A couple of week’s ago I was in ironmonger Lane in the City of London, a narrow lane running between Cheapside and Gresham Street.
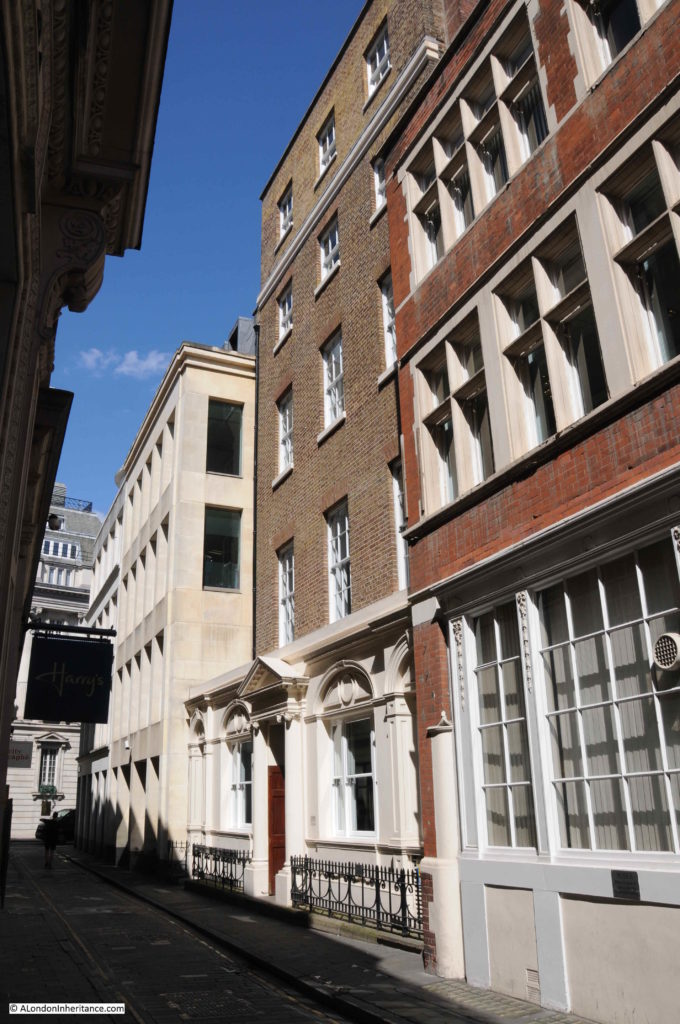
The buildings in the lane are relatively recent, and difficult to photograph due to the width of the lane, however Ironmonger Lane has a fascinating history, so for this week’s post, let me take you on a journey through time starting with the earliest traces of habitation in ironmonger Lane.
As with many City streets, ironmonger Lane suffered bomb damage in the last war, hence the relatively young age of the buildings that line the lane today.
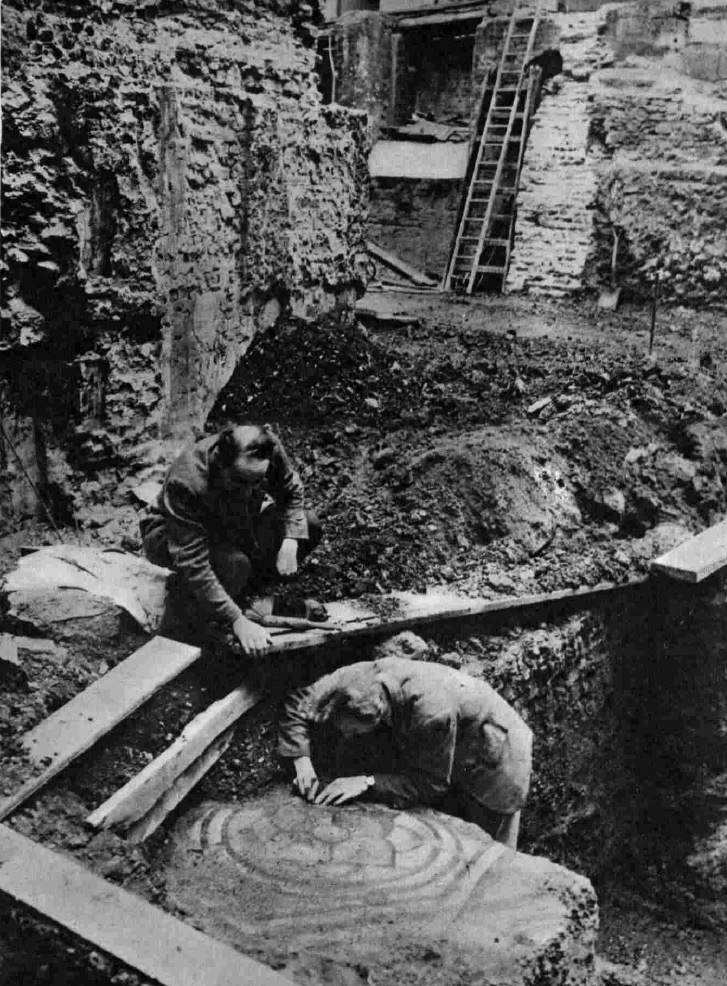
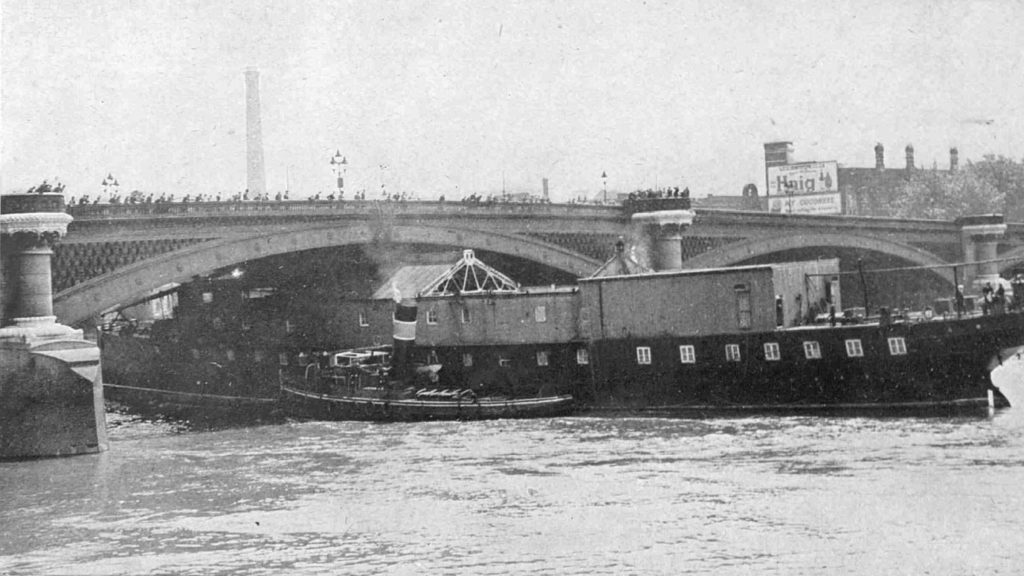
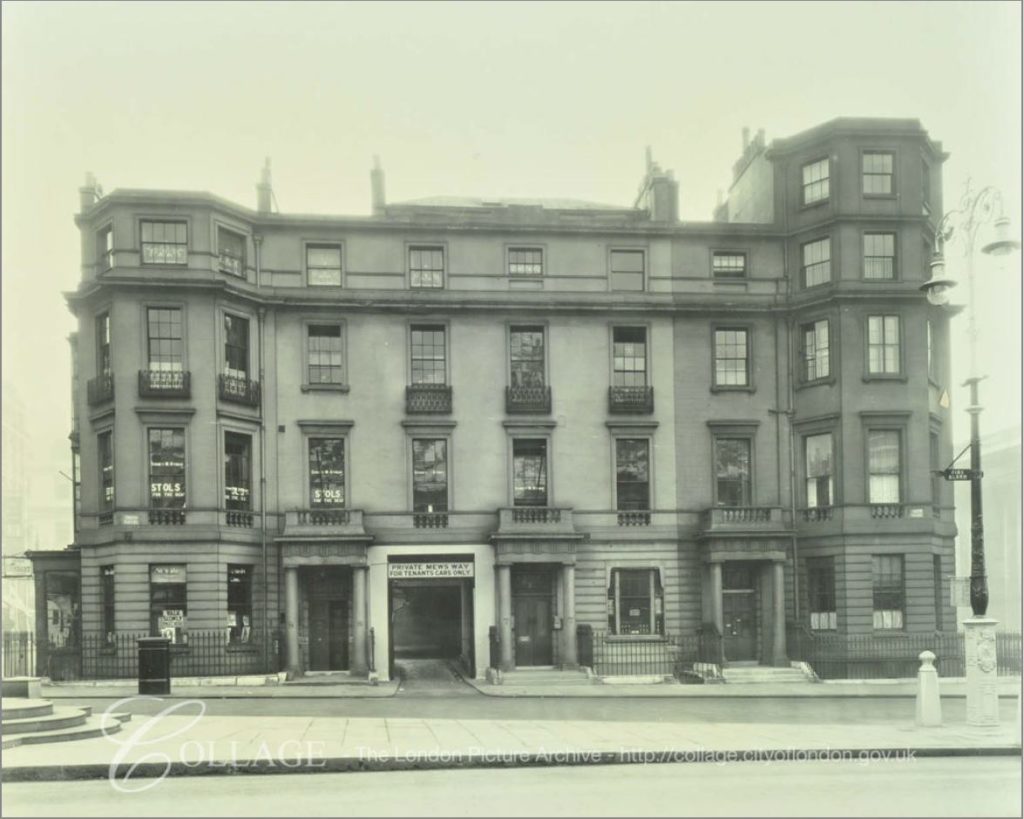
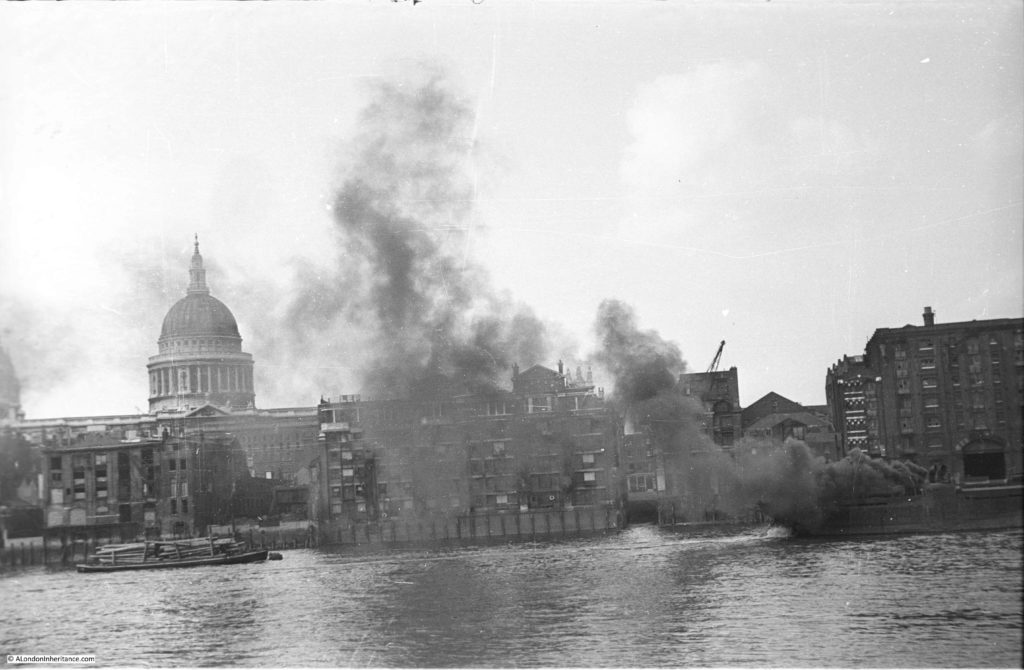
The bomb damaged remains of number 11 Ironmonger Lane were being demolished after the war and the Guildhall Museum led an excavation of the site.
Number 11 is in the centre of the photo below:
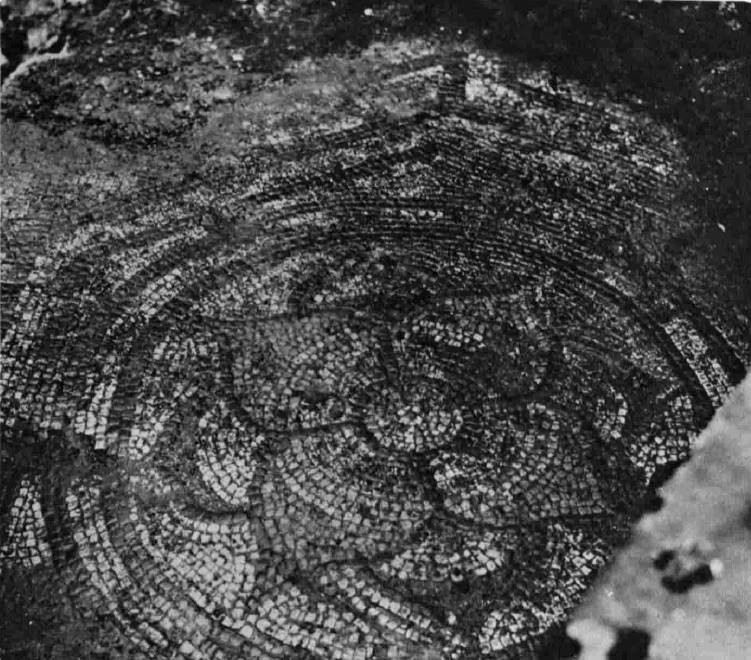
Adrian Oswald, working on behalf of the Guildhall Museum excavated the site, and 16 feet below street level the remains of a Roman house and Roman mosaic were found.
The excavation was notable at the time as this was the first Roman mosaic that had been found since excavations at the Bank of England.
The mosaic and house were dated to around the 2nd and 3rd centuries.
It is intriguing to imagine that Ironmonger Lane was a street in Roman times, and this was the earliest traces of the buildings and people living in this part of the City.
The next traces of occupation in Ironmonger Lane are possible 9th to 11th century foundations found in the churchyard of St. Olave during an excavation in 1985 / 86. The churchyard is in the centre of the lane, and Roman bricks were also found during the excavations, providing further evidence of Roman building.
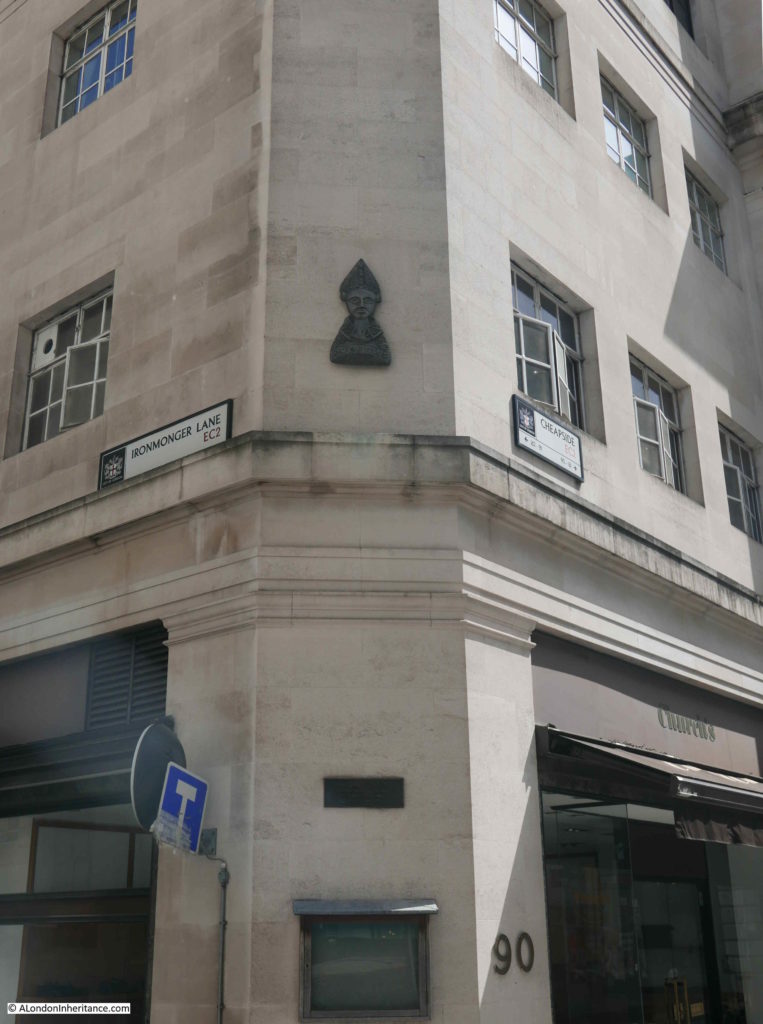
Early in the 12th century, Thomas Becket, who would become Archbishop of Canterbury and murdered at Canterbury Cathedral at the apparent command of King Henry II, was born in a house on the corner of Ironmonger Lane and Cheapside, a plaque marks the site today:
The Becket family owned part of the land at the southern end of Ironmonger Lane and alongside Cheapside.
Also in the 12th century, we see the first references to the church of St Olave (roughly half way along the lane), although certainly much older, and also to the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon (dedicated to Thomas a Becket), when hospitals were mainly religious establishments.
The Hospital of St Thomas of Acon was founded in 1227 on land at the southern end of Ironmonger Lane, between ironmonger Lane and Old Jewry, facing onto Cheapside.
The hospital would be important for how we see the southern end of Ironmonger Lane today.
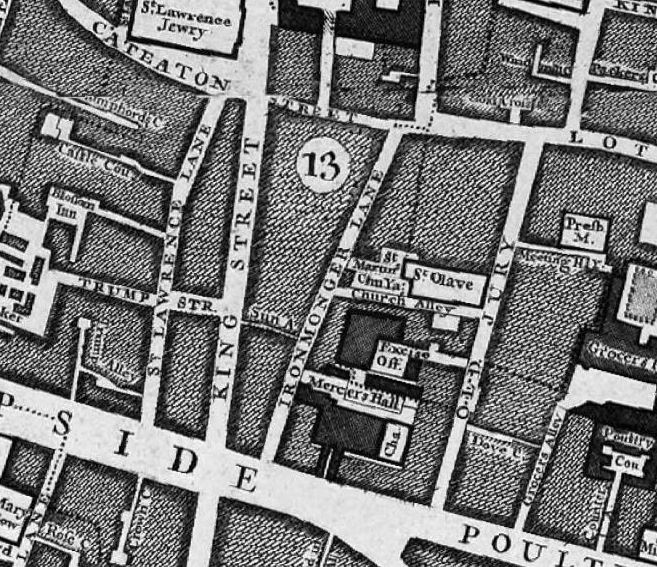
Now for my first map. This is John Rocque’s map of 1746, although I have not yet reached the 18th century, the map is helpful in showing the location of some of these 12th century establishments.
Ironmonger Lane is in the centre of the map. Cheapside at the southern end, and Cateaton Street (which would later become Gresham Street) at the northern end.
Look to the southern end, and to the right of Ironmonger Lane is a block of building and the abbreviation “Cha” for Chapel – this is the area where Thomas a Becket was born and also the site of the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon.
The hospital was built on land purchased from the Becket family. The name Acon is the anglicised version of Acre (now part of Israel), and dates from the Third Crusade between 1189 and 1191, and possibly originates from an order of monks / knights formed during the Crusade and the siege of Acre.
In Rocque’s map, you can see that the Mercers Hall is also shown where the hospital was located.
The Mercers Company represented the interest of merchants who traded in materials such as wool, linens and silks and it was the Mercers who became patrons of the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon, and used the hospital’s chapel as a ceremonial meeting site from when the chapel was built in the 13th century in 1248.
Also in the 13th century, the second church in Ironmonger Lane is first mentioned. This is the church of St Martin Pomary which was located between the church of St Olave and Ironmonger Lane – two churches adjacent to each other. To see how close these churches were, look at Roqcue’s map above, to the left of St Olave, you will see the text “St Martin’s Church Yard”.
I have not yet mentioned anything about the name – Ironmongers Lane.
The name relates to the trade of Iron Mongers as in the medieval City, trades generally clustered around specific streets. The first mention of the name is from the 13th century, and there were many variants of the name, starting with Ysmongeres Lane, with other variations between the 13th and 14th centuries. The Agas map of 1561 records the street as Iremongers Lane.
The ironmongers would not stay too long in the area as it appears they have moved to the Fenchurch Street area in the 15th century – so the name is a remarkable survival of a medieval trade with a specific area.
In the 15th century, the Mercers were continuing their long association with the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon as in 1407 the Mercers purchased their own chapel in the Hospital’s church.
Moving a century later, and the 16th century was a time of dramatic change in ironmonger Lane.
In 1524, the Mercers built their first Hall on land purchased from the Hospital.
In 1538, the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon was taken over by the Crown during the dissolution. The Mercers negotiated the purchase of the land, and subsequently purchased all the hospital’s properties, and the company built the Mercers School on part of the land. I suspect they were a company never to pass by a good commercial opportunity.
The Agas map of 1561 shows Ironmonger Lane densely built, with the church on the east side of the street and the Mercers Hall facing onto Cheapside.
Now travel forward to the 17th century and in 1665, as with the rest of London, the occupants of Ironmonger Lane lived in dread of the plague, and as a preventative measure, the Mercers closed their school.
The following year, 1666, the Great Fire took hold of the area and burnt down the churches of St Martin Pomary and St Olave, along with the Mercers Hall.
Wren rebuilt the church of St Olave in the 1670s, but St Martin Pomary was not rebuilt, the parish was amalgamated with that of St Olave.
The Mercers second Hall and Chapel on the site were also rebuilt, opening in 1676 to continue the Mercers long association with ironmonger Lane. The fire had also destroyed all remaining evidence of the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon.
In the 19th century, Ironmonger Lane was a busy commercial street in the heart of the City.
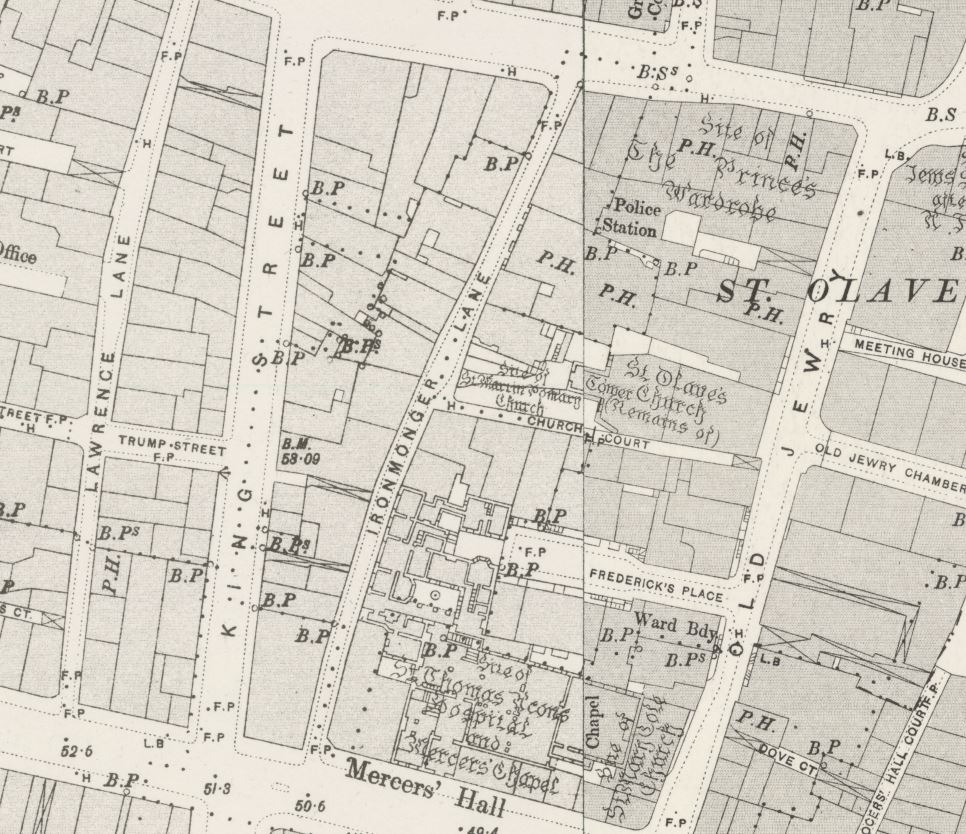
The 1895 Ordnance Survey map shows St Olave and Mercers Hall, along with a Police Station and a Public House at number 11 – this was Mullen’s Hotel.
Credit: ‘Reproduced with the permission of the National Library of Scotland’
Census reports provide an insight into Ironmonger Lane, and the City of London in general. In the 1861 census, it was recorded that there were 23 people living in the Mullens Hotel at number 11:
- 5 family members and the owner of the hotel
- 8 workers, all female and listed as servants
- 10 visitors to the hotel including;
- Drapers from Ireland
- Drapers from Cornwall (one with two sons)
- A Commercial Traveler from Norwich
As ever, London was a temporary home for travelers who had business in the City.
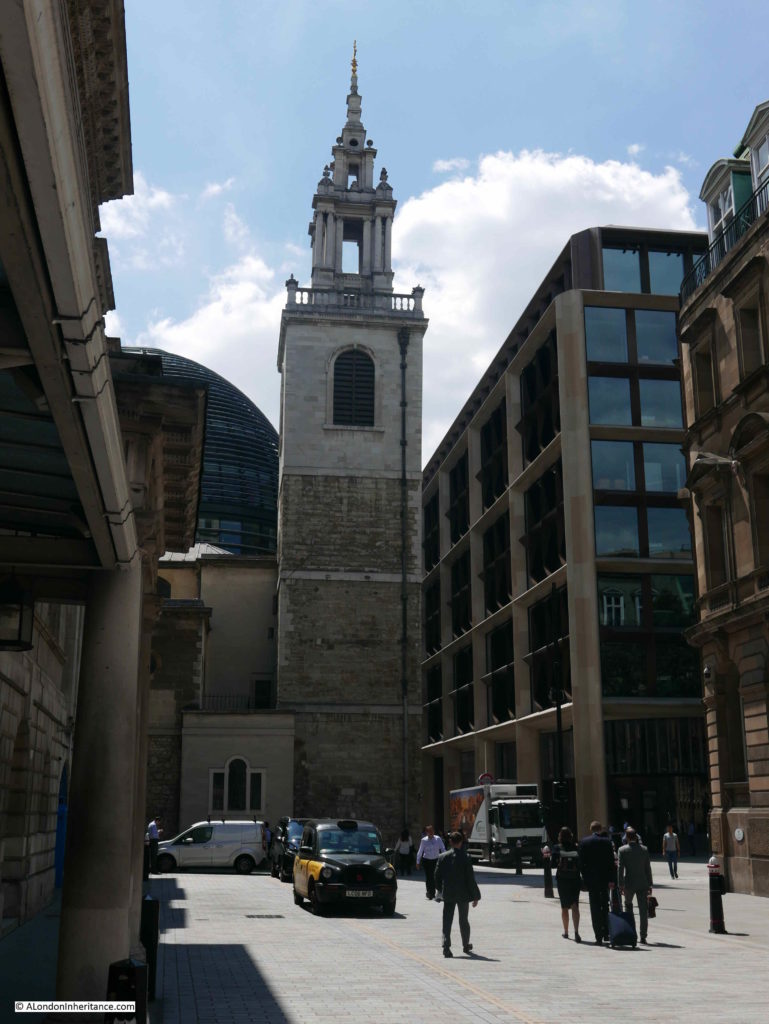
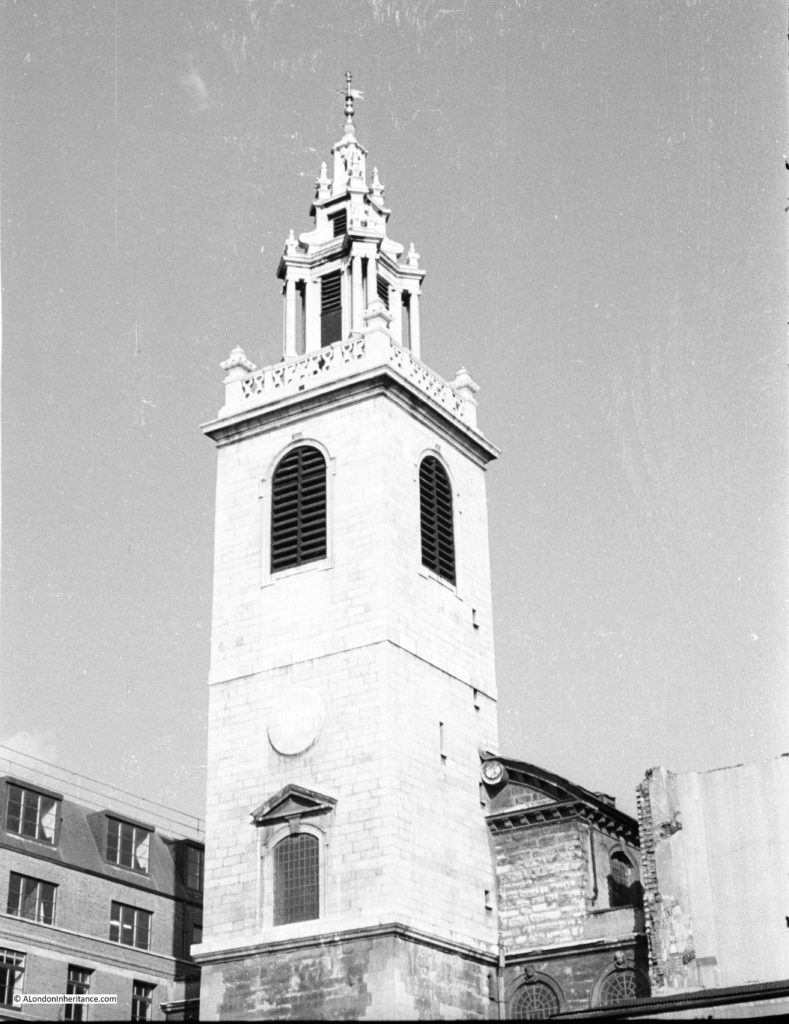
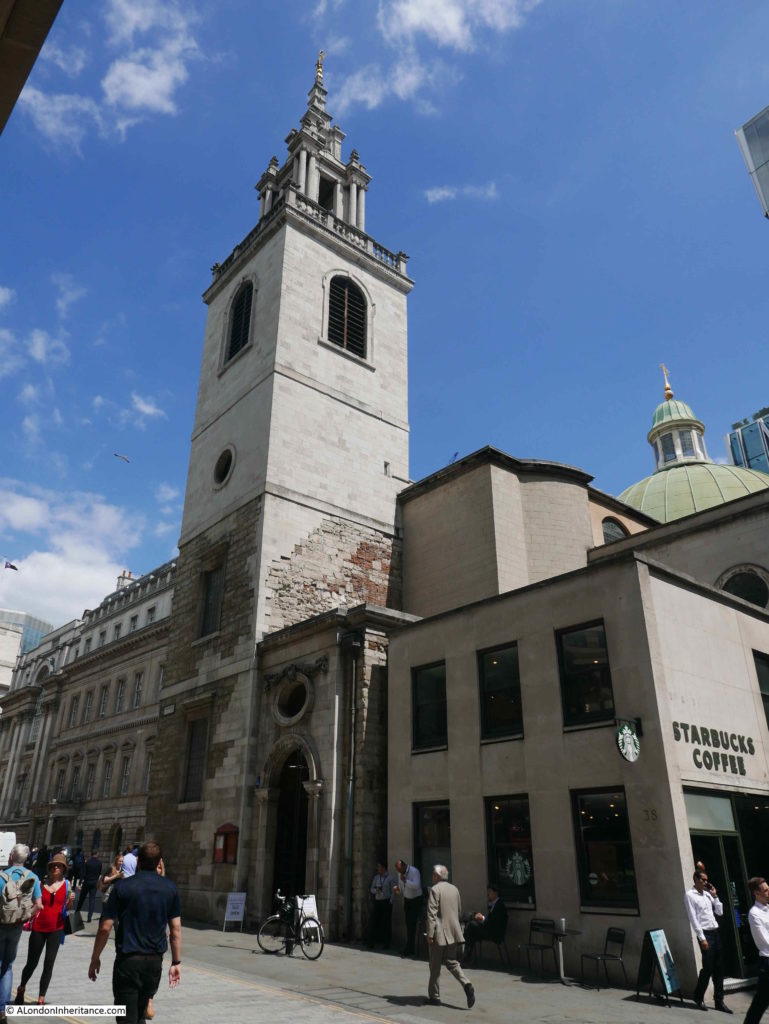
In 1892, the church of St Olave was demolished, apart from the tower of the church. The demolition was under legislation brought in to reduce the number of City churches. The tower was converted into a rectory for St Margaret Lothbury.
The tower is difficult to photograph from street level when the trees are in leaf, but it is there.
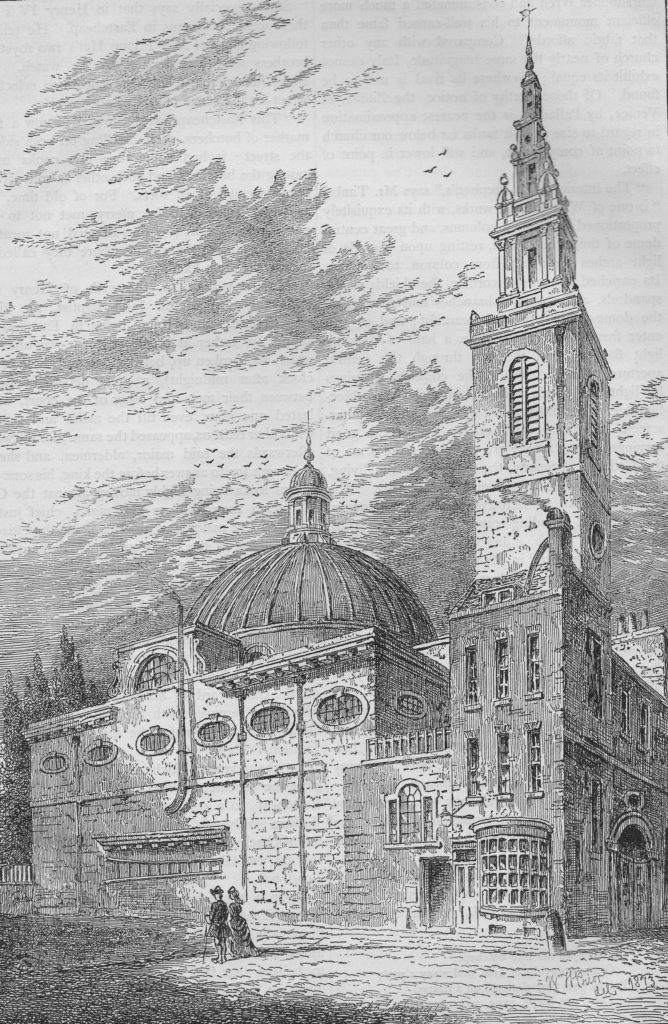
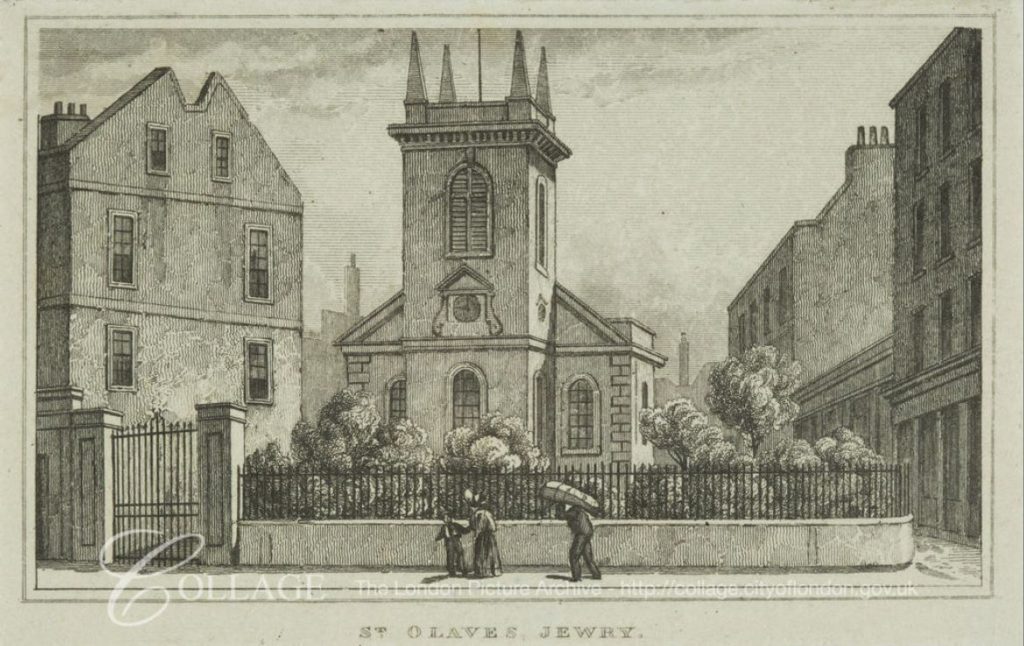
View of St Olave as it appeared in 1830, before demolition of the body of the church and with the tower visible from ironmonger Lane.
Image credit: London Metropolitan Archives, City of London: catalogue ref: q8051273
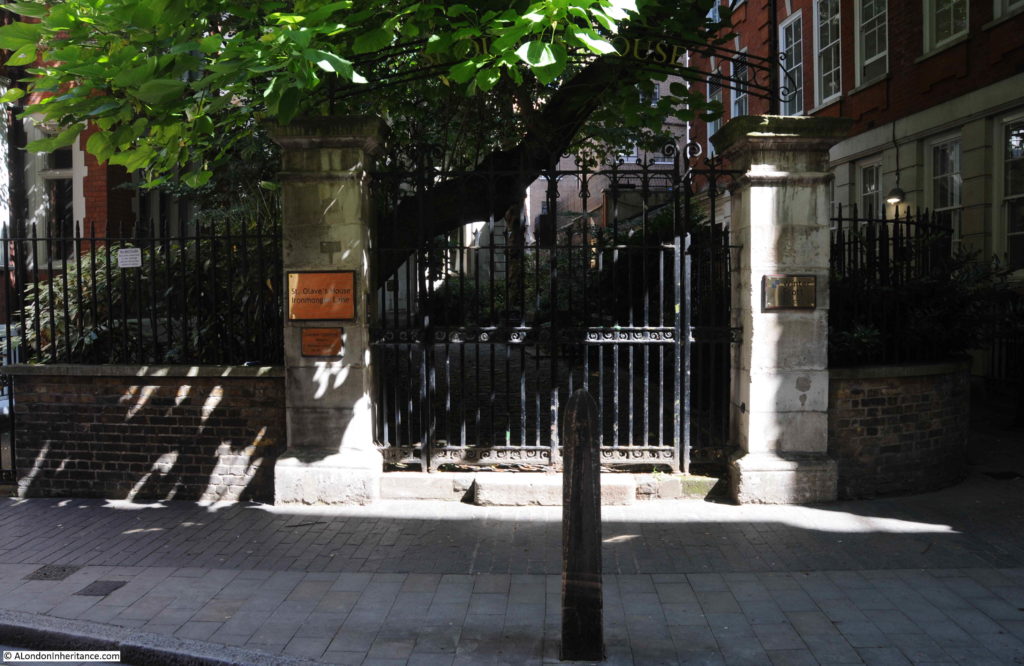
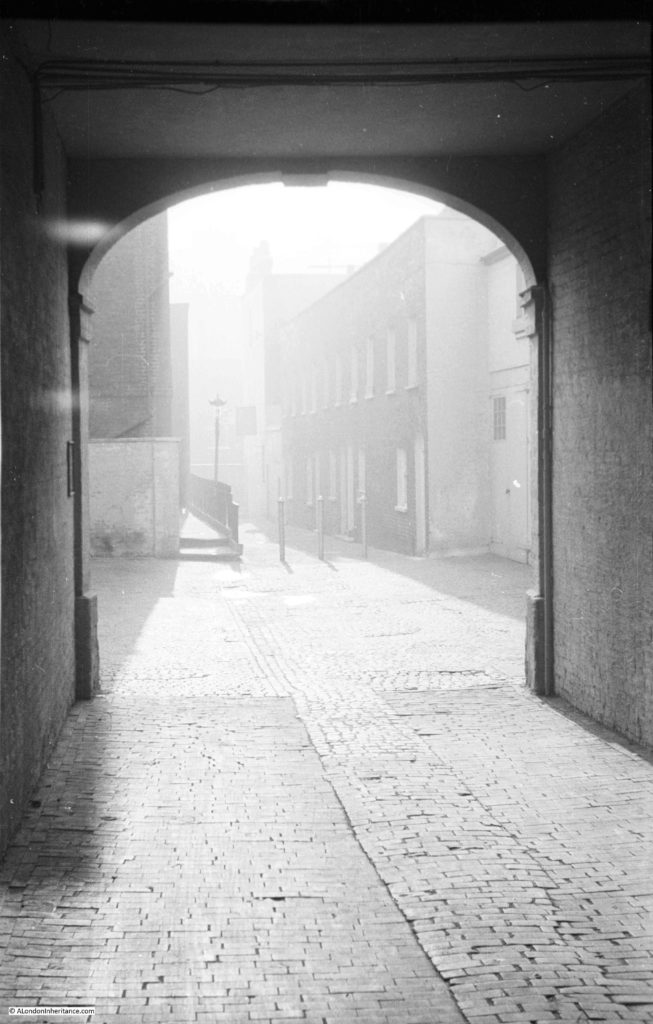
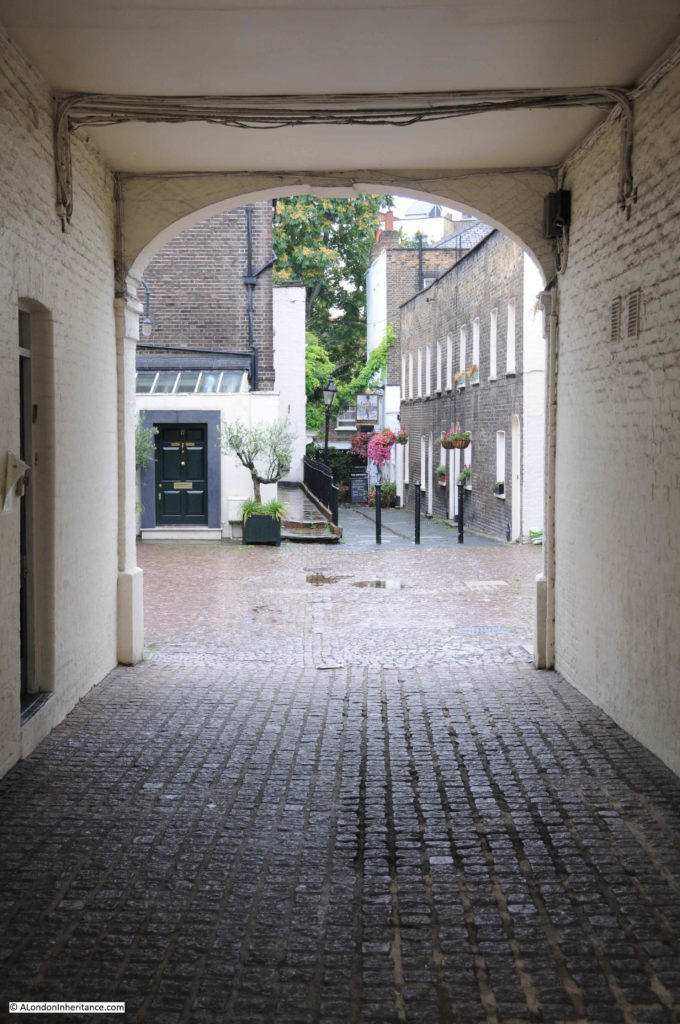
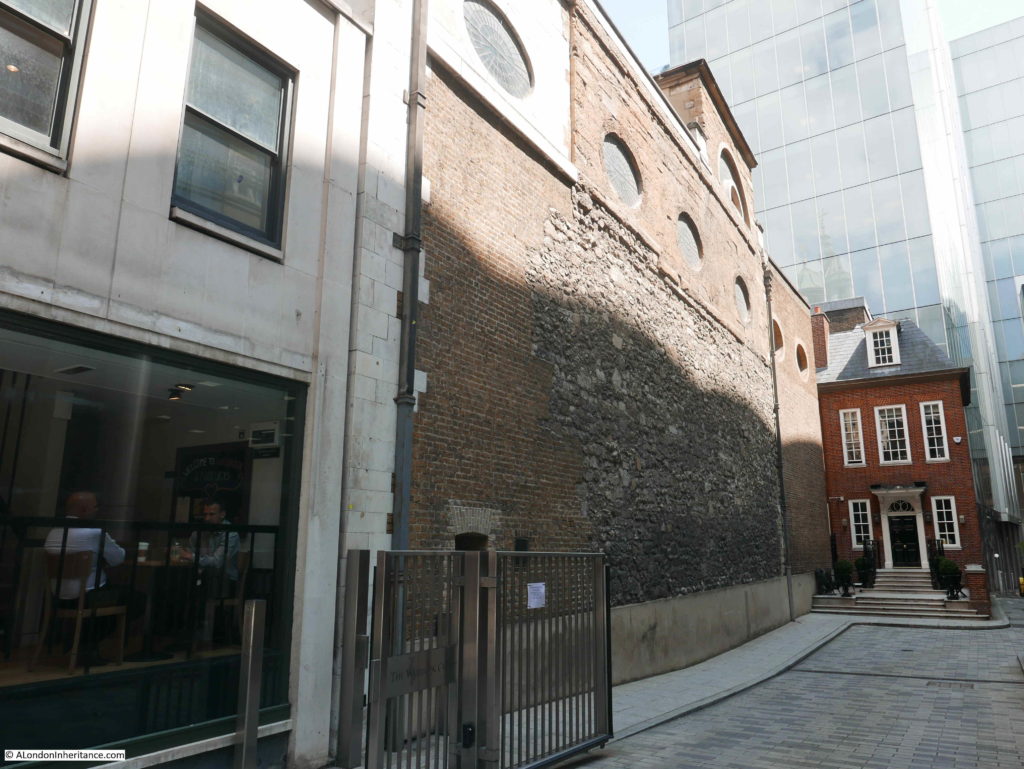
The gates that lead from the street into the old churchyard of St Martin Pomary with the tower of St Olave behind.
So into the 20th century, and Ironmonger Lane suffered badly from bombing during the Second World War.
The Mercers Hall, built after the Great Fire, was destroyed during the night of the 10th / 11th May 1941, and it was bomb damage that opened up number 11 to the excavation work that revealed the Roman house and mosaic.
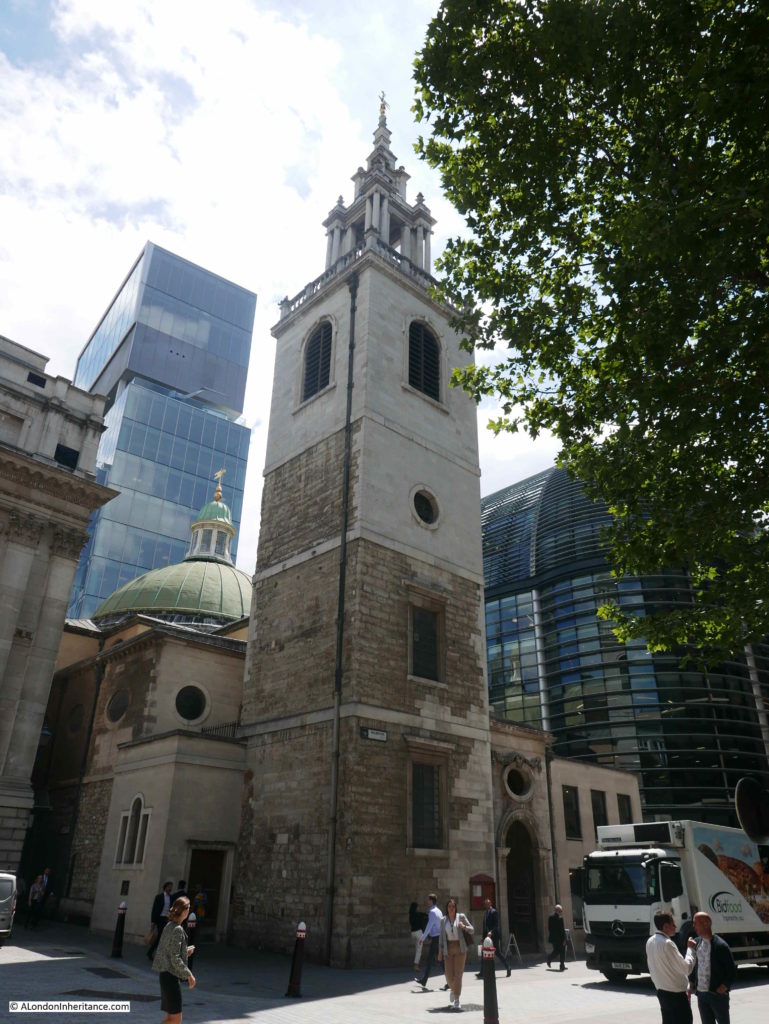
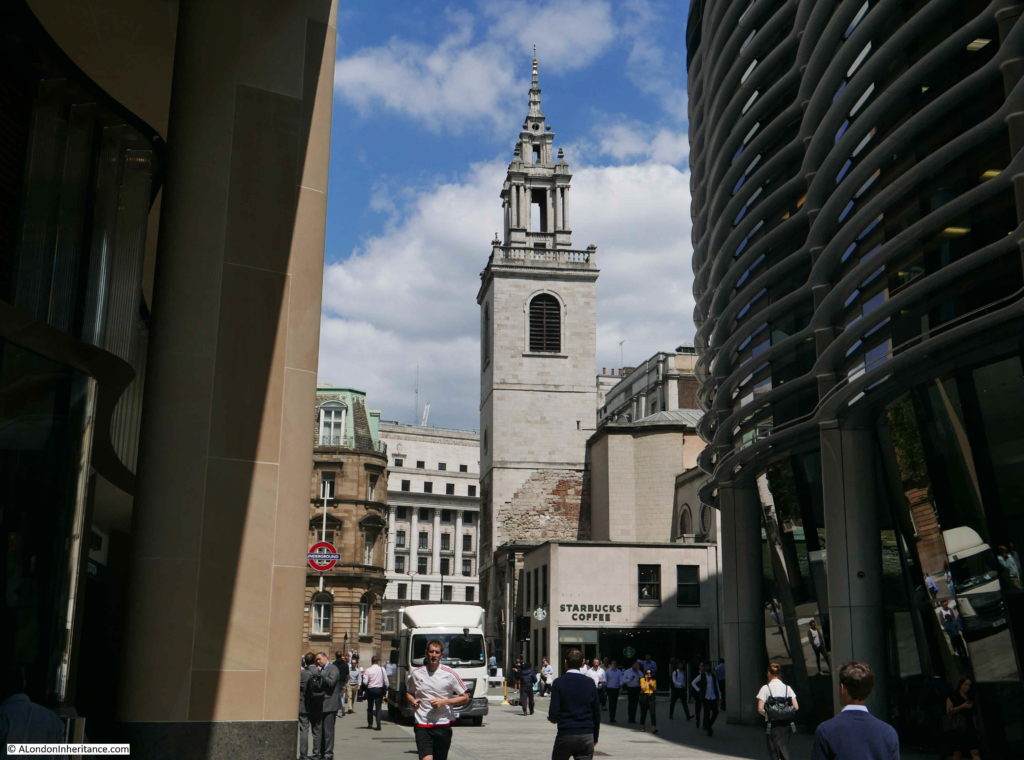
Walking the street today, and we can still see the tower of St Olave, the old church of St Martin Pomary would have been just to the right and in front of the tower.
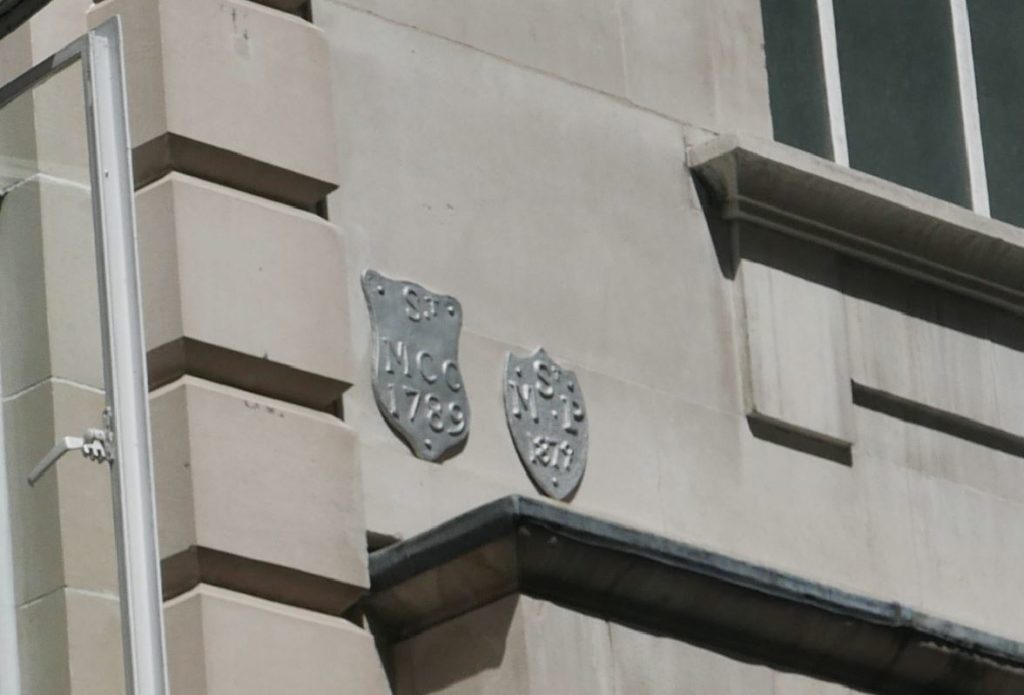
A number of parish boundary markers can be seen on the walls of buildings along the street, including that of St Martin Pomary:
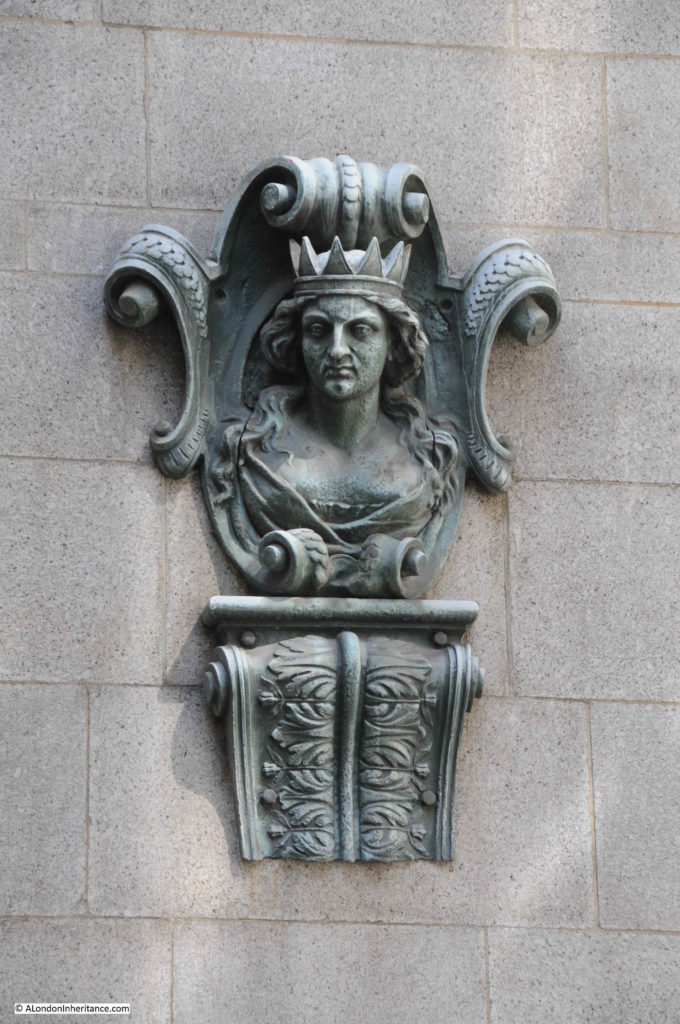
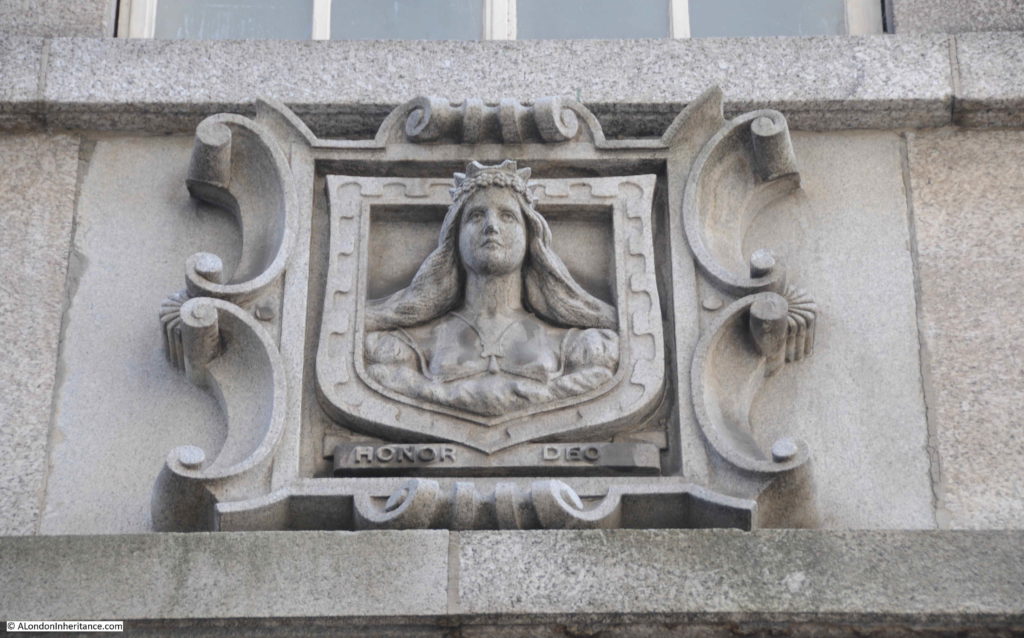
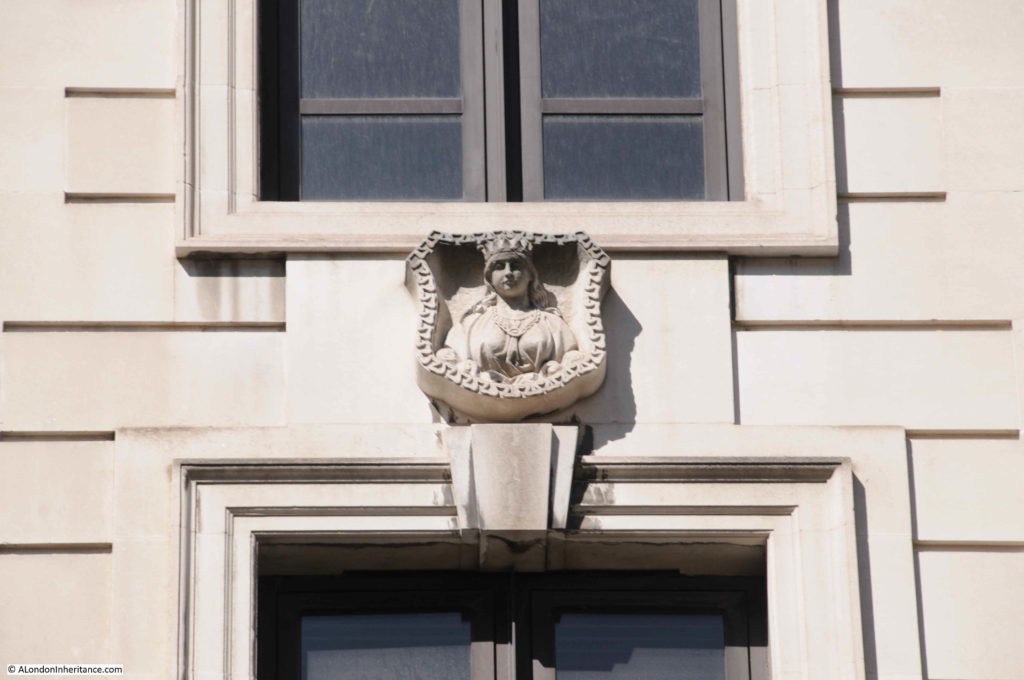
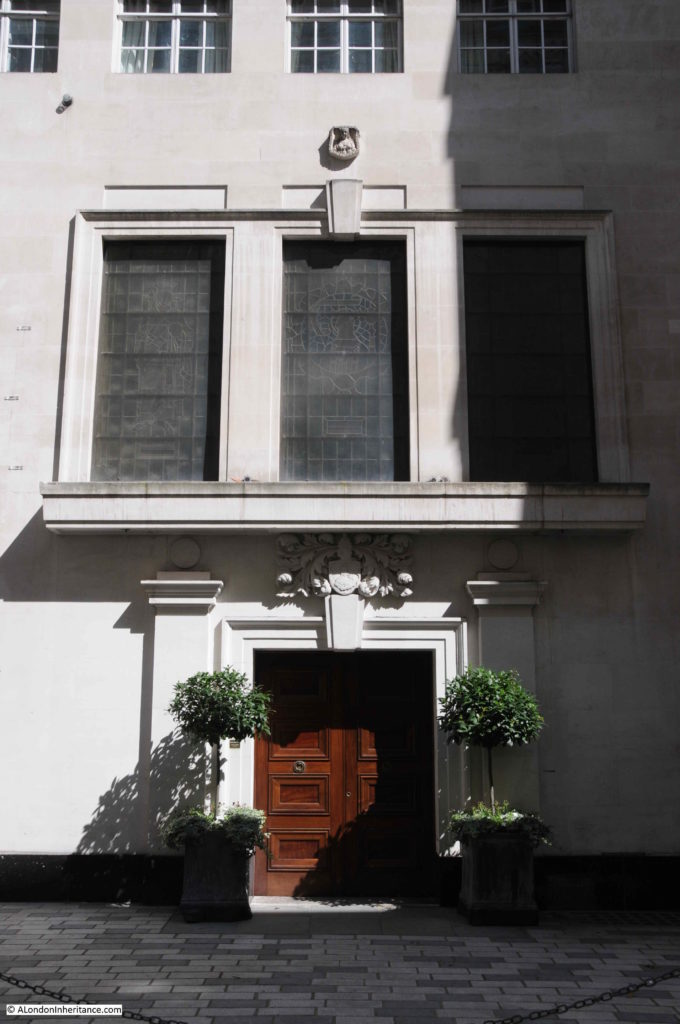
The third Mercers Hall is at the southern end of the street, rebuilt after the Second World War. If you look on the corner of the hall, and along the hall and buildings along the south eastern side of Ironmonger Lane, you will see several carvings of the head and shoulders of a woman with a crown.
The figure is part of the armourial bearings of the Mercers Company, known as a Mercers Maiden, the figure is probably that of the Virgin Mary, although there is no written evidence to confirm this.
The Mercers have long been associated with the charitable building of houses across London, and there would have been a carving, or statue of a Mercers Maiden on the outside of the building. I have photographed a number of these including a very fine example alongside the church of St Dunstan and All Saints Stepney, and also along Hardinge Street.
The Ironmongers Lane entrance to Mercers Hall:
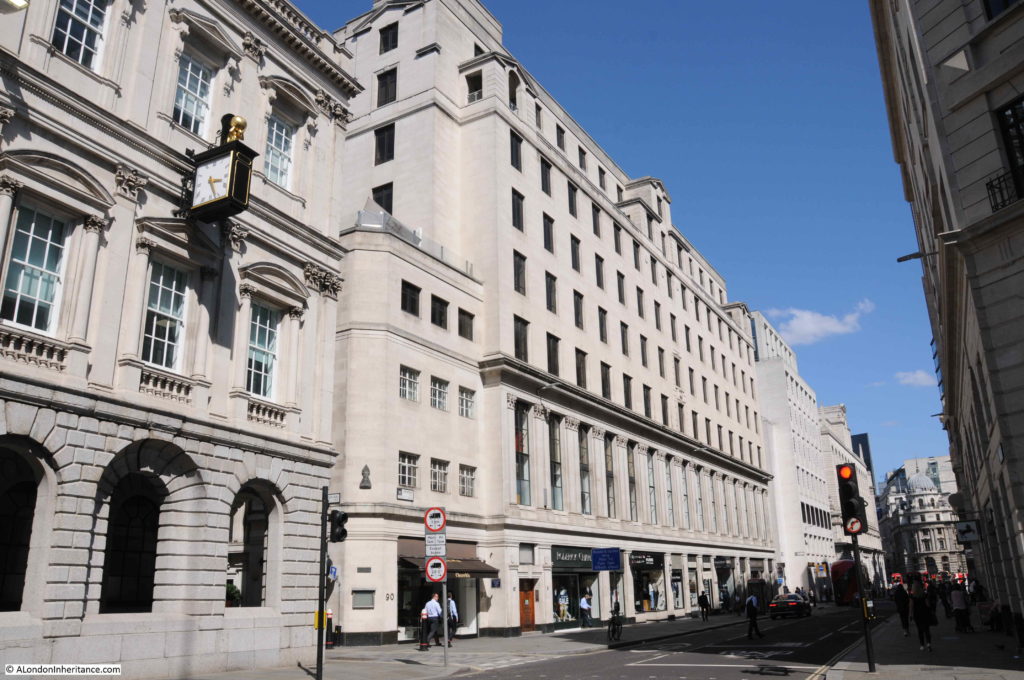
The following photo shows the view along Cheapside. The entrance to Ironmonger Lane is just to the left of the red circled street signs..
The large building running along Cheapside in the centre of the photo occupies the land between Ironmongers Lane and Old Jewry originally the location of the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon.
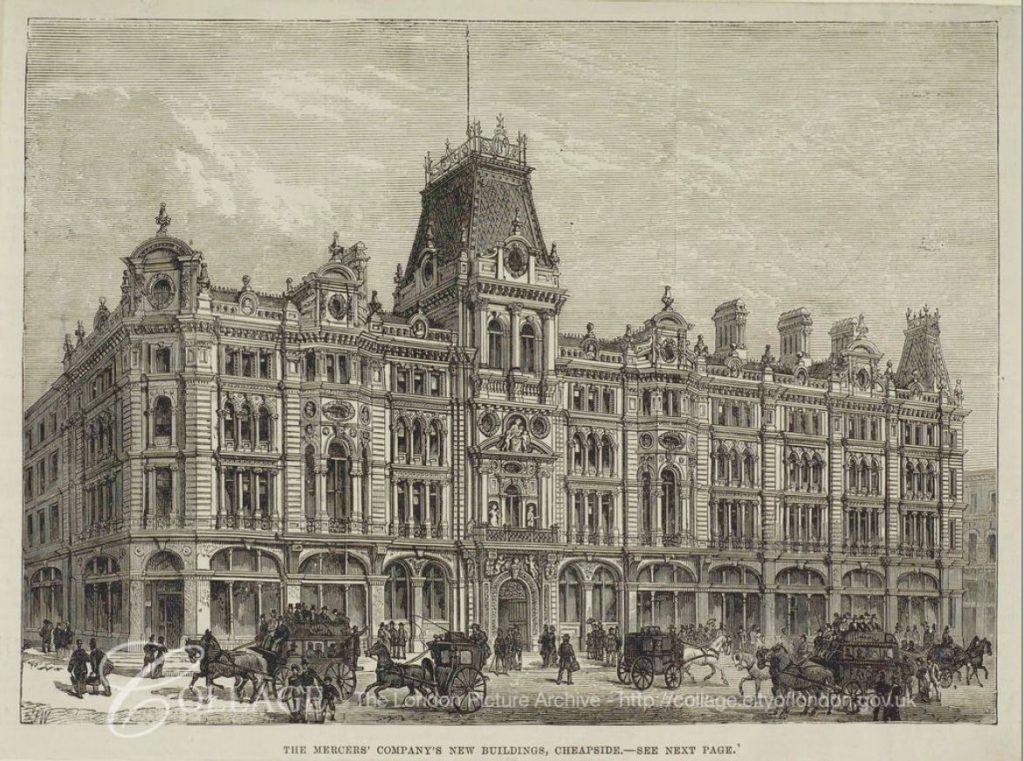
The following drawing shows the Mercers Hall occupying the same site in 1881. Ironmonger Lane is at the left.
Image credit: London Metropolitan Archives, City of London: catalogue ref: q7707062
The above view shows the post Great Fire version of the hall after considerable refurbishment. It was this version of the hall that was destroyed in May 1941.
The photo of the building from Cheapside shows more memorials to Thomas a Becket on the building corner at the junction of Ironmonger Lane and Cheapside..
It was the original association of the Mercers Company with the Becket family dating back to the 12th century, and their patronage of the Hospital of St Thomas of Acon, that almost 900 years later has the Mercers Hall still on the same site.
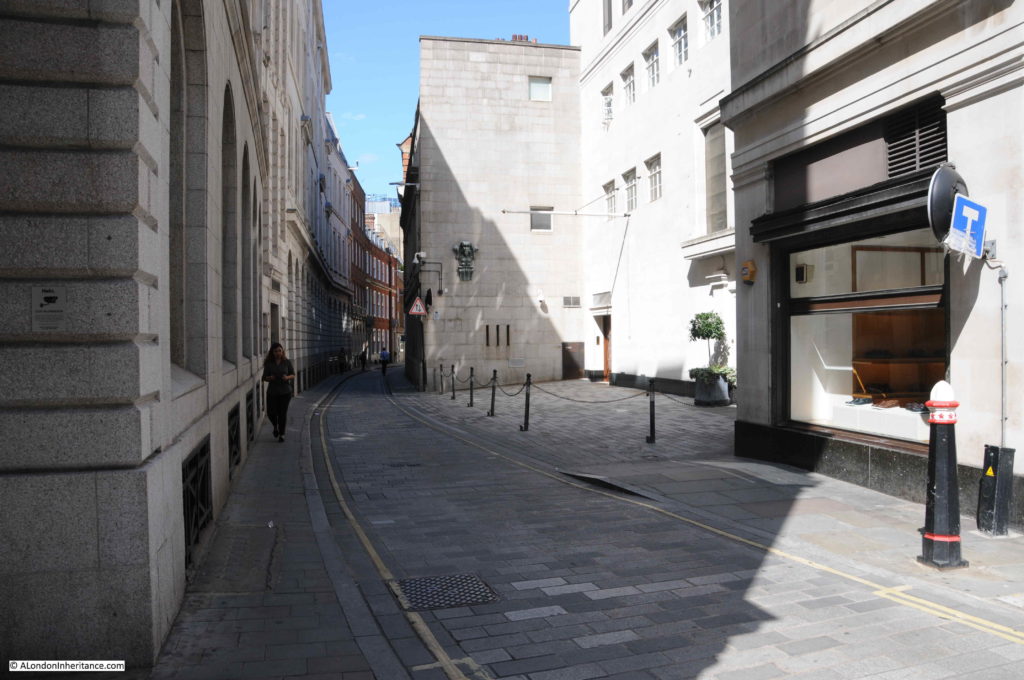
Looking up Ironmongers Lane from Cheapside, the open space on the right is at the entrance to the Mercers Hall, the narrow width of the lane can be seen continuing north.
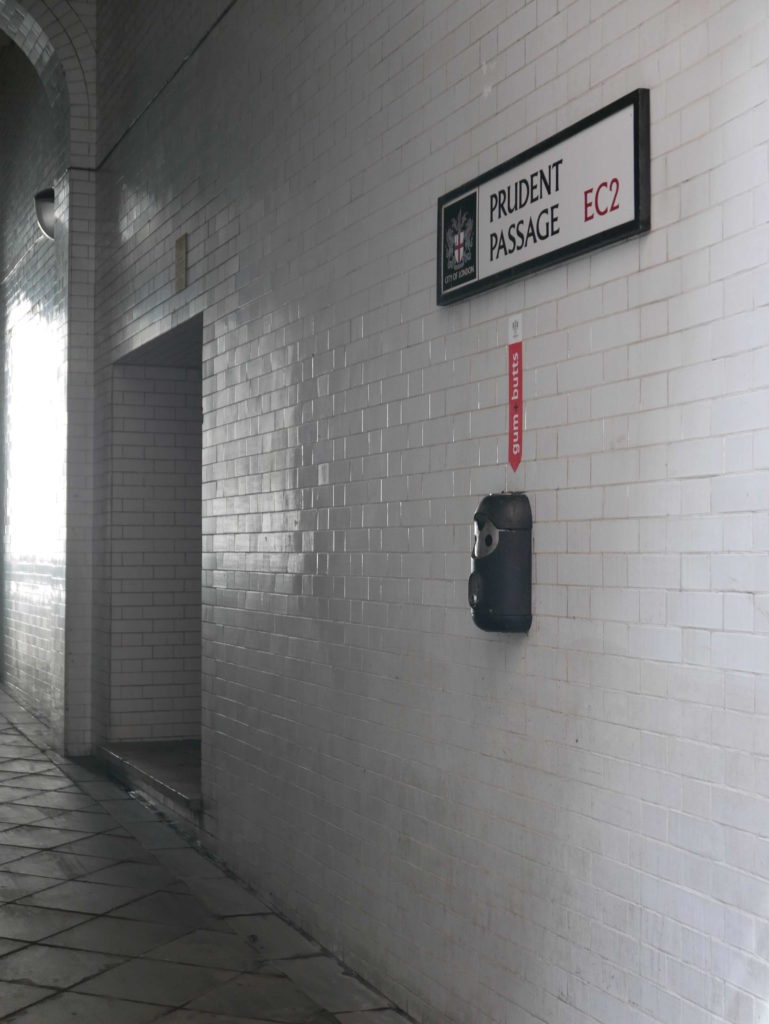
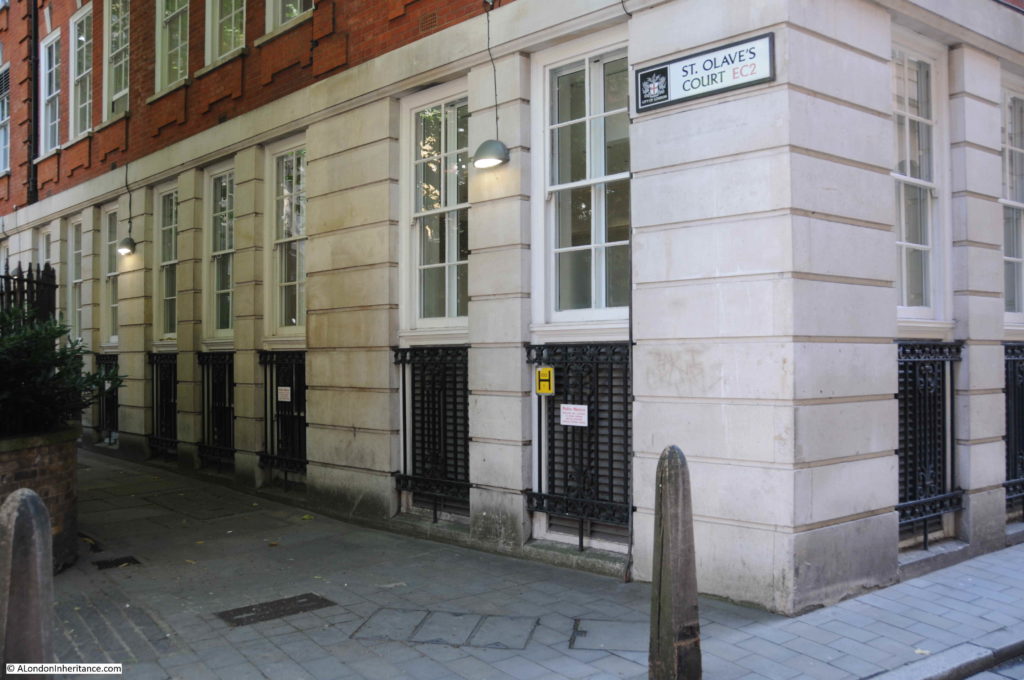
There are a couple of passages leading off from ironmongers Lane.
The wonderfully named Prudent Passage leads to King Street. originally this was Sun Alley, and this original name was in use in the 18th century, with the first mention of Prudent Passage being in 1875.
St Olave’s Court runs to Old Jewry, alongside the location of the church of St Olave, and probably over the site of St Martin Pomary.
The view looking north towards the junction with Gresham Street:
The view south along Ironmonger Lane from Gresham Street showing the narrow width of the lane.
Number 11 Ironmonger Lane is just along the lane on the left. No longer a hotel, a new building was constructed on the site following the 1949 excavations, and refurbished a number of times since, and it is here that the Roman house and mosaics were found, which brings us full circle on almost 2,000 years of history of Ironmonger Lane.