When the 19th century London Bridge was built to replace the original medieval bridge, the new bridge was built slight further west along the river allowing the old bridge to continue in use until the new bridge was completed.
The construction of the 19th century bridge had quite a dramatic impact on the streets on the north bank of the river. I have already covered some examples in my post on the Ticket Porter in Arthur Street which you can find here, and there were more street changes further north.
Today’s post on the church of St Clement Eastcheap provides us with another example.
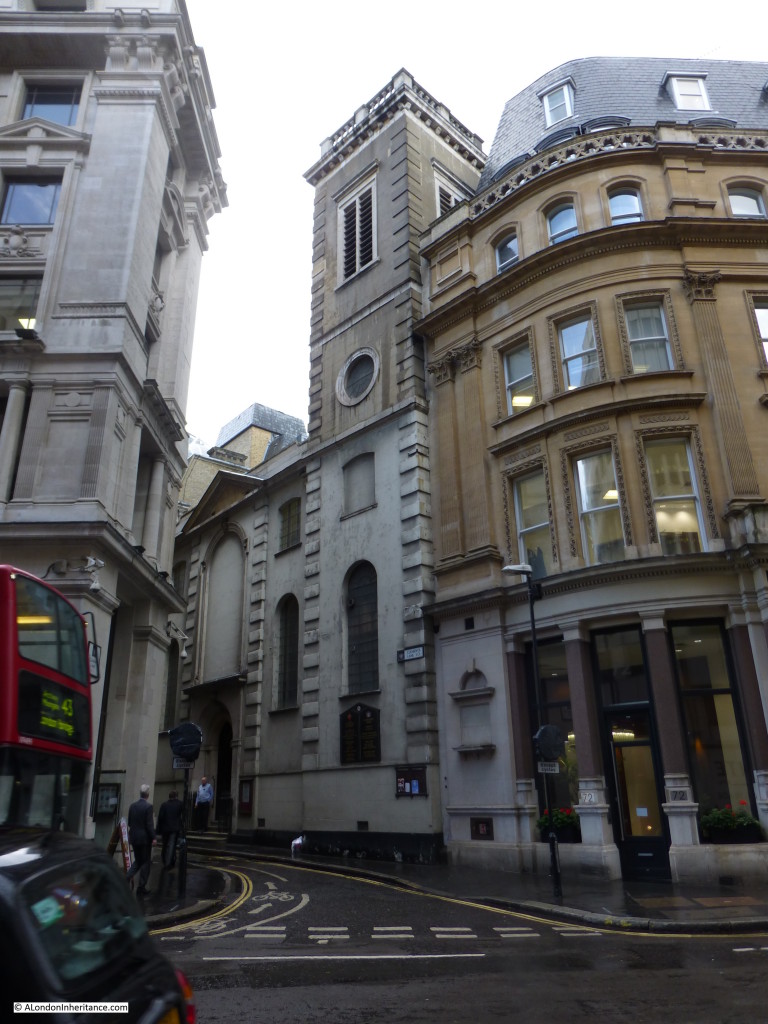
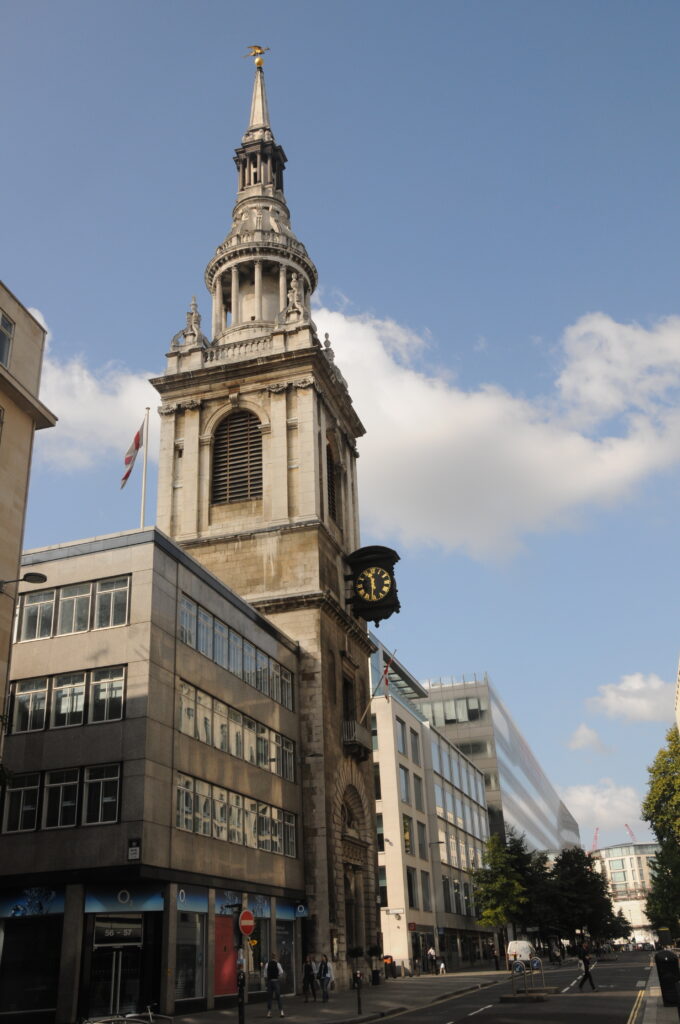
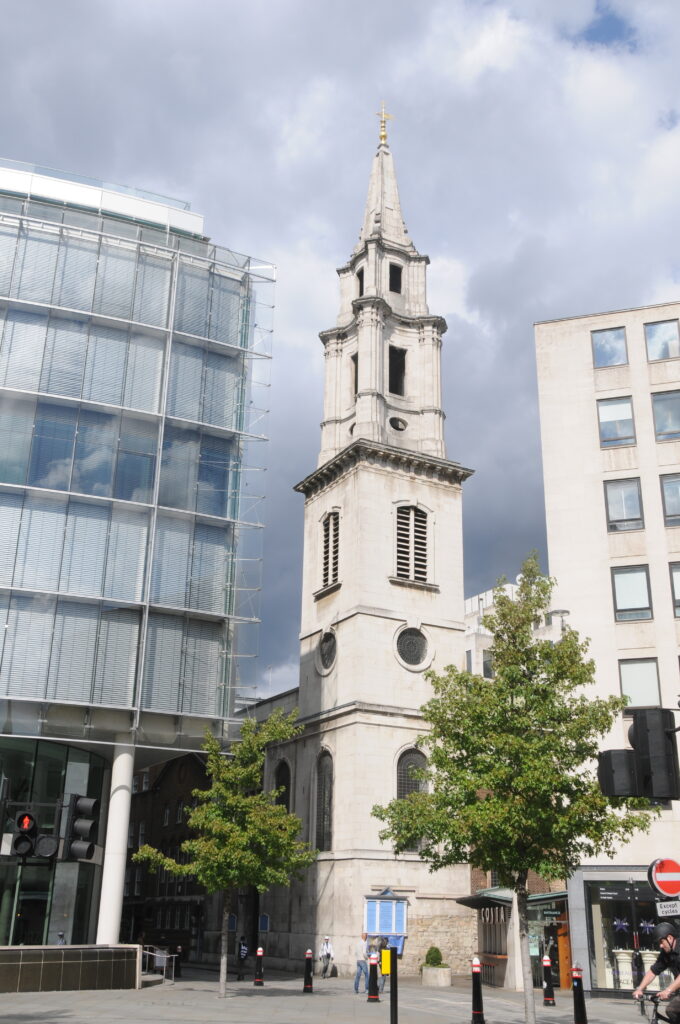
St Clement Eastcheap is a modest church in Clements Lane almost at the corner with Cannon Street. The church does not have a spire and the church tower is at the same level as the surrounding buildings so unlike many other City churches, you will not find a spire to help locate the church.
The church does though have a fascinating piece of early 18th century graffiti in one of the most unusual locations, more on this later.
So, to start, here is St Clement Eastcheap in Clements Lane taken from Cannon Street.
St Clement Eastcheap, located in Candlewick Ward, dates from at least the 12th Century, probably earlier and was originally adjacent to the street Great Eastcheap.
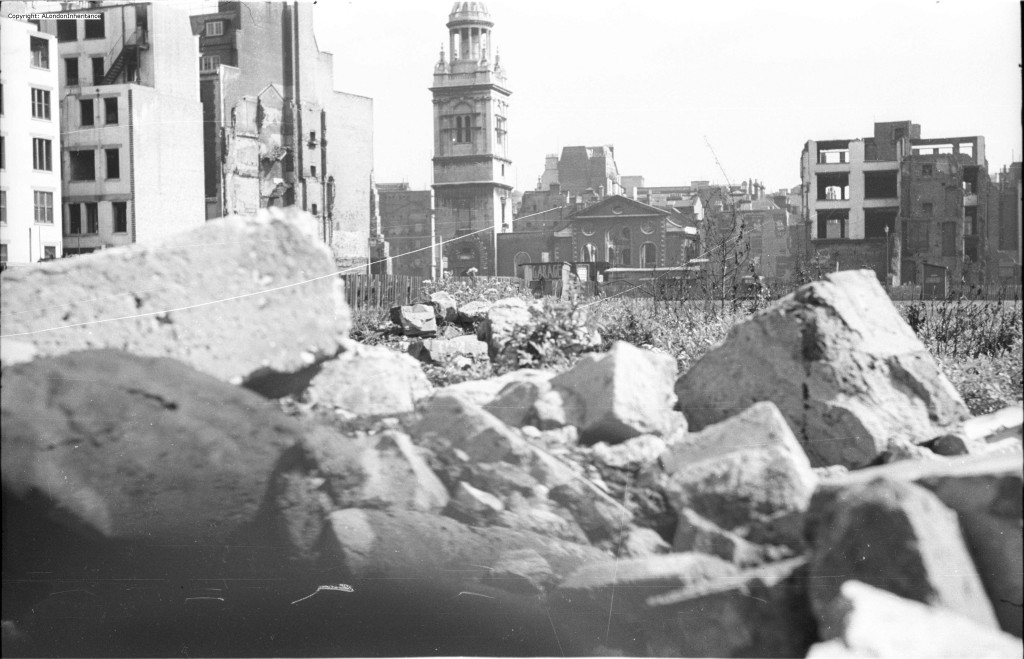
The church was destroyed in the Great Fire of London and rebuilt by Wren between 1683 and 1687. The church suffered very little damage during the 2nd World War which is surprising given the central City location, so the church we see today is much the same as the original Wren construction.
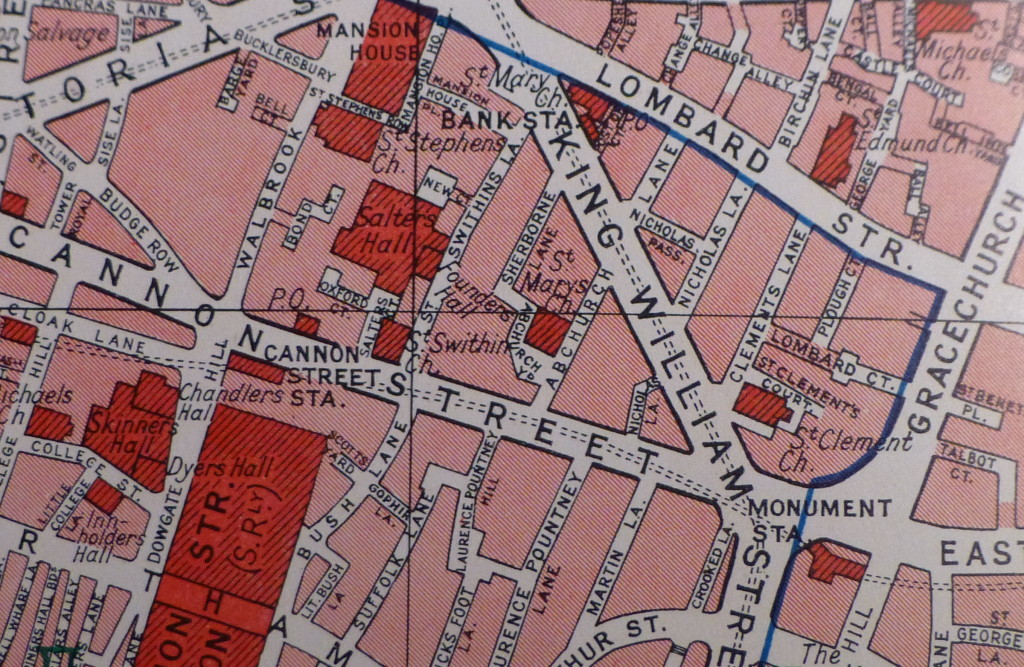
The following map is from the 1940 Bartholomew London Street Atlas. The street plan is also much the same today. St Clement Eastcheap can be seen to the lower right, just above Monument Station.
Clements Lane today, runs between Lombard Street and King William Street which runs on to London Bridge.
Much of this street plan was created to provide an efficient route onto the new London Bridge with King William Street providing direct access from the major road junction at the Bank.
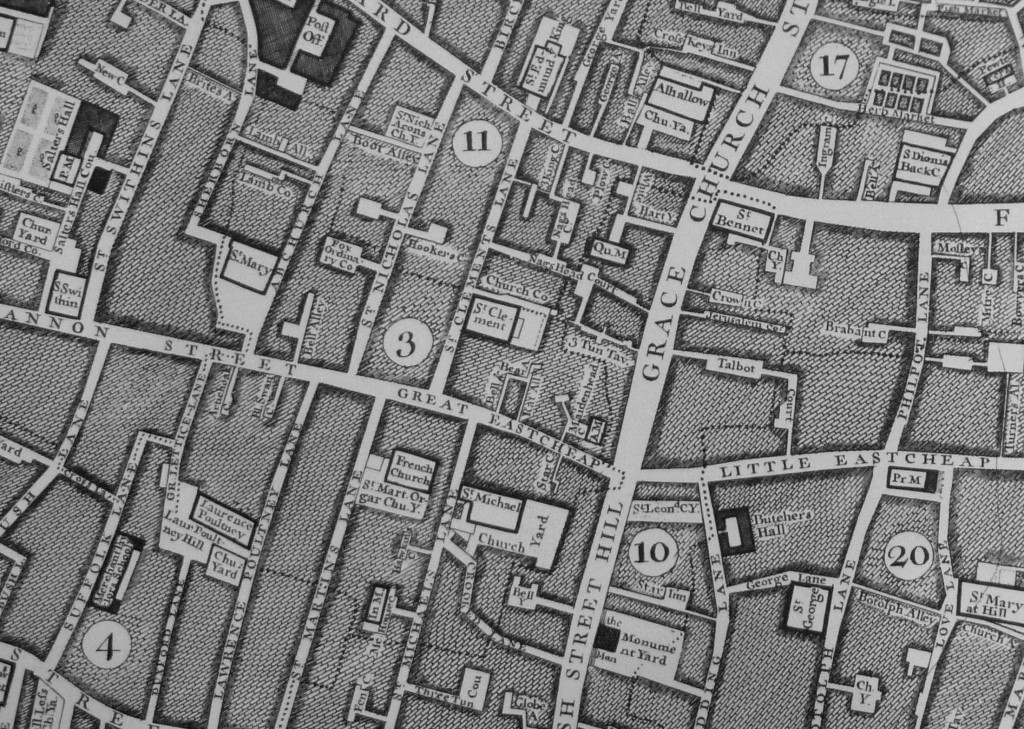
The extract below from John Rocque’s map of 1746 shows the street plan when the original London Bridge was still in place.
Here, Gracechurch Street runs to Fish Street Hill then on to London Bridge. Compare this with the above map where Gracechurch Street now curves past Monument Station to King William Street and the approach to London Bridge, highlighting the slight westward move of the bridge.
Just above and to the right of the number 3 in the map below can be seen St Clement. Here, St Clements Lane runs down to Great Eastcheap. Note also how Eastcheap is split into Great and Little Eastcheap, with Little Eastcheap remaining to this day, but now called simply Eastcheap.
Stowe states in his 1603 Survey of London that:
“The street of Great Eastcheape is so called of the Market kept, in the east part of the City, as West Cheape is a market so called of being in the West.
This Eastcheape is now a flesh Market of Butchers there dwelling, on both sides of the street, it had sometime also Cookes mixed amongst the Butchers, and such other as solde victuals readie dressed of all sorts.”
Great Eastcheap was lost when King William Street was built, with Great Eastcheap being included in the end of Cannon Street, King William Street and the Gracechurch Street, Eastcheap section by Monument Station.
When I visited the church, there was an interesting reminder of the geology of the City. When I entered the church, there was a clear blue sky, however on leaving there was a very heavy rain shower and water was streaming down the narrow Clements Lane, carrying various bits of rubbish in the flow. Whilst today, the water disappeared down the nearest drain, this was a graphical reminder of how much of this side of the City slopes down towards the Thames and how in the past the water and rubbish running down these streets would have been carried straight down towards the river.
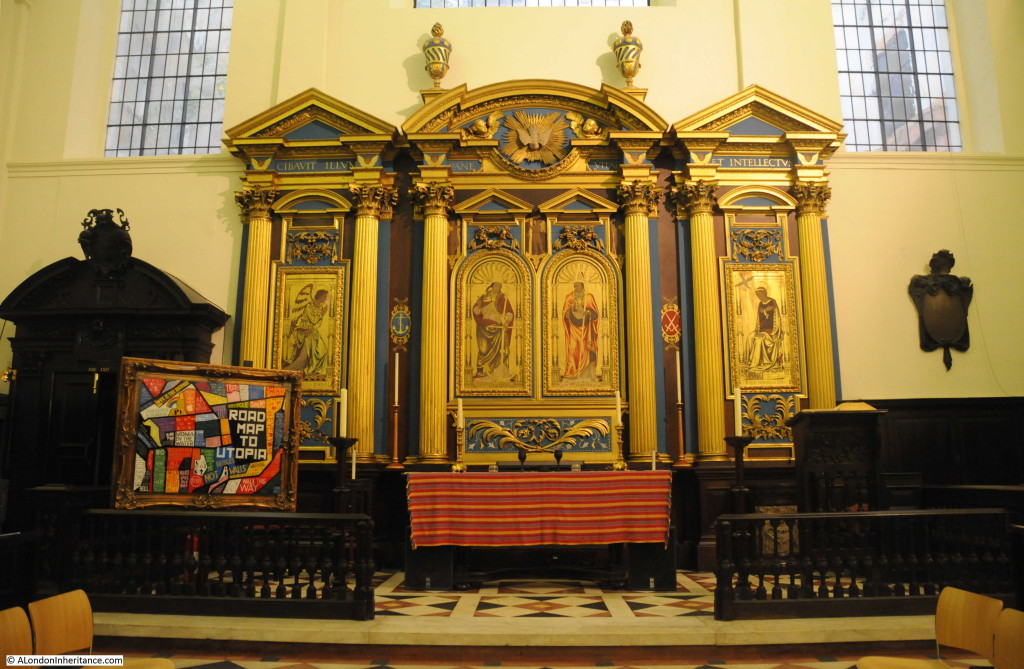
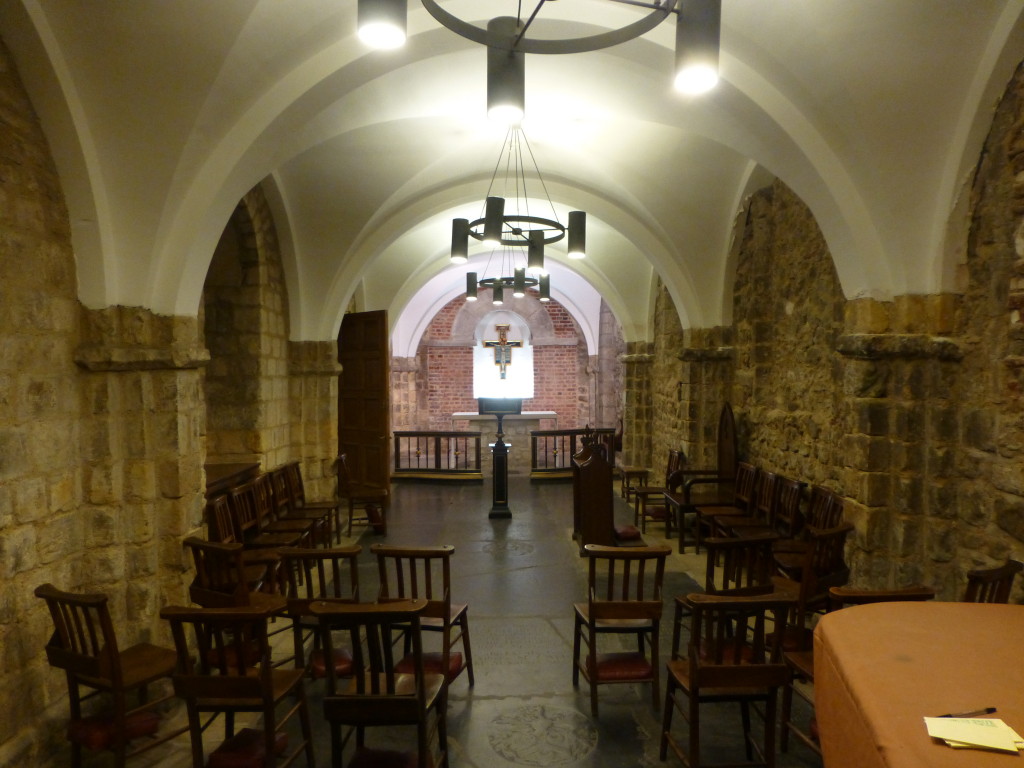
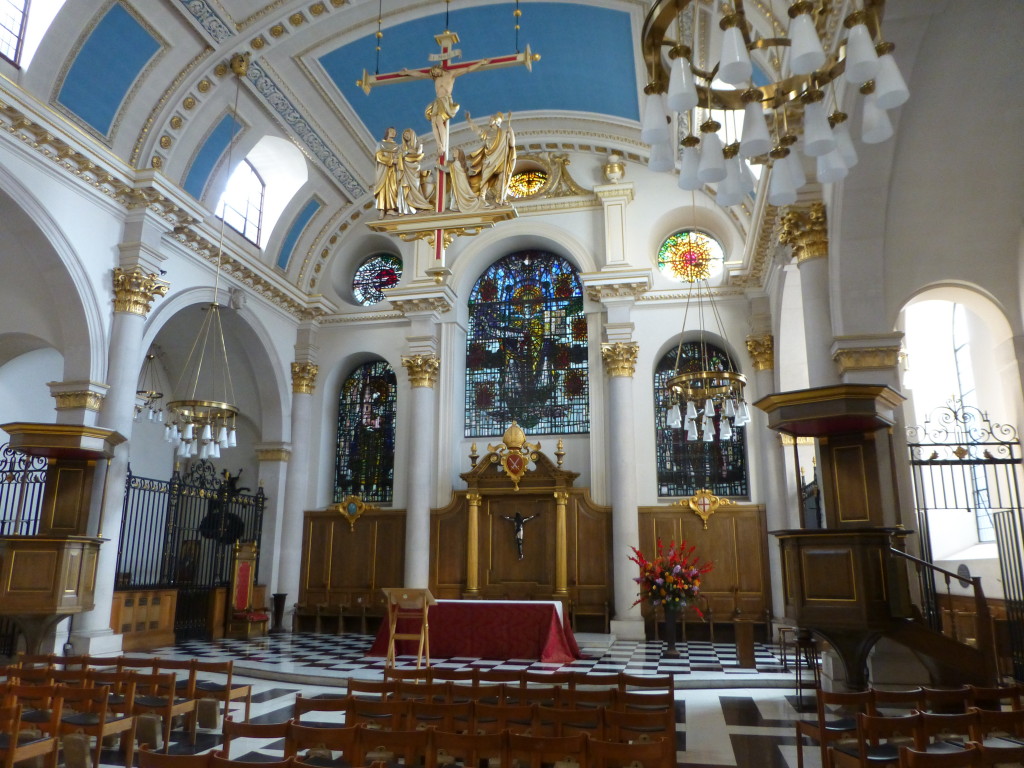
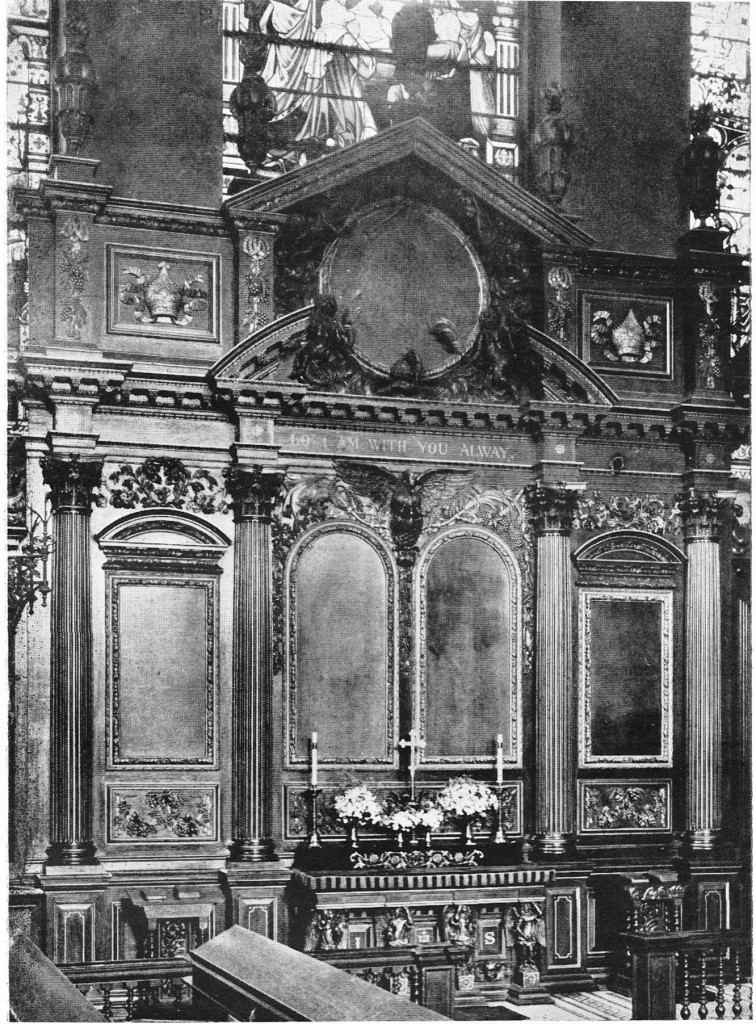
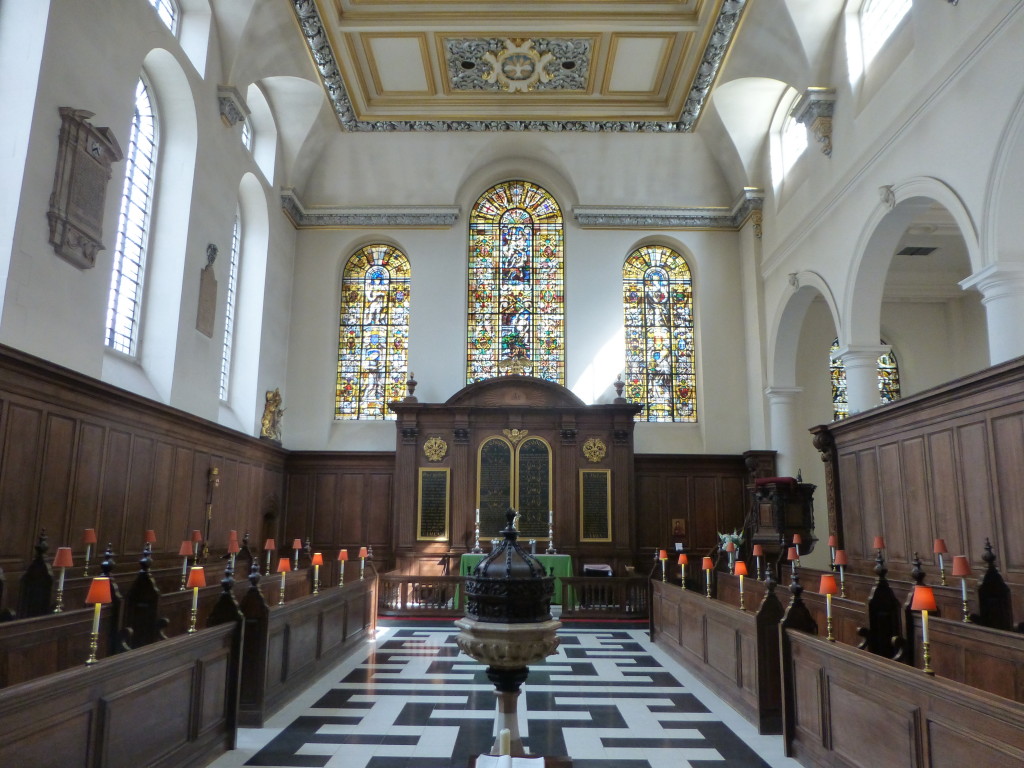
On entering the church from the street we look straight at the gilded reredos behind the altar.
There was some redesign of the interior of the church during the Victorian period and much of the ceiling was renewed in 1925.
The interior of the church has always been relatively simple, Stowe summed up the church as “This is a small church, void of any monuments”, and today the church performs a function which would have surprised Stowe. The pews have been removed and half of the floor space is now office space for charities. A good use and which helps the continued occupation of the church.
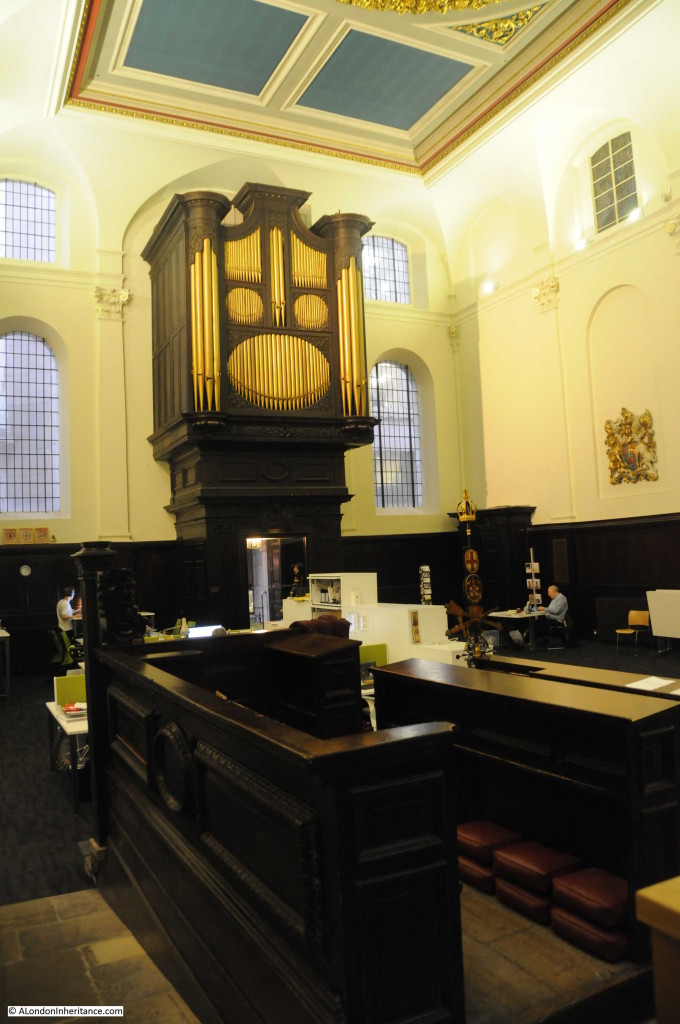
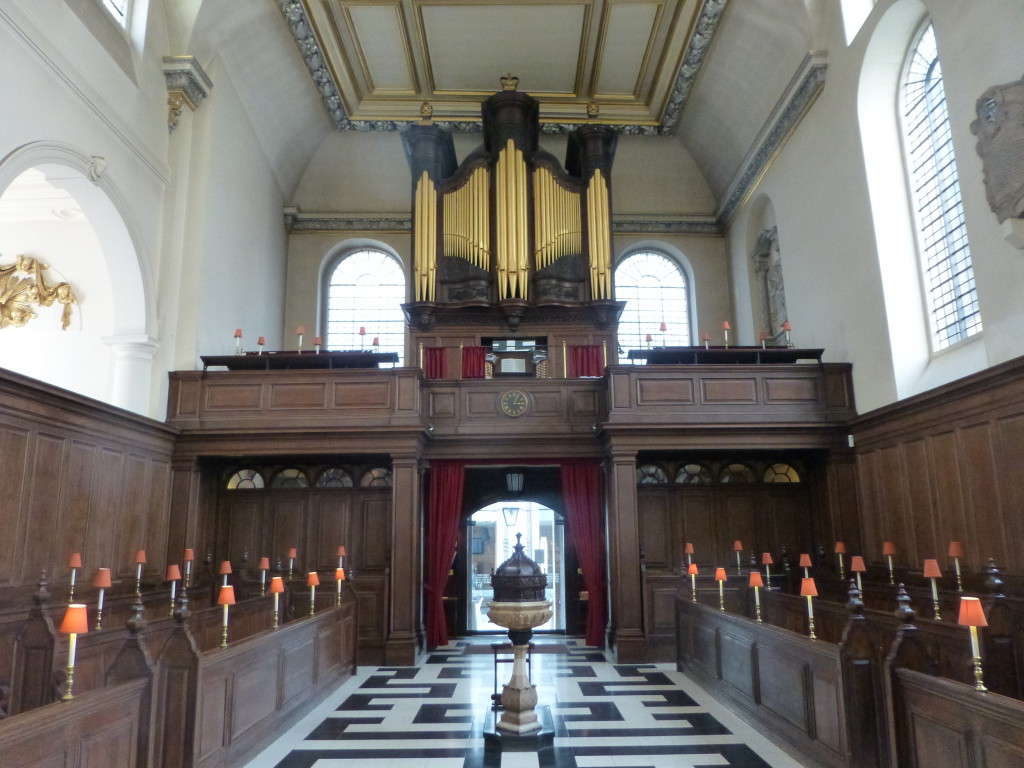
Looking back towards the entrance with the charity office space to the left. The original oak casing surrounding the organ appears to have a look of surprise, perhaps because of the current use of the church.
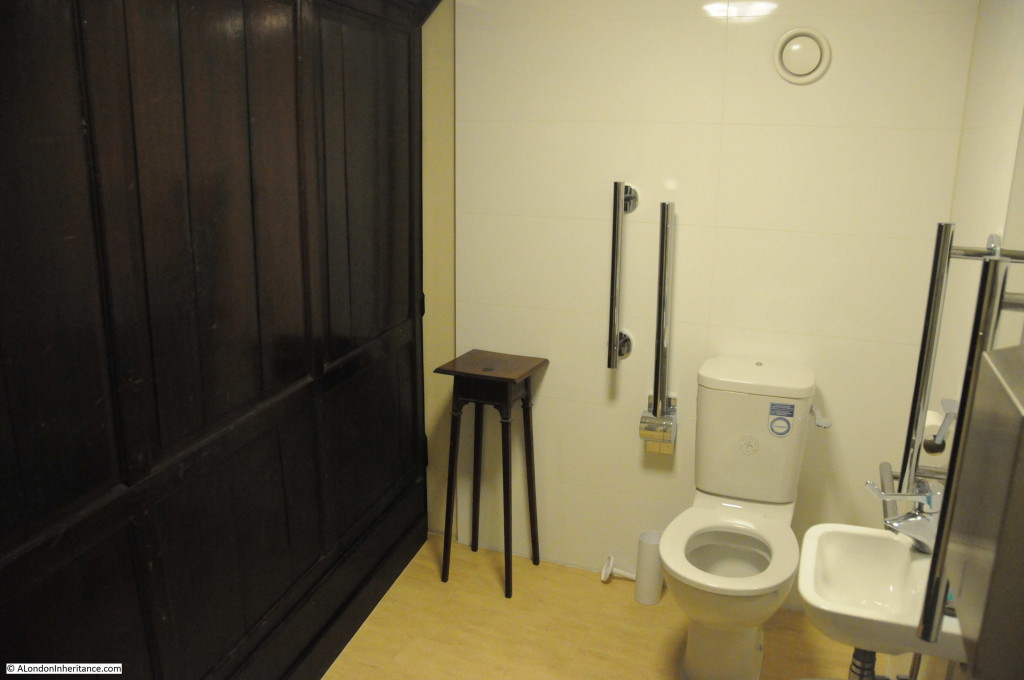
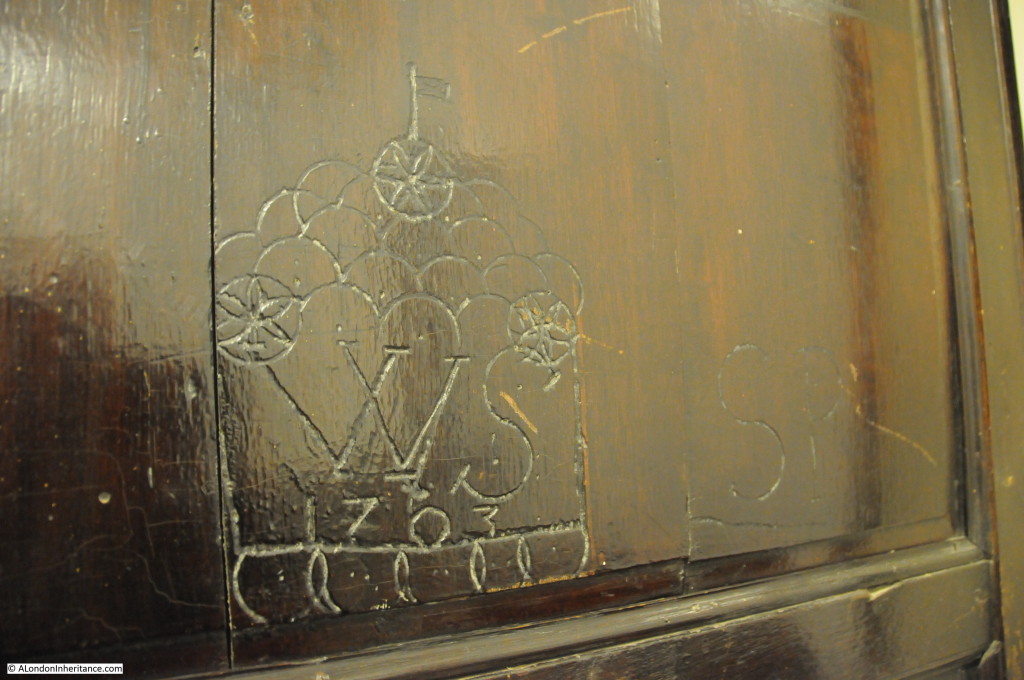
One of the most unique features of the church can be found in the toilets. Modern toilets have been built up against the original wooden wall panelling as can be seen in the photo below. It cannot be seen in the photo due to the lighting and dark panelling, but on the panelling, just to the left of the small wooden table is some very early 18th century graffiti.
A close up of the graffiti, dating from the year 1703, carved 15 years after the church was completed. A remarkable survival and very surprising to find this in such a location.
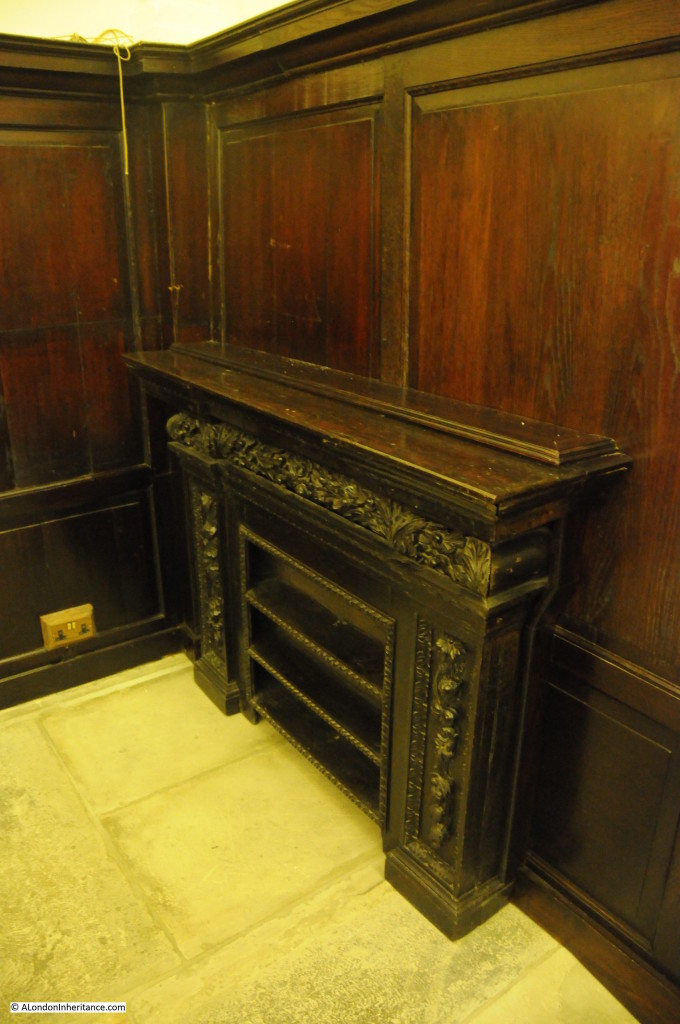
The church also retains some original Bread Shelves, used to store bread ready for charitable distribution.
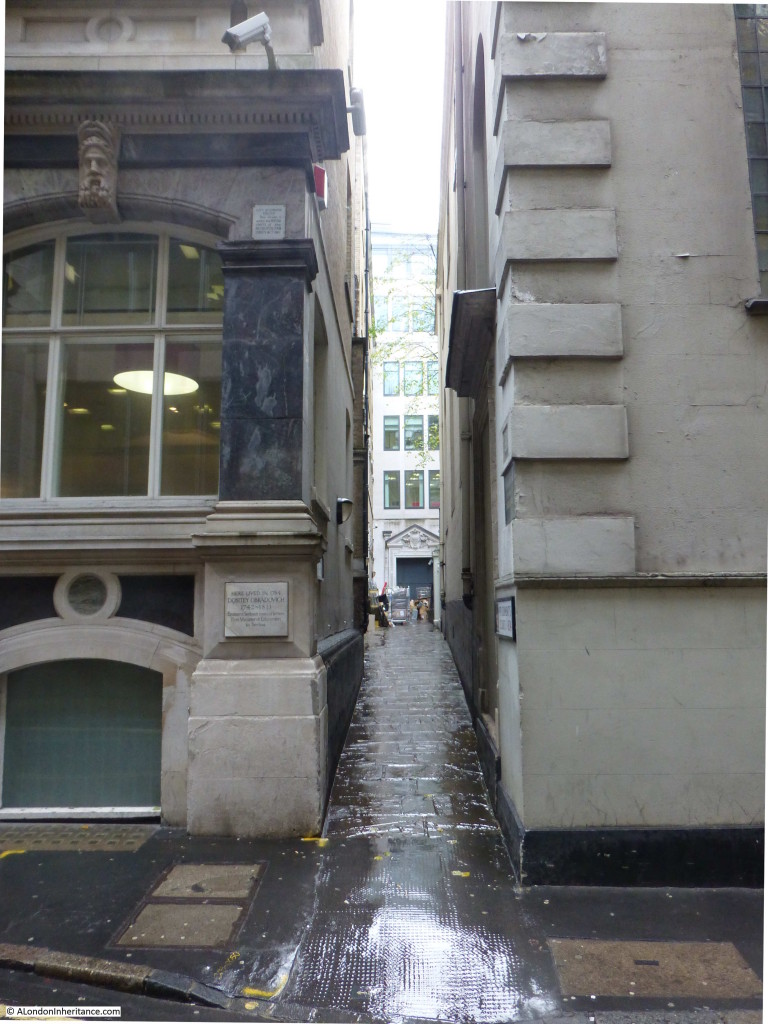
To the side of the church is St Clement’s Court, a narrow lane leading to the small churchyard at the rear of the church.
The plaque on the building on the left reads:
Here lived in 1784
Dositey Obradovich
1742 – 1811
Eminent Serbian man of letters
First Minister of Education
in Serbia
The lane also provides access to some of the office buildings that back onto the rear of the church.
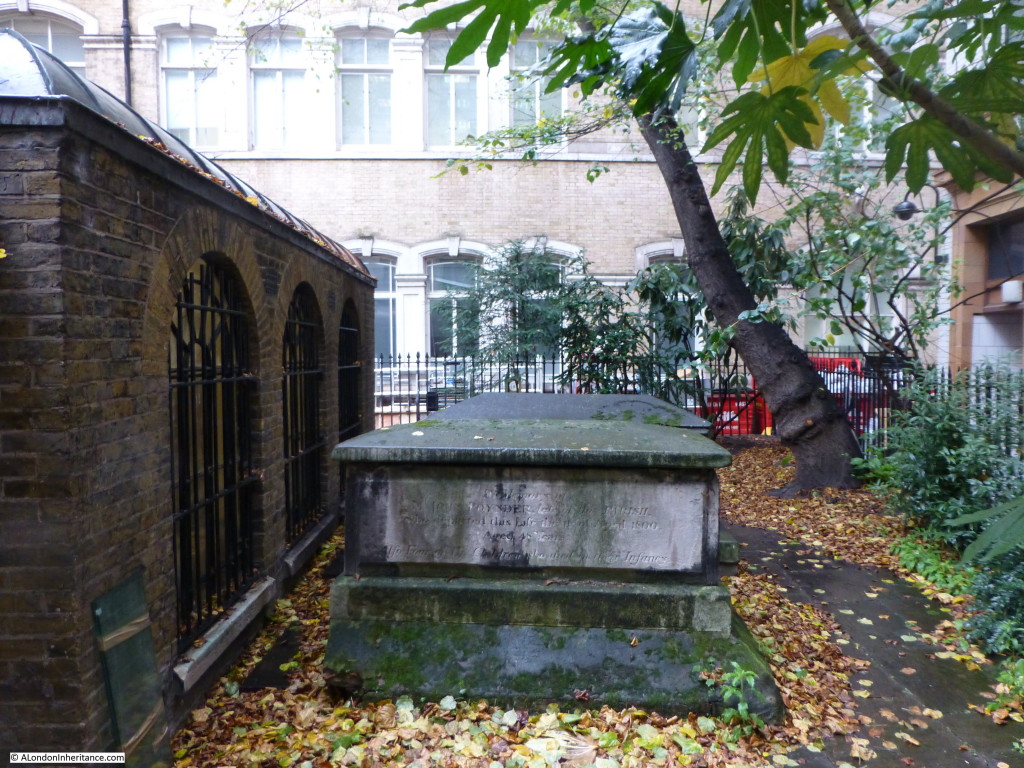
The remaining churchyard is very small with only a couple of in-situ graves. In 1910, Sir Walter Besant wrote of the churchyard:
“In Church Court we come to the ancient graveyard of St Clement, a minute space with one great shapeless tomb in the centre of the asphalt and a few small erect tombstones on the little border running inside the railings”
Not much has changed in the 105 years since that was written.
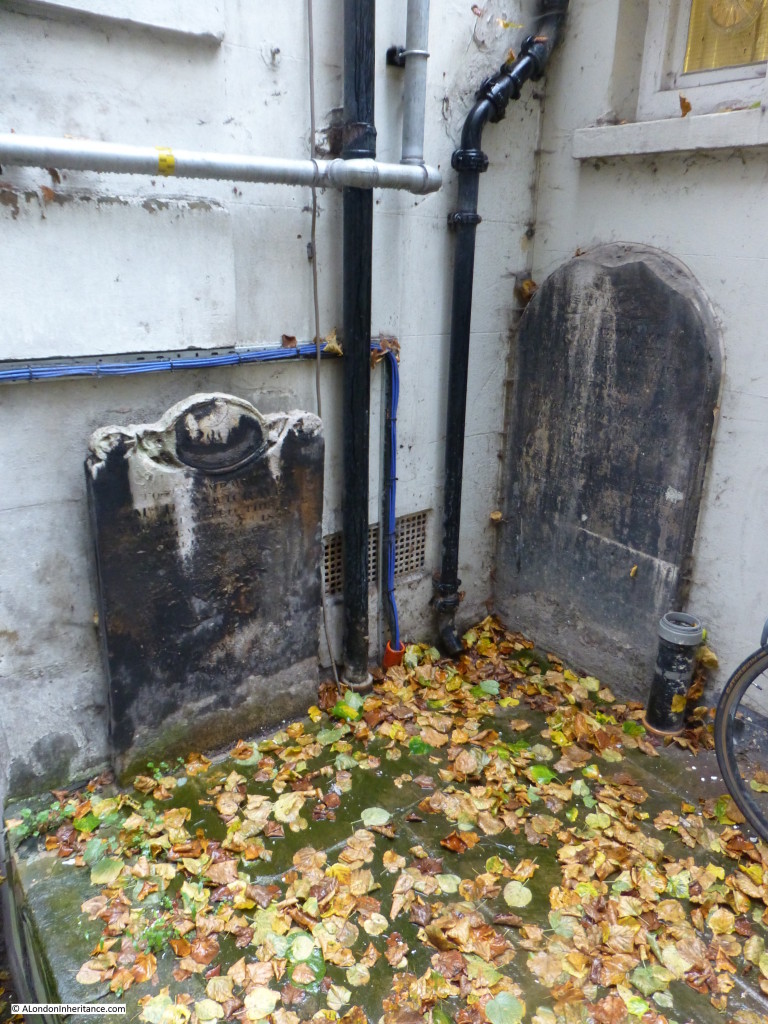
And a couple of gravestones which have been relocated up against the wall of adjoining buildings.
The church of St Clement, Eastcheap is easy to miss when walking in the area, but well worth a visit, including an essential trip to the toilet to see graffiti from 1703.