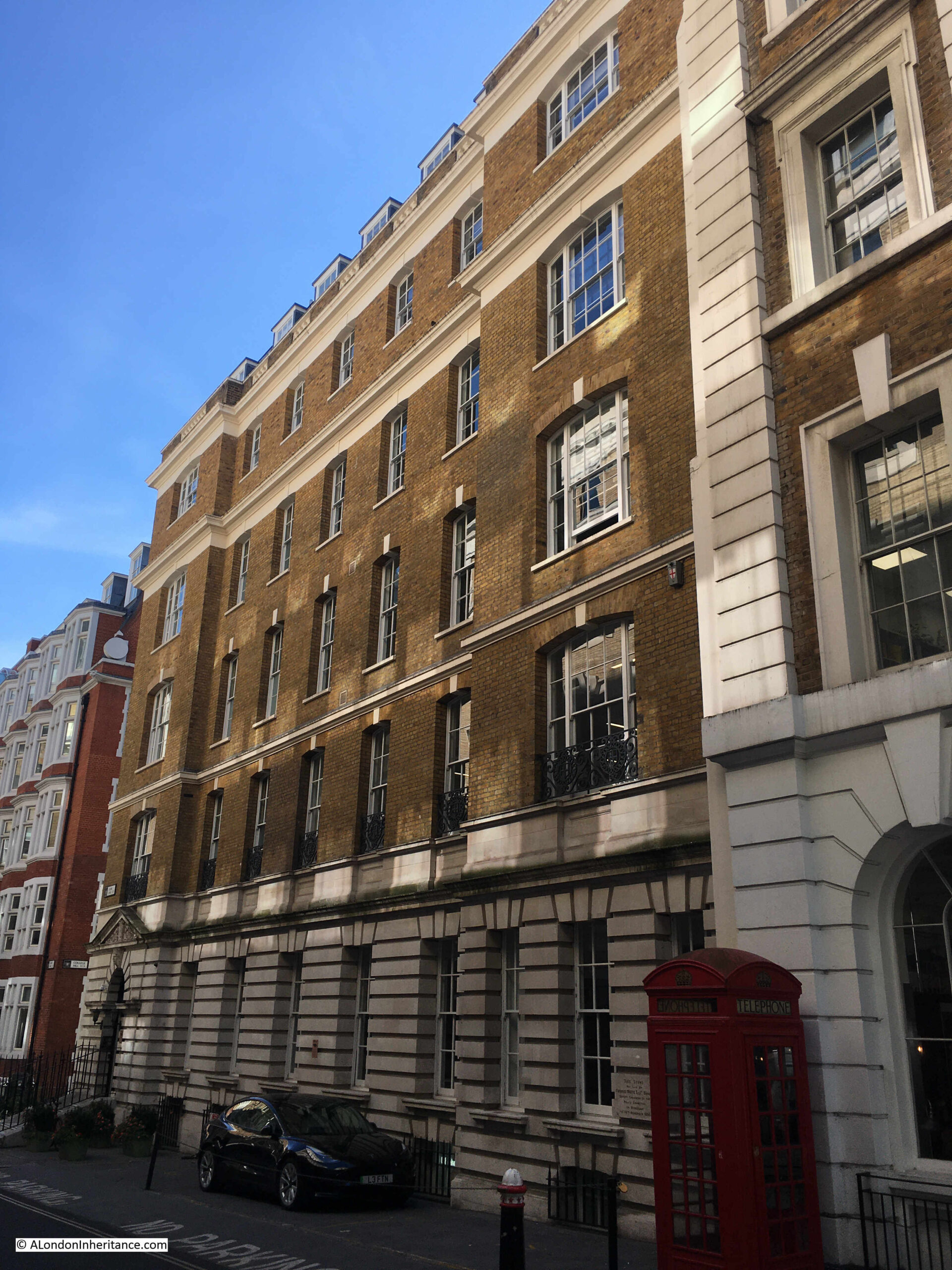

As the foundation stone records, Cloak Lane Police Station dates from 1885.
At the time, Cloak Lane was one of six police divisions across the City. They were centered on police stations at Cloak Lane, Minories, Bishopsgate, Bridewell Place, Snow Hill and Moor Lane.
The City of London Police came into being in 1839 when the City of London Police Act was passed on the 17th of August 1839. Before this act, policing in the City was built around a Day Patrol of Constables, and a Night Patrol which started with elected Ward Constables and Watchmen, with Watch Houses that later became the first Police Stations located across the City.
The 1839 Act provided statutory approval of the City of London Police, appointed a Commissioner of Police who was selected by the City’s Court of Common Council, and probably of more importance to the City of London, the Act ensured that the City’s police would be kept separate and not merged with the Metropolitan Police. A separation which continues to this day.
The City of London Police seems to have been funded by the Corporation of London, and funded by a police rate paid by the businesses and residents of the City.
There appears to have been some concern about the extra costs of the new building as in the City Press in 1885 there was the following: “There is every probability of an increase in the city rating, which is already exceedingly heavy. A new police-station is about to be erected in Cloak Lane which will involve an additional penny in the police rate, unless the cost of the building is spread over several years”.
I cannot find the exact date when the new station opened, however it appears to have been built quickly as by 1886 newspapers were starting to carry reports about events involving the station, including what must have been a most unusual use for the new police station:
“AN ADDER CAUGHT IN A LONDON STREET. There is now to be seen at the Police Station, Cloak Lane, City, an adder, about 15 inches long, which was seen in Cannon Street a morning or two ago basking in the sun on the foot pavement, although large numbers of persons were passing to and fro at the time.
A constable’s attention was drawn to the strange sight, and he managed to get it into a box and take it to the station. It is conjectured that it must have been inadvertently conveyed to town in some bale or other package of goods. The creature, which is pronounced to be a fine specimen, has been visited by large numbers of persons.”
I could not find any record of what happened to the adder after its appearance at Cloak Lane police station.
Cloak Lane is to the south of Cannon Street, and runs a short distance west from Cannon Street Station.
The building did suffer bomb damage during the war (although it is not marked on the LCC Bomb Damage Maps). A high explosive bomb did penetrate the roof and caused considerable internal damage. There are a number of photos of the damage in the London Picture Archive, including the photo at this link.
As a result of this damage, there may have been some repairs and rebuilding of the structure, and it is hard to be sure how much of the building is the original 1886 station.
The longest axis of the building is on Cloak Street, with the shortest axis running down College Hill as the building is on the corner of these two streets.
What is strange is that the main entrance to the building is on Cloak Lane, and the building was known as Cloak Lane police station, however as can be seen to the left of the door in the following photo, it has an address of 1 College Hill:
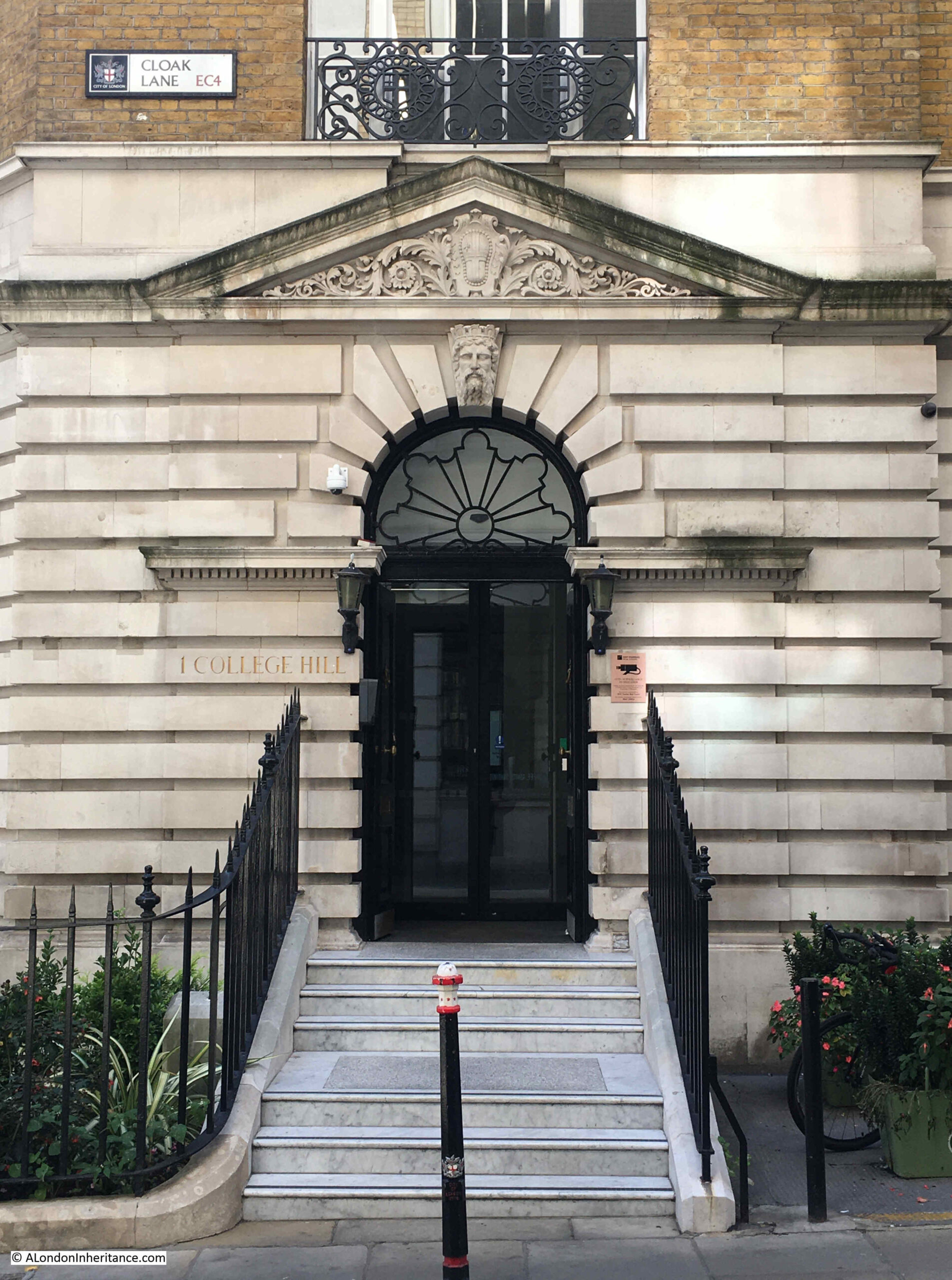

The arms of the City of London can be seen in the pediment above the door. I am not sure who the figure on the keystone is meant to represent, however it could be Neptune / Old Father Thames, as Cloak Lane police station covered the area along the river not far to the south of the building.
I find it fascinating to use these fixed points in London as a reference to finding out about life in the City over the years, and Cloak Lane police station tells us much about crime in the City of London.
Financial crime seem to be a feature of many of those of who found themselves in Cloak Lane police station. Probably to be expected given the businesses within the City. Two examples:
In September 1952, Colin Vernon Ley was awaiting trial, charged with “while being a Director of Capital Investments Ltd. he unlawfully and fraudulently applied £3,000 belonging to that body to his own use”.
The report of his arrest reads as you would perhaps expect of an arrest in the 1950s:
“At 6.45 p.m. yesterday, said the Inspector, I was with Detective Sergeant Reginald Plumb in Bruton Street, Mayfair, when I saw the prisoner outside the Coach and Horses public house.
I said to him ‘You know who we are, and I hold a warrant for your arrest issued at the Mansion House today.
I cautioned him, and he said ‘I suppose I have to come with you now’. At Cloak Lane Police Station, the warrant was read to him, and he said ‘You were in a position to prove it, no doubt before you got the warrant’. I was present when he was charged and he made no reply.”
On the 10th of October 1959, papers were reporting on the arrest of a solicitor for one of the largest, in value, financial frauds. Friedrich Grunwald, described as a 35 year old Mayfair solicitor was arrested and charged under the Larceny Act with the fraudulent conversion of £3,250,000 entrusted to him by the State Building Society to secure mortgages on properties owned by 161 companies. His arrest was described that:
“At a nod from a colleague, a bowler-hatted Detective-Superintendent Francis Lee, head of the City Fraud Squad, intercepted him on the Embankment near Temple Underground Station and escorted him to a car which drove to Cloak Lane police station”
In January of the following year, Herbert Murray, secretary and managing director of the State Building Society was also arrested and taken to Cloak Lane and would later appear in court with Grunwald.
The problem with using old newspapers for research is that there are so many random interesting articles to be found on the same page. If you have ever wondered why and when the Guards at Buckingham Palace moved into the secure area behind the railings, then on the same page as the above article there was:
“PALACE GUARD TO RETREAT BEHIND RAILINGS – Sentries at Buckingham Palace are to retreat behind the railings. They are making their tactical withdrawal to prepared positions to avoid clashes with sight-seers.
It will stop fashion photographers posing scantily dressed models under the men’s noses. It will stop those pictures of kindly small boys tie sentries undone bootlaces. Too often the boys tied the laces of both boots together.”
The River Thames features in a number of events that involved Cloak Lane police station. These normally involved some form of tragedy, due to the nature of police work, and the dangers of the river, such as in April 1924:
“POLICEMAN VANISHES – BELIEVED TO HAVE BEEN BLOWN INTO THE THAMES. Police Constable Albert Condery is believed to have met with a tragic death by being blown into the Thames during a storm last night.
It is learned that Condery, who has been in the City Police Force for 20 years, left Cloak Lane Police Station last night to go on duty at Billingsgate Market. He was seen there by the sergeant, but later he was missed, and his helmet was found floating on the Thames near the market. The body has not been recovered.”
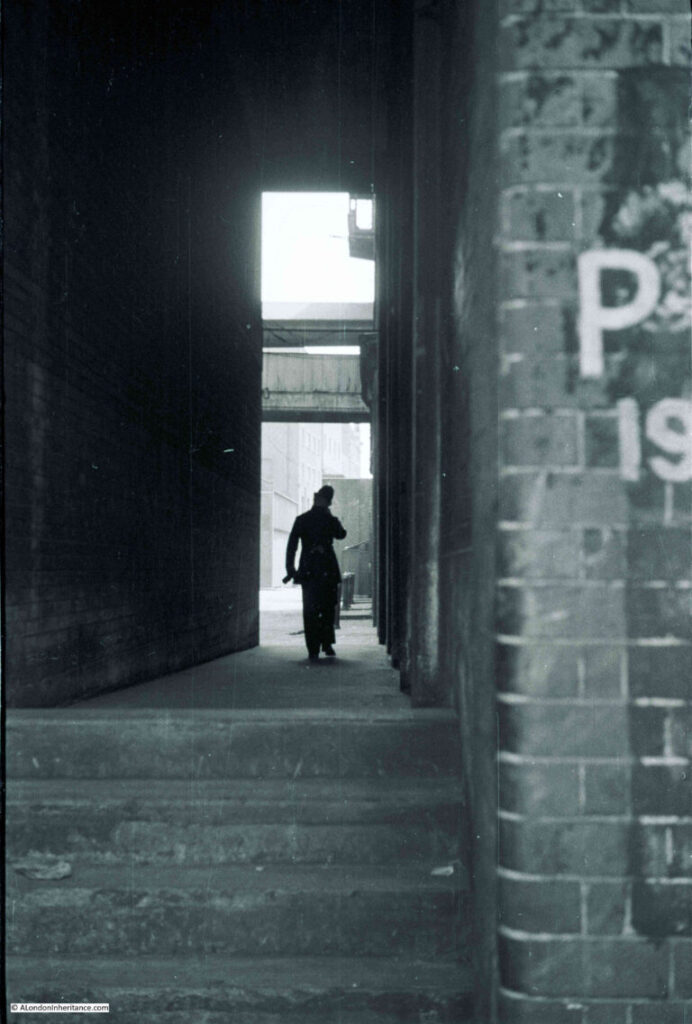
The above report was from a time when lone police officers patrolled the city’s streets. Although the following photo was taken by my father in Bankside, not the area covered by Cloak Lane, it does show the traditional image of a policeman patrolling their beat:

There were many strange events across the City in which Cloak Lane was involved. In November 1902, papers had the headline “EXTRAORDINARY AFFAIR AT BANK OF ENGLAND – ATTEMPT TO SHOOT THE SECRETARY. A sensation was caused in the Bank of England yesterday by the firing of a revolver by a young man who had entered the library. As he seemed about to continue his firing indiscriminately the officials overpowered and disarmed him. The police were called in, and he was removed to the Cloak Lane Police Station.”
He was unknown by anyone in the Bank of England and whilst at Cloak Lane, he was examined by a Doctor, who came up with the diagnosis that “the man’s mind had given way at the time”.
In August 1891, there were reports of a “Raid on a Cheapside Club”, which officers from Cloak Lane had been watching for some time, with a couple of Detectives having infiltrated the club. Finally there was a raid, when: “A party of 14 plain-clothes officers made a descent upon the premises. At first, admission was refused, and the officers proceeded to smash the glass paneling in the upper portion of the door. Resistance being of course in vain, the door was thrown open, and the detectives rushing in, arrested everyone found in the establishment. twelve persons were taken into custody, and removed to Cloak Lane Police Station.”
The report does not mention why the club was illegal, however reports in later papers when those arrested were in court reveal that it was an illegal betting club, known locally as the United Exchange Club, held in the basement in Cheapside that had been home to the City Billiard Club.
Another view of the old Cloak Lane Police Station. College Hill is the street leading down at the left of the photo. Cloak Lane is where the longest length of the building can be seen, but strangely the address on the main entrance is 1 College Hill:

In 1914, two of the original six divisions were closed, and the City of London police force was reorganised into four Divisions. These were changed from numbered divisions 1 to 6 to lettered divisions A to D, with Cloak Lane becoming D Division.
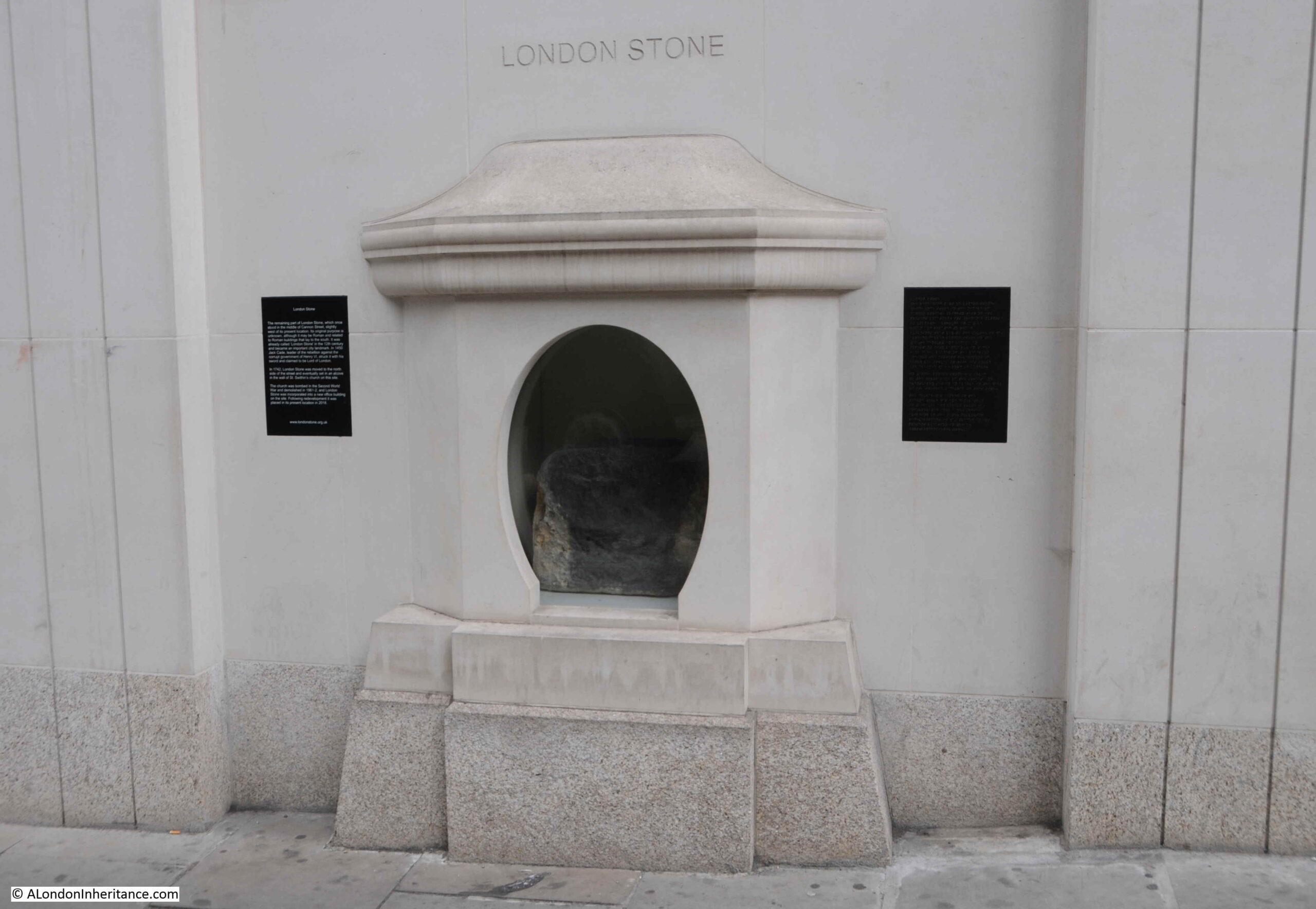
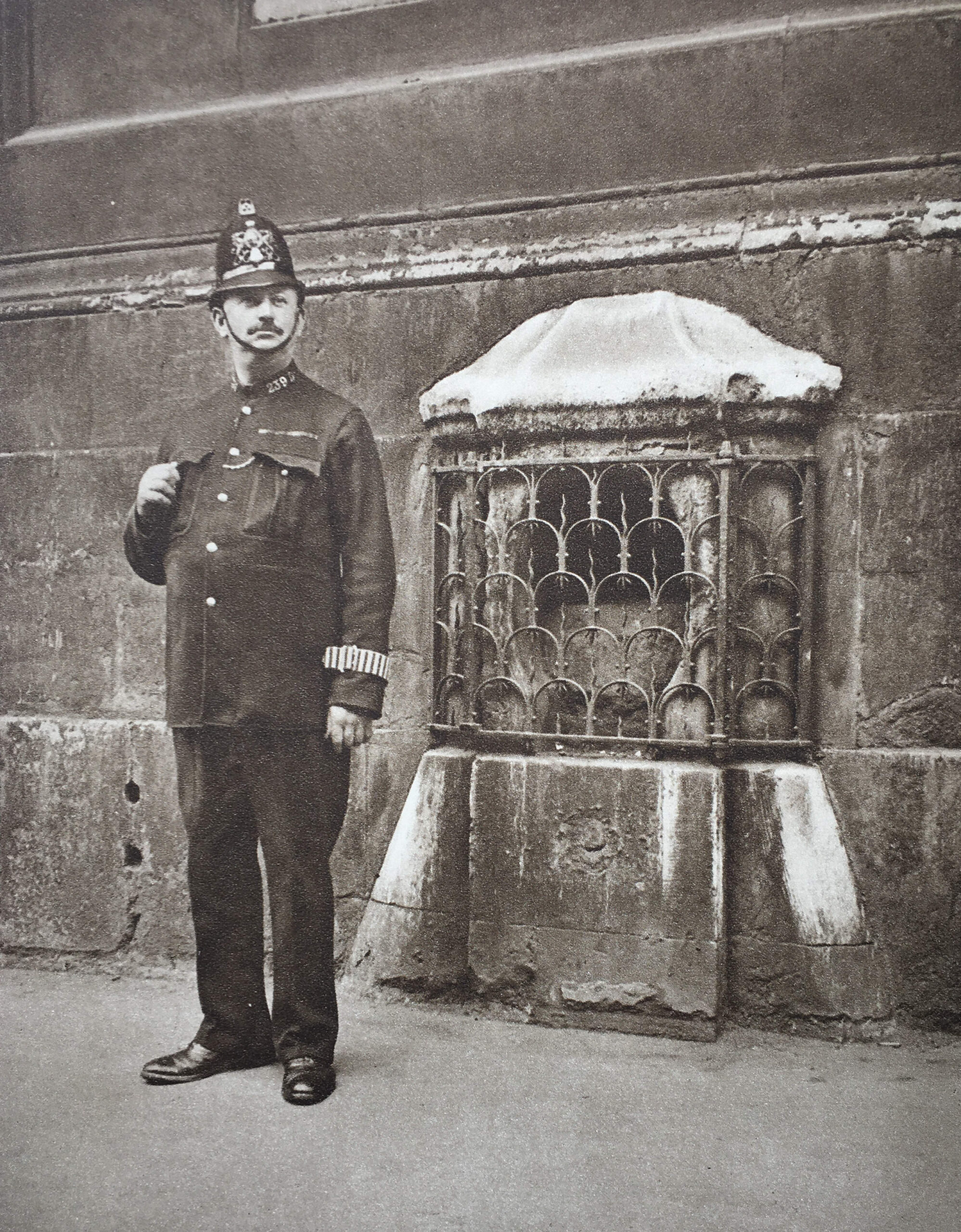
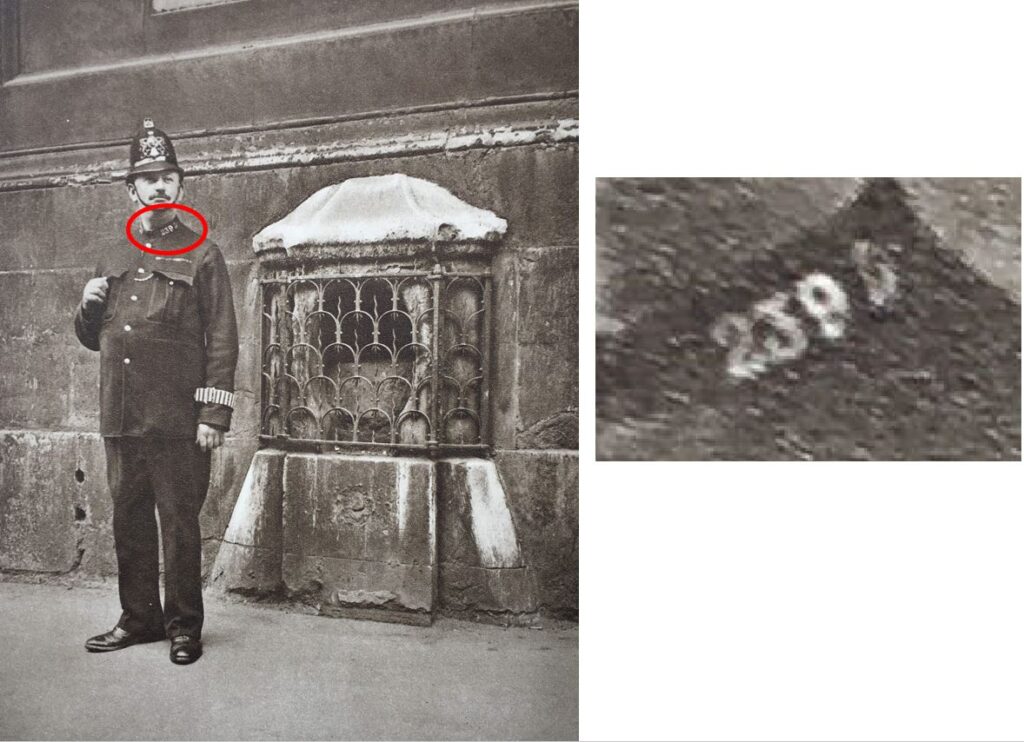
In last week’s post on the London Stone, I included a photo from the 1920s publication Wonderful London where a policeman was standing guard over the London Stone.
City of London police had their individual number, followed by a letter for their division on their collar, and looking at the collar number of the policeman shows he was from D Division based at Cloak Lane, which makes sense as Cloak Lane covered Cannon Street.
Cloak Lane Police Station survived until 1965, when it closed and Wood Street became the D Division police station.
The very last report mentioning Cloak Lane Police Station was from December 1965 when an article titled “Foolish Driver in The City” reported on a driver who was seen driving down Friday Street and only just stopping at the junction with Cannon Street. He was arrested on suspicion of being drunk and taken to Cloak Lane Police Station, where he “had to be supported by two officers because he was unsteady on his feet”.
And so ended 80 years of policing from Cloak Lane.
Wood Street (designed by McMorran and Whitby, and built between 1963 and 1966), and which took over from Cloak Lane is shown in the photo below:
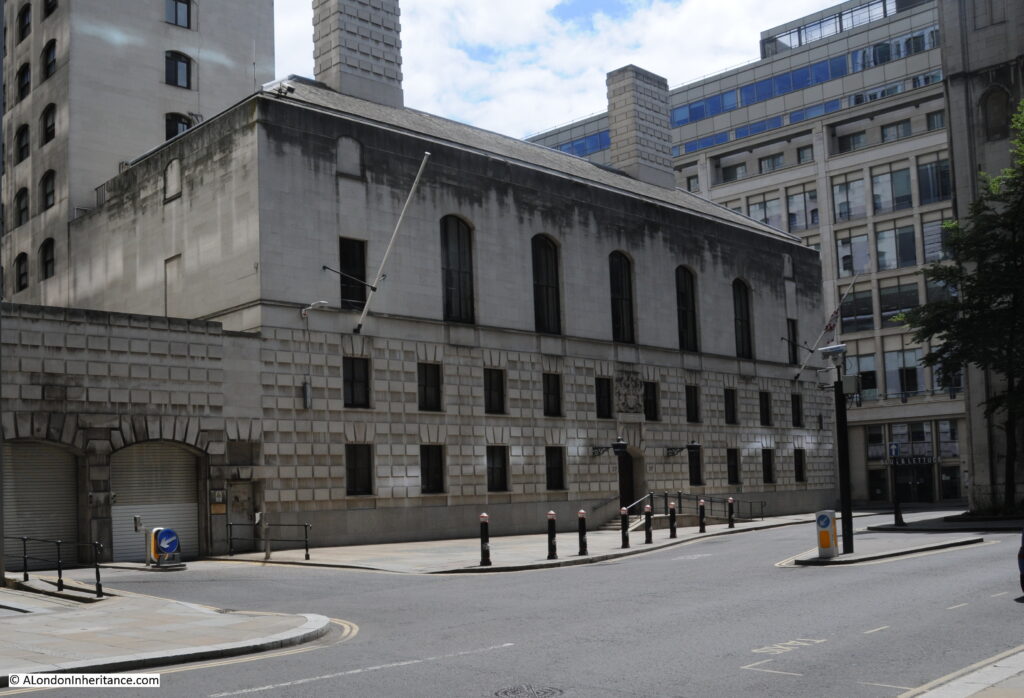

Wood Street Police Station has in turn been closed.
In the announcement from the Corporation of the City of London, it is stated: “The Grade II* Listed building has been sold to Wood Street Hotel Ltd (wholly owned by Magnificent Hotels) after it was declared surplus to operational requirements by the City of London Police. The developers have purchased the property on a 151-year lease and will turn it into a boutique 5-star hotel, subject to planning permission.”
The architects plans for the building can be seen at this link.
The only indication that the building on the corner of Cloak Lane and College Hill was a police station is the foundation stone laid by the deputy chairman of the police committee.
It now has a very difference use, and those who enter the building are now presumably doing so voluntarily, unlike very many of those who entered the building between 1886 and 1965.