A couple of months ago, I featured a photo that my father had taken in Bermondsey. He had written the following notes to explain when and where the photo was taken “Flockton Street looking south from Bermondsey Wall. 19th century slum dwellings ravaged by the blitz – Summer 1948”. When I visited what remains of Flockton Street I was doubtful that this was the right location. Many features of the existing streets and in the photo did not line up.
I am really gratefull to a number of readers who identified the correct location as being Bevington Street in Bermondsey, and that a couple of the features in the original 1948 photo can still be seen to confirm. A quick look at Google Streetview clearly showed the location, however I was not content just to use Streetview as the purpose of this project is to revisit and photograph from the same viewpoints as in my father’s photos, so a couple of weeks ago I took another walk to Bermondsey to photograph Bevington Street – a location I have walked past a number of times, but for reasons I will explain later in the post, I was looking in the other direction.
My revisit also enabled the location of another photo to be confirmed, and I also found the location of a building photographed for the Wonderful London series of books published in 1926.
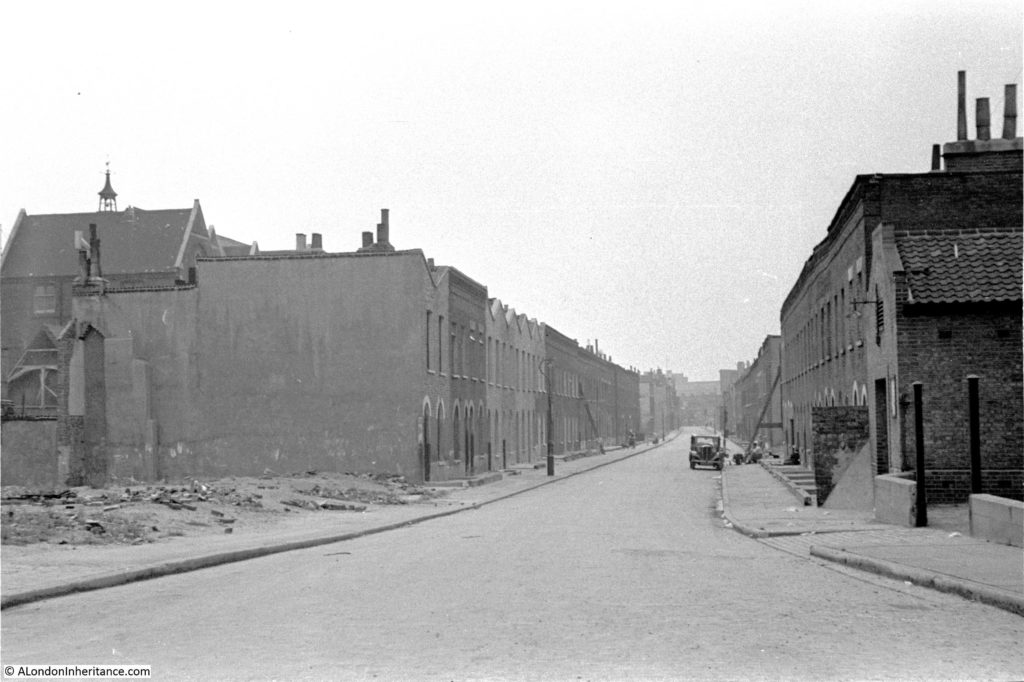
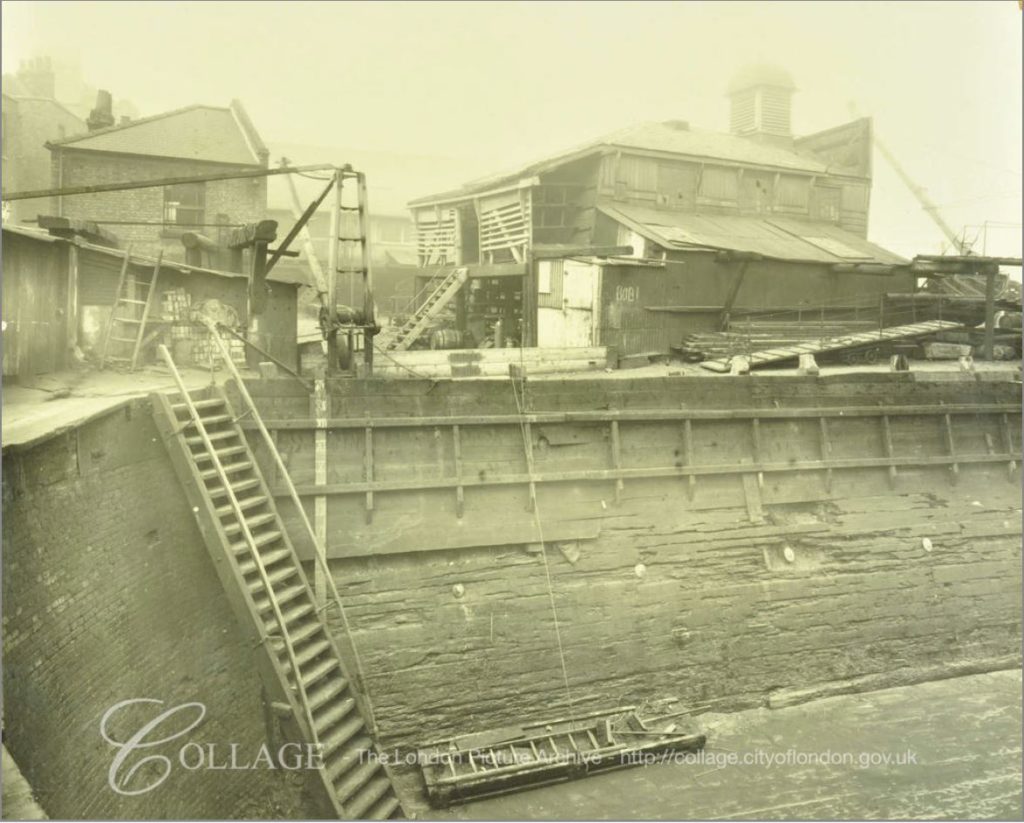
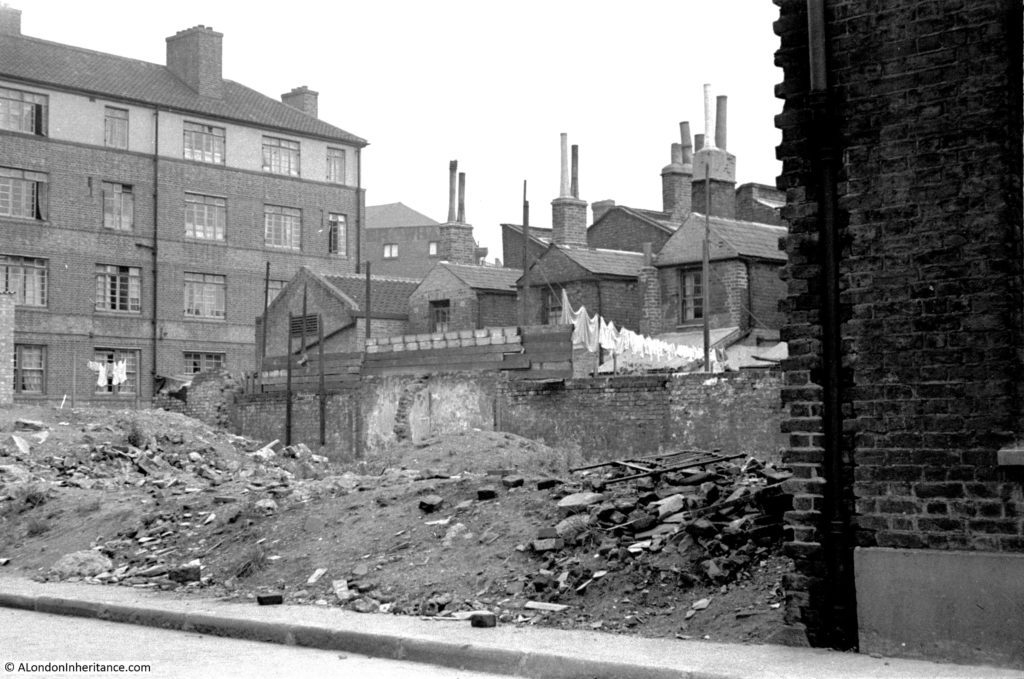
This is the view of Bevington Street from Bermondsey Wall photographed by my father in 1948:
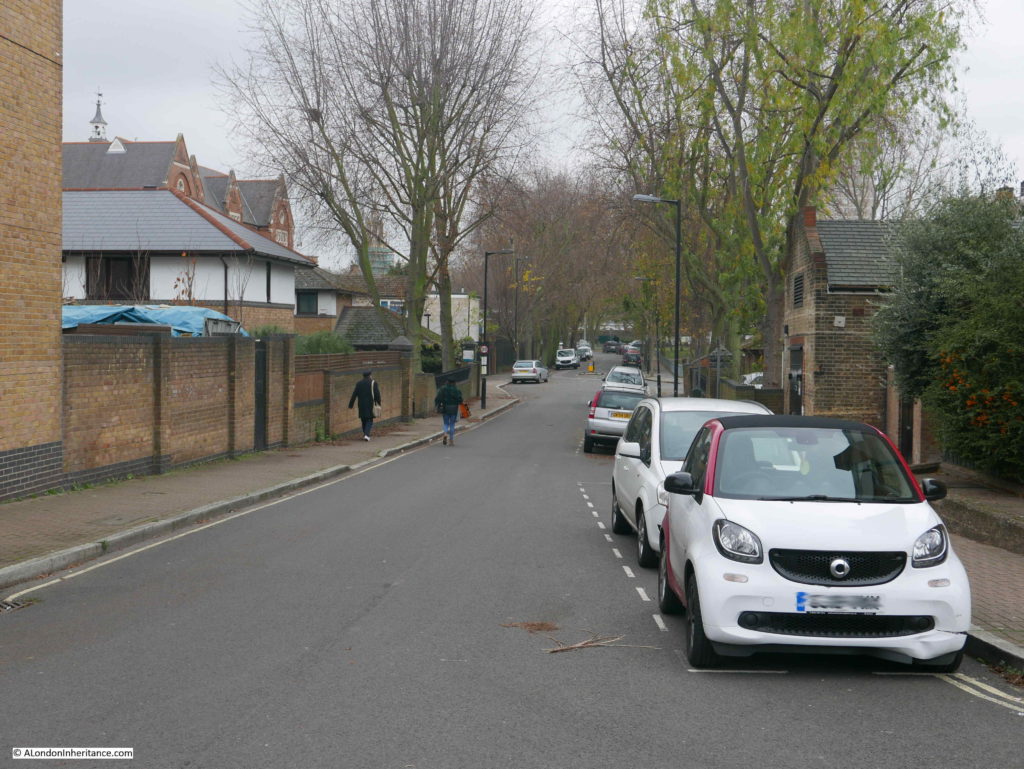
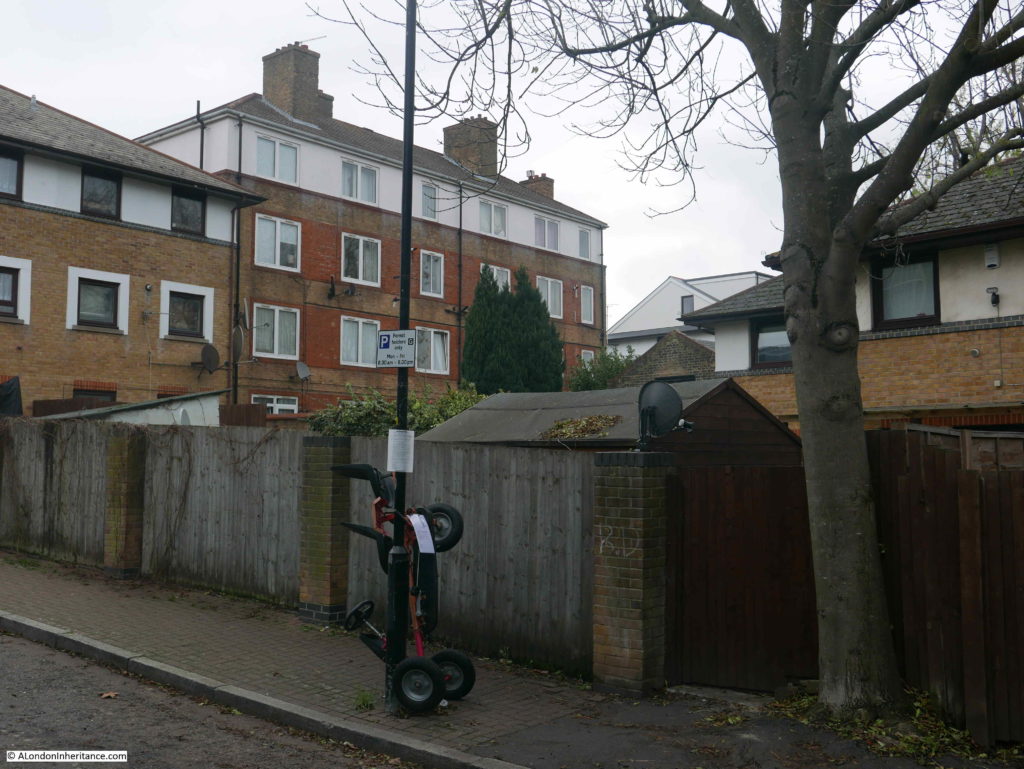
And this is the same view today:
There are only two features that remain the same, but serve to confirm the location. The school on the left and the small brick building on the right which now appears to house an electrical substation – remarkable that in all the redevelopment of the area this small building has survived.
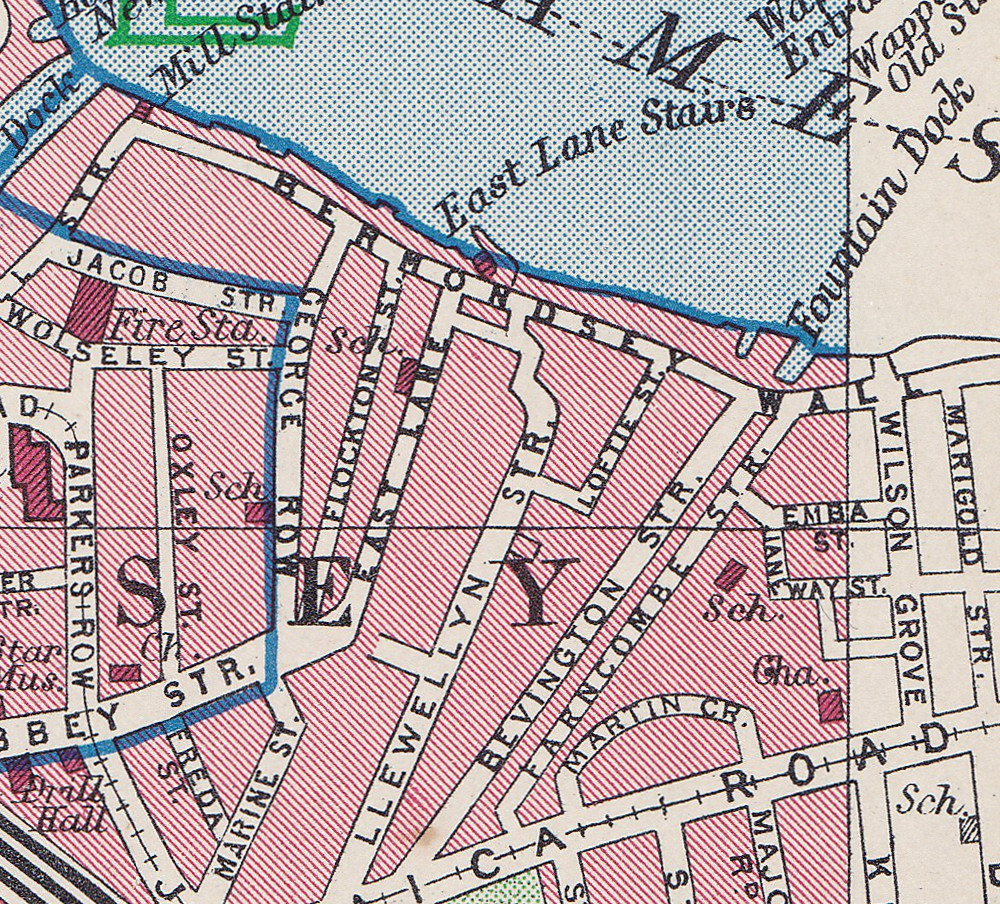
So where is Bevington Street? The following extract from the 1940 Bartholomew’s Atlas of Greater London shows the location. Bevington Street can be seen just to the right of the large Y. The school is further to the right, just across Farncombe Street.
Flockton Street, the wrongly identified location can be seen to the left, leading off from Bermondsey Wall, so these streets are very close. I suspect my father wrote up his notes for the photos after developing the negatives and looking at his route on the map, accidentally picked the wrong street.
I have used this 1940 map as it helps to explain a feature that can be seen today.
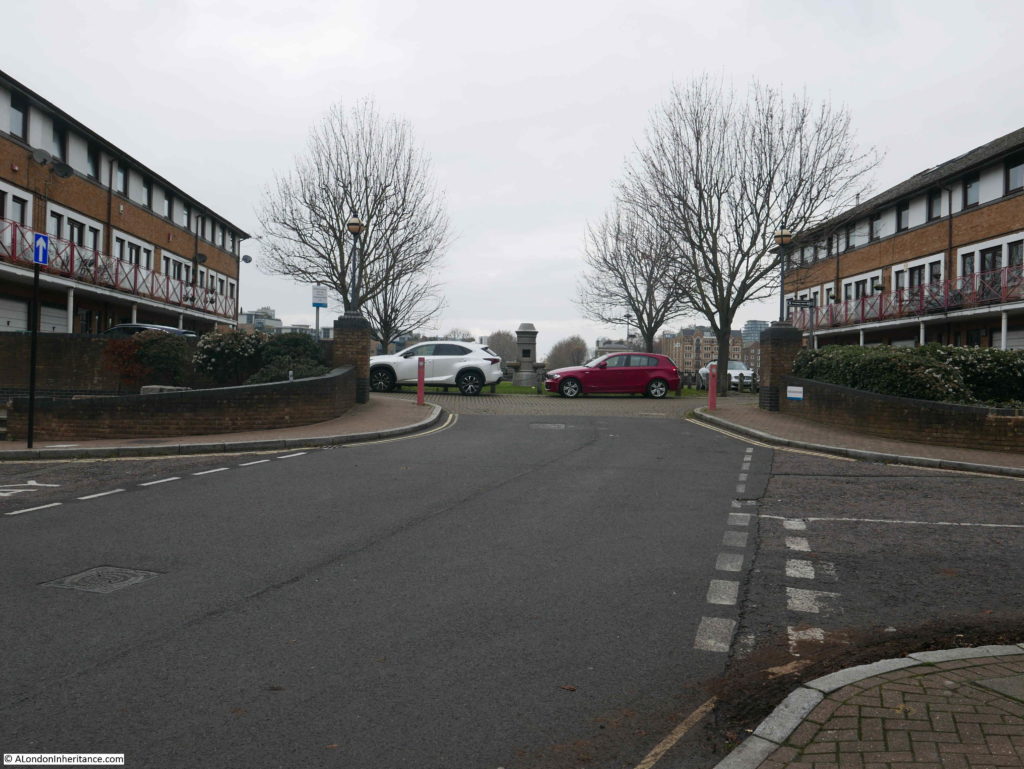
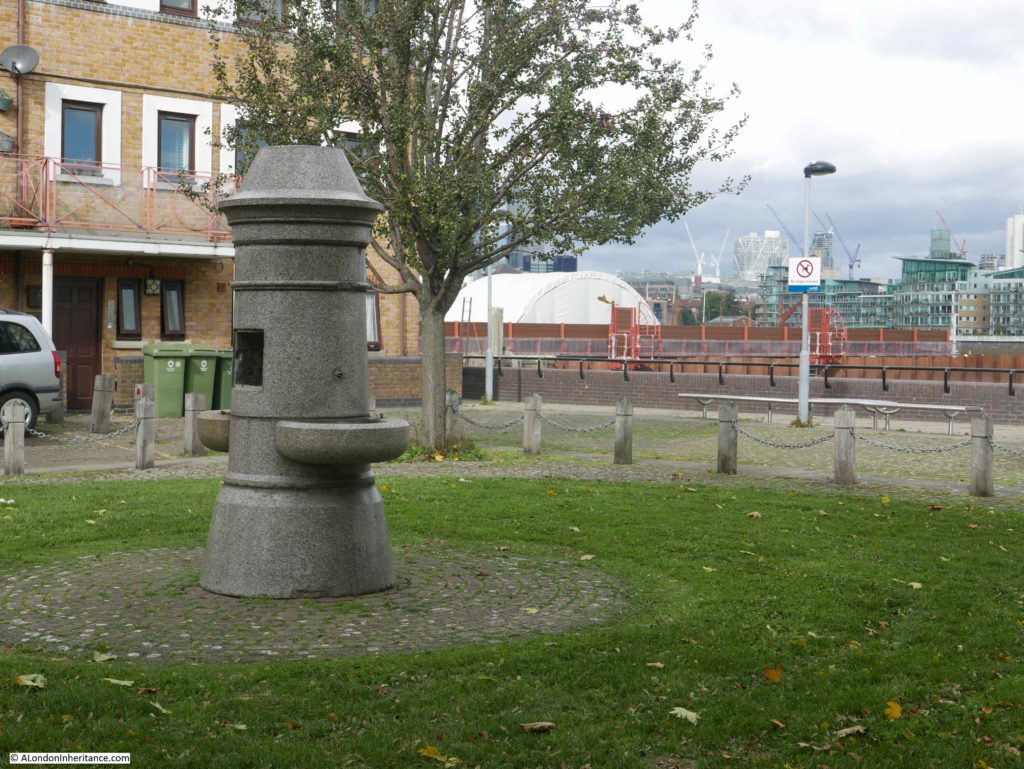
Bevington Street ends at Bermondsey Wall, and directly across from Bevington Street, between Bermondsey Wall and the River Thames is Fountain Green Square. The following photo is the view from the end of Bevington Street, looking across Bermondsey Wall to Fountain Green Square.
The name is very appropriate as there is a central green with a stone fountain in the centre. New housing is arranged around two sides of the green and the River Thames is alongside the far side of the green.
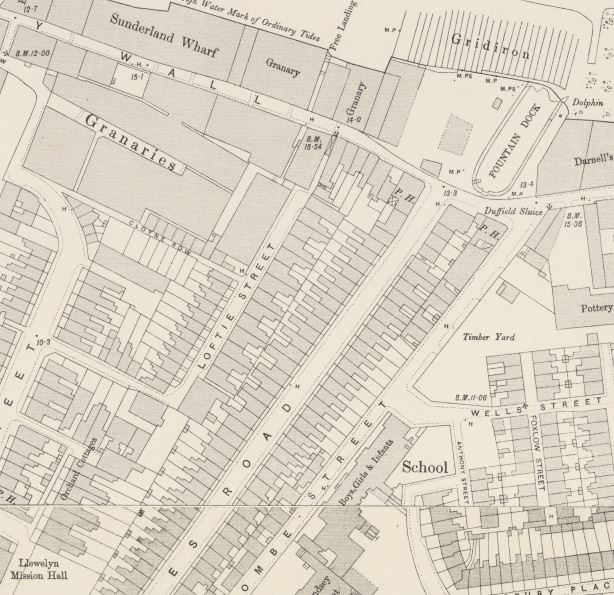
Looking back at the 1940 map and there is a feature here called Fountain Dock. The 1895 Ordnance Survey Map provides some additional detail and shows the shape and location of Fountain Dock.
Credit: ‘Reproduced with the permission of the National Library of Scotland’
The Southwark Council Conservation Area Appraisal (February 2013) confirms that the site of Fountain Green Square was the site of Fountain Dock, and that the dock was one of the few dry docks that operated along this part of the river.
Checking the overlay feature on the National Library of Scotland site, the dry docks appears over the easterly part of the green and partly under the houses on the eastern edge of the green, rather than occupying the full space of the green.
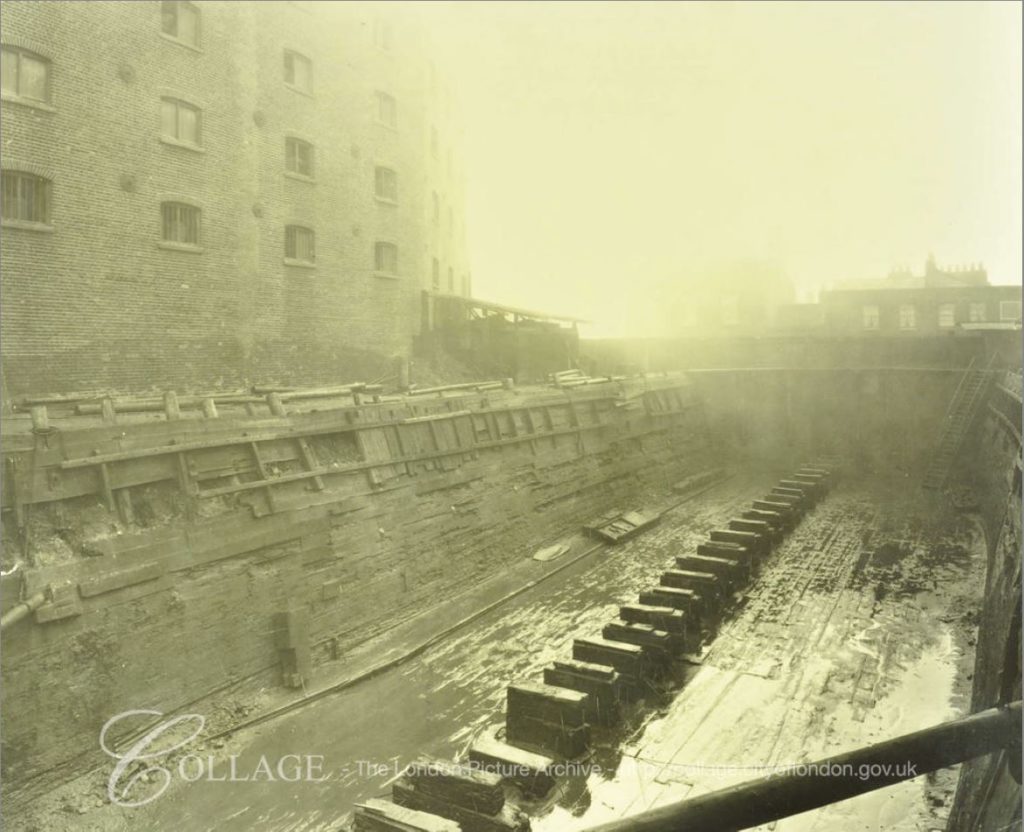
I checked the London Metropolitan Archives, Collage site and there are two photos from 1929 that show the dry dock. The first is looking from the north west corner of the dock, back towards where Bermondsey Wall runs right to left.
Image credit: London Metropolitan Archives, City of London: catalogue ref: SC_PHL_02_0912_A52734
The second photo, also from 1929, is looking from the south east corner of the dock, towards the river and the direction of the City.
Image credit: London Metropolitan Archives, City of London: catalogue ref: SC_PHL_02_0912_A5273
These photos from 1929 show Fountain Dock much as it must have been in the 19th century. Dry docks are important as they allow the hull of a ship to be inspected and worked on. The ship was moved into the dock, gates to the river closed and water pumped out from the dock, so somewhere alongside there must have been a building that housed the pump.
In an advert for the dry dock in Lloyd’s List on the 13th May 1893, the dimensions are given as a length of 161 feet and depth of 16 feet. The dock was owned by Mills & Knight who also owned the larger Nelson Dry Dock in Rotherhithe.
In addition to numerous adverts for the dry dock, 19th century newspapers included reports of accidents at the dock, as well as ships for sale. It appears to have been standard practice to offer a ship for sale when the ship is in dry dock for repair. The earliest example I could find was from the Shipping & Mercantile Gazette on the 27th August 1850, when the following ship was in Fountain Dry Dock and advertised for sale:
“The A1 Liverpool-built Barque BRAZILIAN, 345 tons, now lying in the Fountain Dry Dock, and ready for inspection; is in the course of re-coppering, &c., and, if not sold within a reasonable time, will be sent out again by her present owner. Length, 107 feet; breadth, 23 1-10 feet; depth 13 3-10 feet; carries a large cargo at an extraordinary light draught of water, and shifts without ballast”.
The following photo is the view taken from roughly the same viewpoint as the above photo. Today there is a fountain in the centre of the green.
The 1895 Ordnance Survey Map does not show a fountain, so I do not know if the fountain was moved here when the green was created to provide some relevance to the name. I doubt the fountain was here originally as it looks of rather fine construction to have been in such an industrial area – however I also do not know how Fountain Dock was named.
The origin of the name Bevington Street is interesting. When looking for this street on the 1895 OS map, whilst the street is there, in 1895 is was named Princes Road. It had changed to the current name sometime between 1895 and the 1940 map.
Although I have not been able to find any written confirmation of this, I suspect the name change may have been in the first decade of the 20th century. Bevington probably refers to Colonel Samuel Bourne Bevington.
When Bermondsey Borough Council was formed in 1900, Samuel Bevington was the first mayor and he was reelected the following year. He came from the family that had established Bevington and Sons, a company that manufactured leather products at Neckinger Mills in Abbey Street, Bermondsey. He was also a Colonel of the West Surrey Regiment, Justice of the Peace, on school boards and coming from a Quaker background, used family money to support a number of philanthropic activities.
Samuel Bourne Bevington died on the 14th April 1907 leaving a considerable estate to the value of £133,195. His will included money to provide income for four men and four women over the age of 60 who had been engaged in the leather trade.
Because of his role in the leather trade in Bermondsey, that he was the first mayor of Bermondsey Borough Council, and his other activities, I suspect that after his death, the council looked at ways to commemorate him, and one of the ways within their power was to rename one of the local streets, so Princes Road became Bevington Street.
There is much else of interest to be seen from the junction of Bevington Street and Bermondsey Wall.
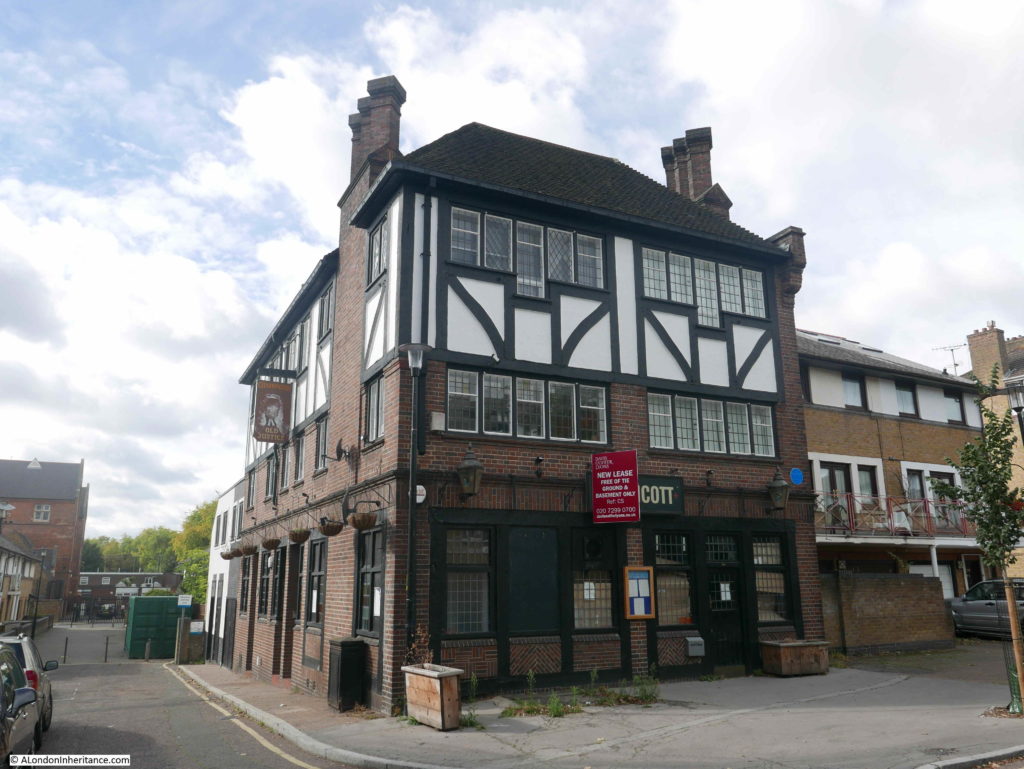
A very short distance to the east along Bermondsey Wall is a rather unique, listed pub – the Old Justice.
The pub, as with so many London pubs, has closed, however the building is Grade II listed.
The reason for the listing is that the pub is a rather well preserved example of a style of pub design from the inter-war period. The majority of Victorian London pubs were small and focused on drinking. The design initiatives after the First World War, focused on improving the pub environment, the provision of space for other activities apart from basic drinking, for example with the provision of restaurant space and a function room.
The Old Justice was designed by Sidney C Clark in 1933 for the Hoare & Co brewery. It followed a mock Tudor design that was frequently used on many pubs of the period.
Hoare & Co were taken over by Charringtons and the pub has a pair of Charrington lanterns on the frount, these probably date from the 1960s.
Alongside one of the lanterns is a plaque recording that Sir Paul McCartney used interiors and exteriors of the Old Justice as locations in his film “Give My Regards To Broad Street” and in the music video to “No More Lonely Nights”.
As well as the pub, the film also has some fascinating shots of the front of the warehouses along the Thames in Bermondsey.
I looked in through the windows of the Old Justice and the interior looks to have been reasonably well gutted, although the wooden paneling remains on the walls and the fireplace is still intact.
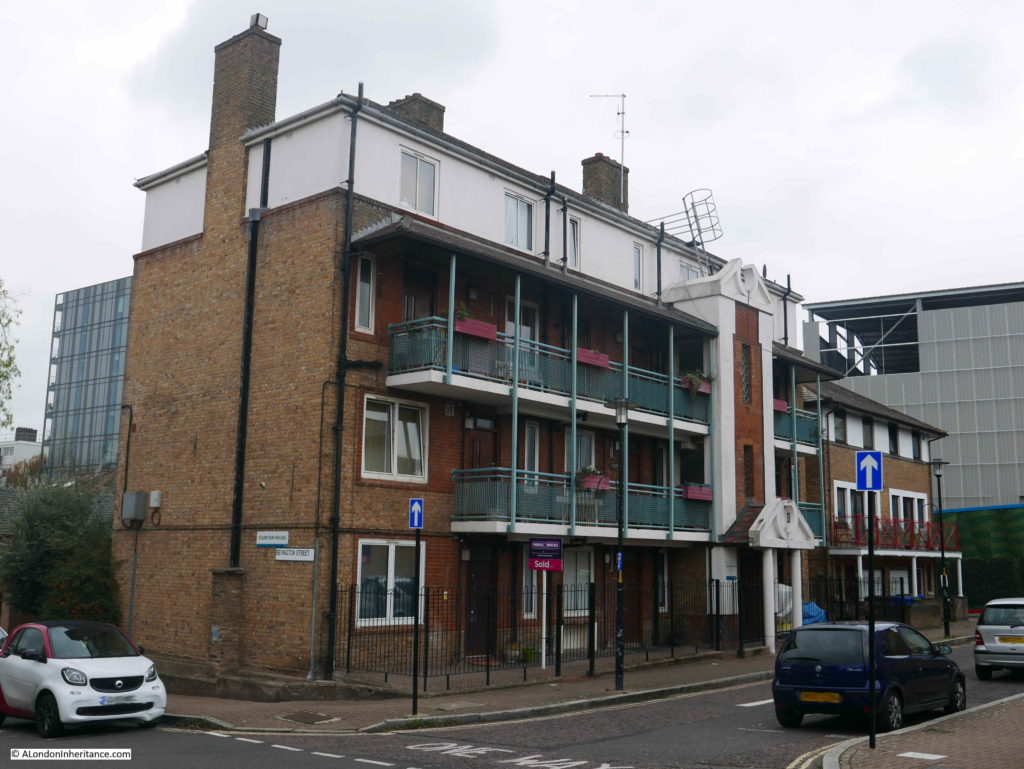
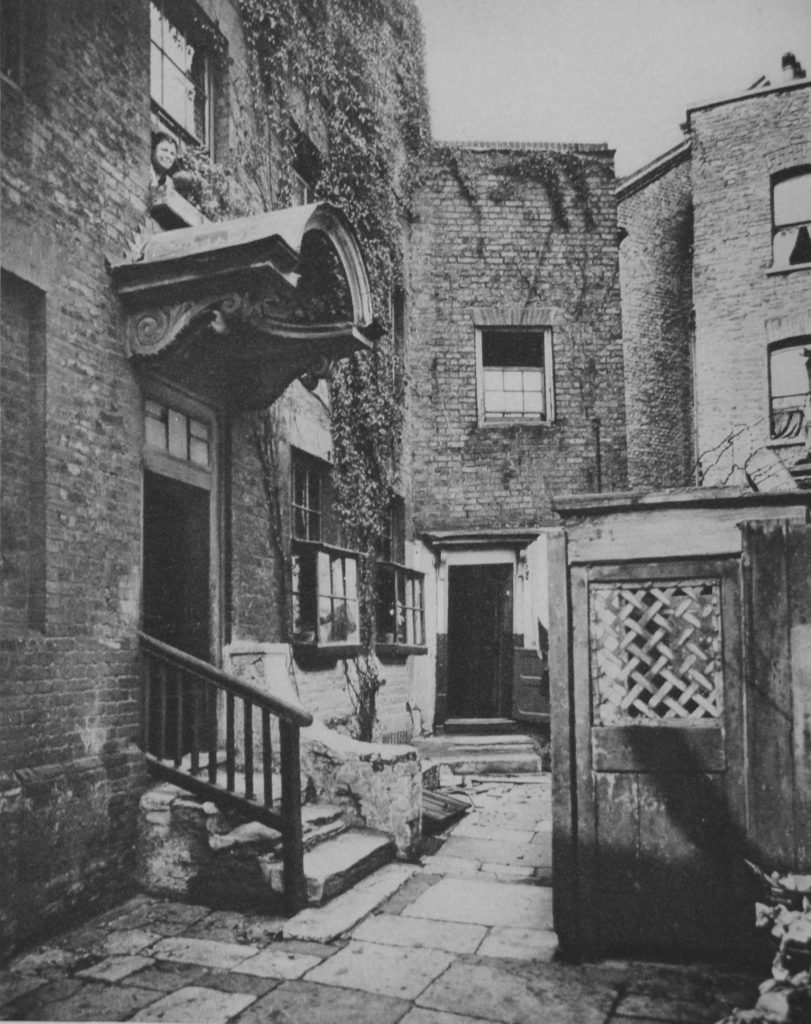
The Old Justice is just to the east of the junction of Bevington Street and Bermondsey Wall. To the west is another building that is earlier than the majority of buildings in the area. This is Fountain House:
I am not sure when Fountain House was constructed, or whether the name is original. however it did feature in another of my father’s photos of Bermondsey. I have now been able to identify the following photo as having been taken in Loftie Street, which runs parallel to part of Bevington Street.
The rear of Fountain House is on the left of the photo, but what confirmed the location was the rear of the electrical substation building that was one of the surviving features in the photo of Bevington Street. The rear of this building can be seen in the above photo, to the right of Fountain House.
The houses are the rear of the houses that front onto Bevington Street. Washing is hanging to dry at the rear of one house, and I am fascinated by the height of the chimneys on these houses.
What must be the remains of a bomb site is to the front of the photo.
I tried to take a photo from a similar position today, but it was not easy with the buildings and fences that now occupy the area, however in the following photo, the rear of Fountain House can be seen, and just to the right, a small part of the top of the rear wall of the electrical substation building is just visible.
There was one additional place I wanted to track down. When I was looking for Flockton Street, I walked along George Row, which runs parallel to the original route of Flockton Street. The name George Row was familiar and I recently remembered where I had seen the name.
In 1926 a three volume set of photos and articles titled “Wonderful London” was published and the first main photo in volume 3 was titled “The Bridge House In George Row, Bermondsey”.
The caption with the above photo read:
“Bermondsey has had its royal palace dating perhaps from Edward the Confessor, and it was only in 1805 that the North Gate of its Abbey was taken down. The building in the photograph is called the Bridge House, since it stands where a bridge was built over one of the creeks that entered the river and made, with what is called St. Saviour’s Dock, Jacob’s Island. This was a densely populated quarter a hundred years ago, and its many canals and ditches had a Dutch air, according to the chroniclers”.
George Row today is a wide street that runs from Jamaica Road down to Bermondsey Wall. There are no buildings that look like the above photo and I was doubtful that I could find the location, however I turned to the 1895 Ordnance Survey map, and at the northern end of George Row, close to the junction with Bermondsey Wall, there is a building clearly labelled Bridge House. The map also shows the steps leading down from the building with what appear to be steps leading down from the building on the eastern side and sidesteps on the western side. This would confirm that the photo from Wonderful London was taken of the eastern face of the building.
Credit: ‘Reproduced with the permission of the National Library of Scotland’
It was easy now to find the location of Bridge House, the map overlay feature helped confirm exactly where to look. Bridge House was not directly on George Row. In the above map there is a space, which appears to be open space between the building and street, and this configuration remains today.
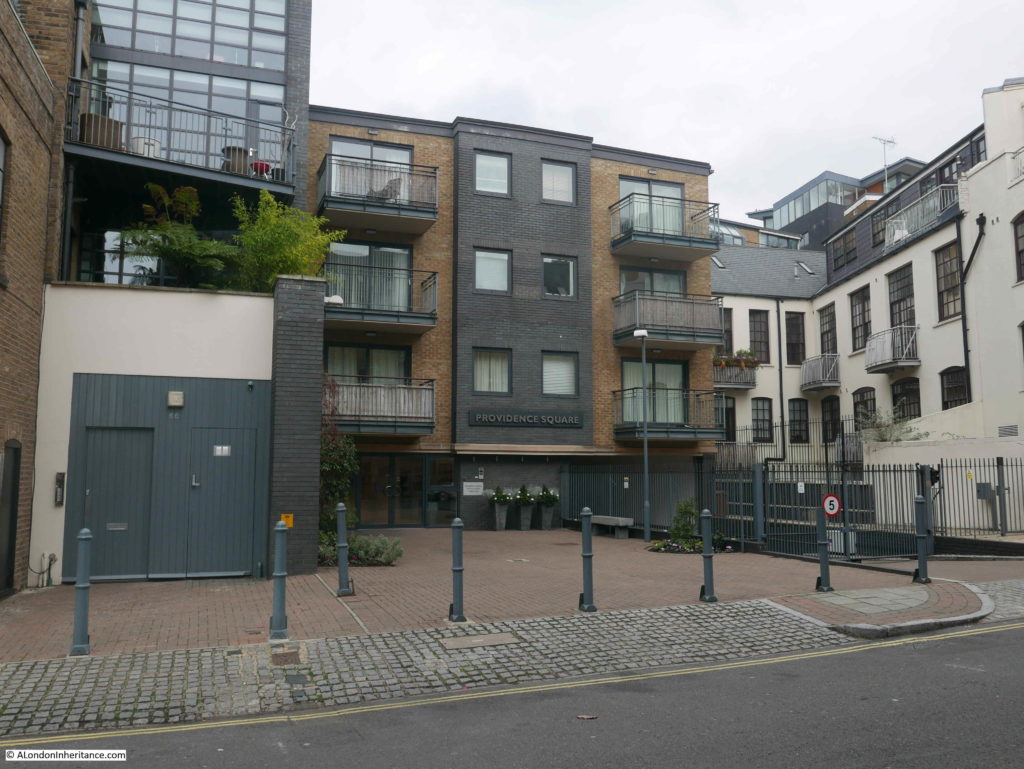
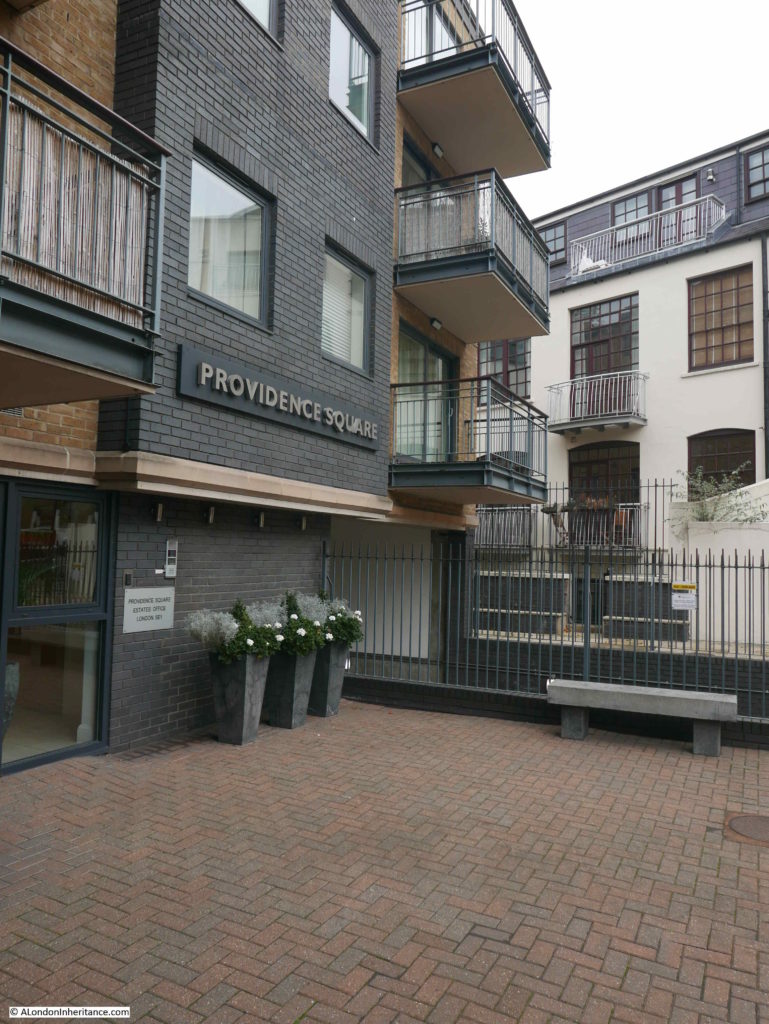
The following photo shows the location of Bridge House today, with a 4 storey block of flats – Providence Square – now standing in what appears to be almost the same footprint of Bridge House.
It would be interesting to know why the new building did not extend to George Row. Developers tend to maximise the amount they can build and make use of every available bit of space and the area between the building and George Row serves no apparent purpose.
I walked up to the edge of the building to take a photo from roughly the same position as the photo from Wonderful London.
The caption to the photograph in Wonderful London explains the source of the original name for the building: “The building in the photograph is called the Bridge House, since it stands where a bridge was built over one of the creeks that entered the river and made, with what is called St. Saviour’s Dock, Jacob’s Island”.
There are no signs of the creek today, however maps provide some indications.
In the 1895 Ordnance Survey map the word Neckinger can be seen running alongside George Row. This refers to the River Neckinger. I have read many different accounts of where the Neckinger entered the River Thames, most claim that St. Saviour’s Dock was the main estuary of the Neckinger into the Thames, however this was always low lying marsh land, and there have been many canals and ditches built in this area (I mentioned the 19th century walled drain in my post on Flockton Street, and the outline of this drain can still be seen running across the street).
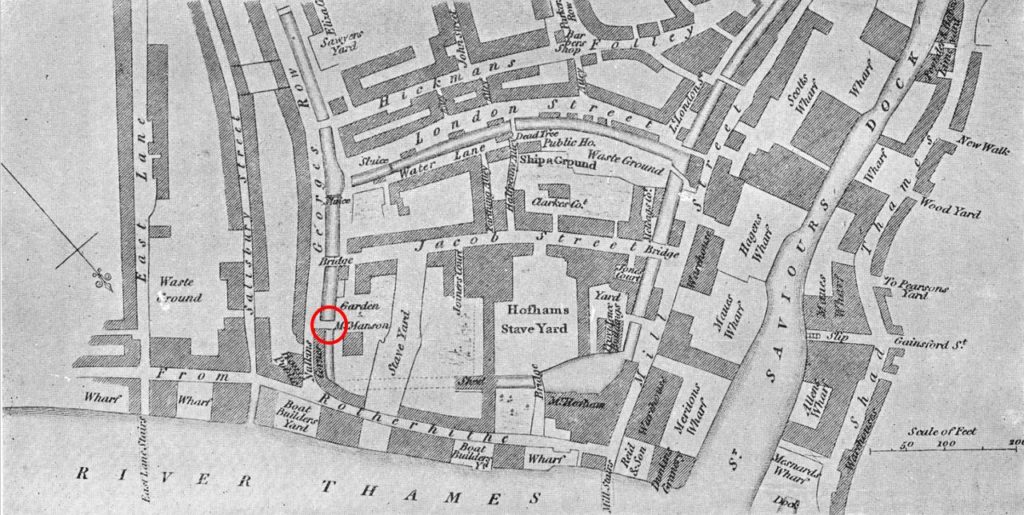
The book “Bermondsey, Its Historic Memories And Associations” written by E.T. Clarke and published in 1902 provides a location for the creek and bridge. The book includes the following map of the area.
The so called Jacob’s Island is in the centre of the map, bounded by the Thames at the bottom of the map, St. Saviours Dock to the right, a canal running alongside London Street to the top, and on the left, a canal running along the full length of George Row.
Based on the locations of streets that can still be found today, I have circled in red the bridge that gave Bridge House its name.
This is pure speculation, but it may be that Bridge House is the rectangular building on the above map to the lower right of the red circle.
I do not know when this canal or extension of the Neckinger was filled in – it had disappeared by the time of the 1895 map, but it is interesting that the open space between George Row and the building that now occupies the location of Bridge House would have been where the canal ran.
Finding the location of Bridge House helps to understand how this area has developed over the centuries. Fountain Green Square provides a link to the dry dock that once occupied the site, and Bevington Street records the first mayor of Bermondsey and the leather industry of area.
Finding Bevington Street means I can tick off another of my father’s photos from 70 years ago. My thanks again to everyone who identified the correct location of the photo.