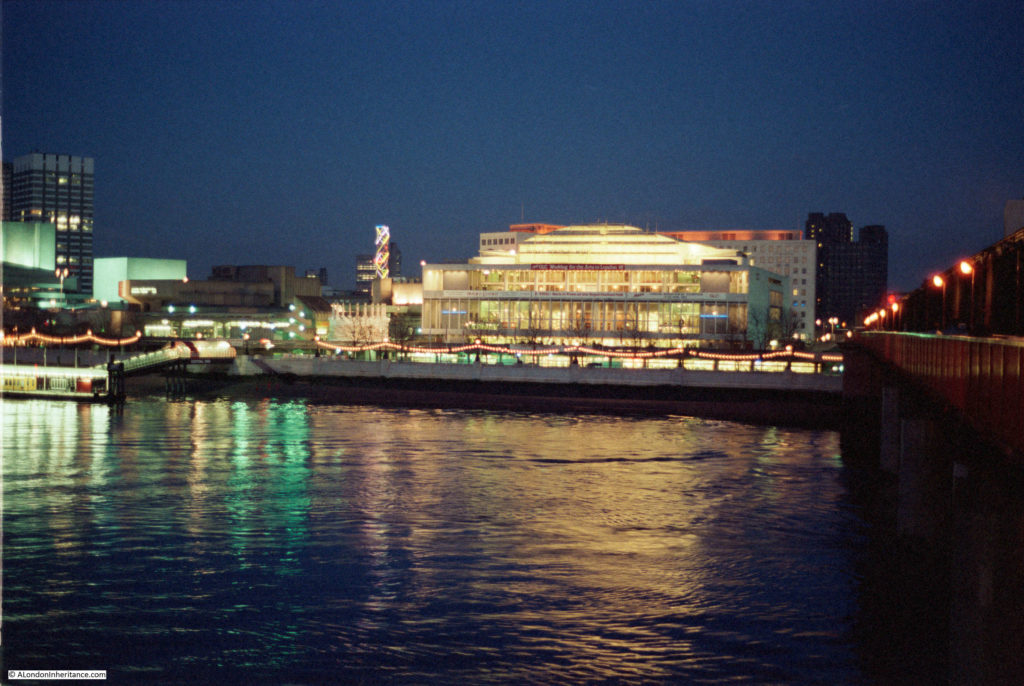
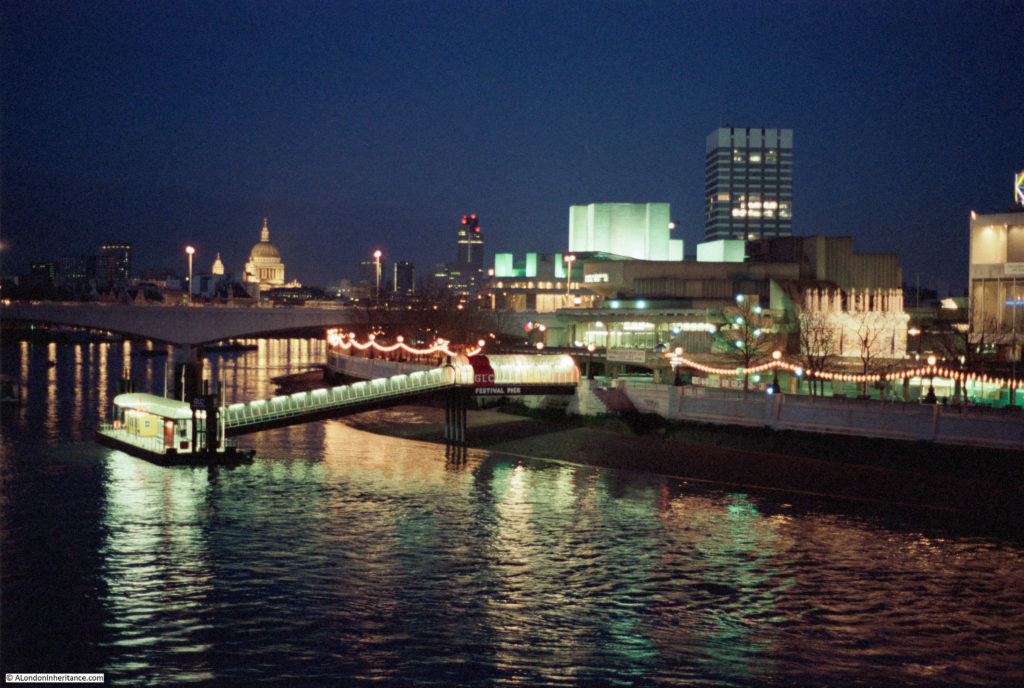
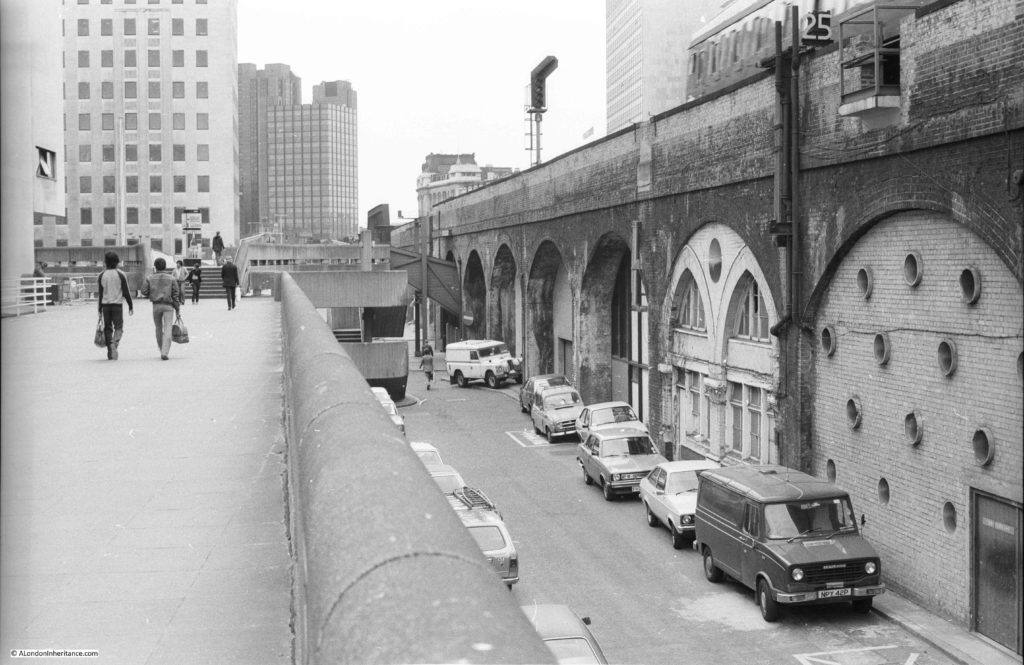
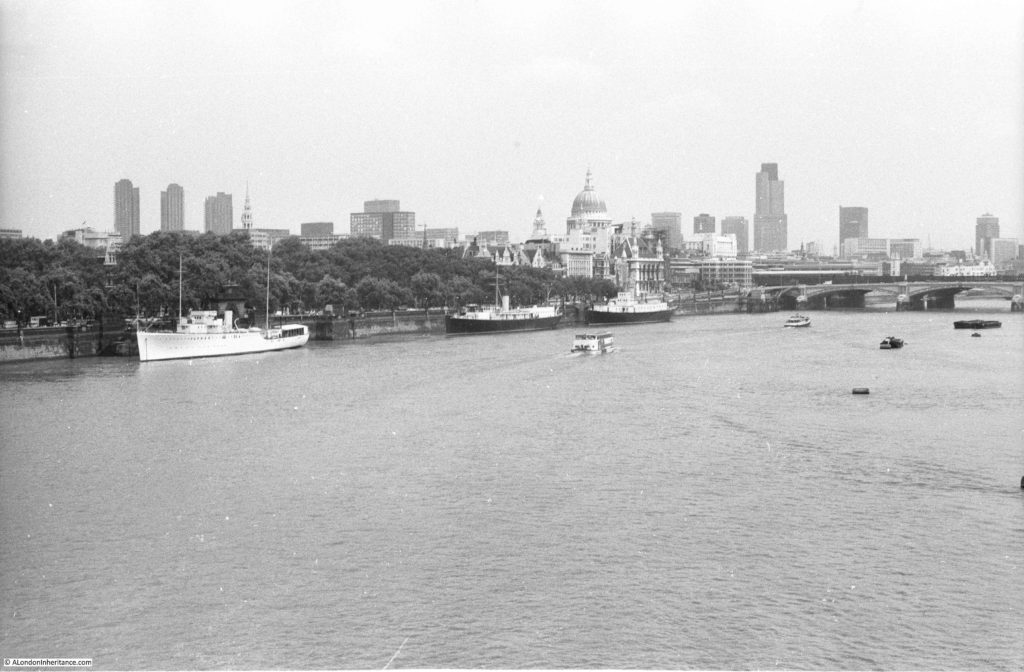
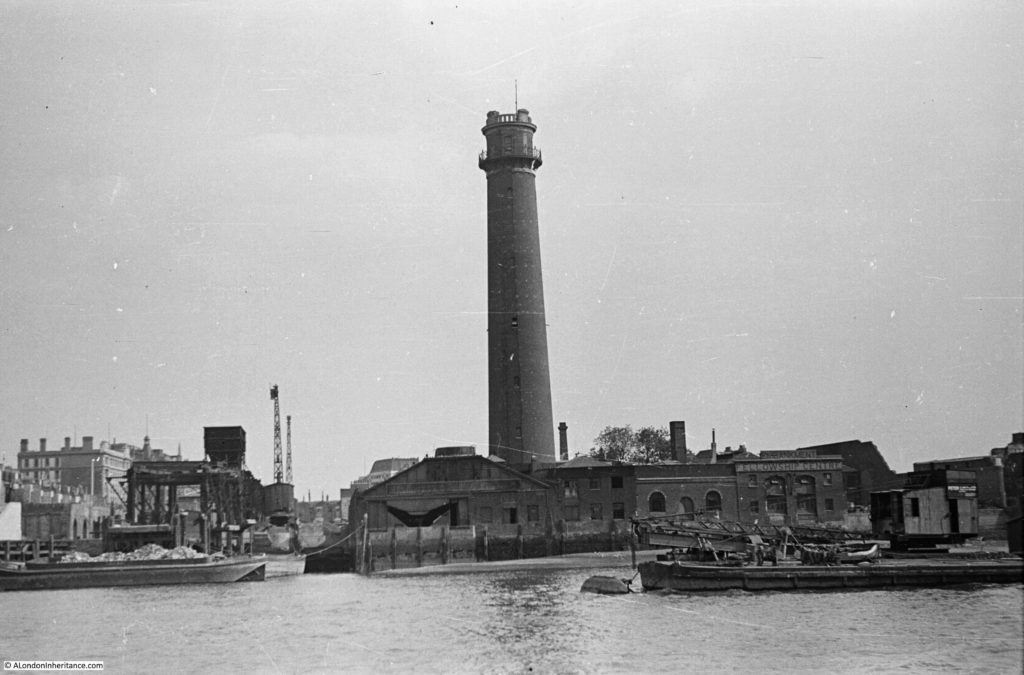
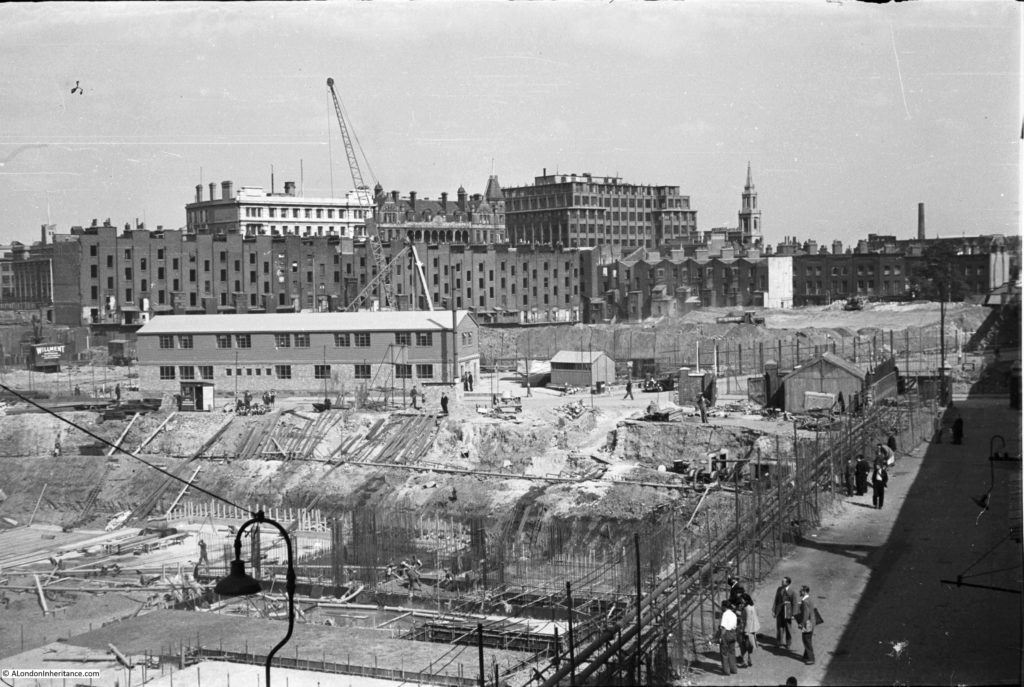
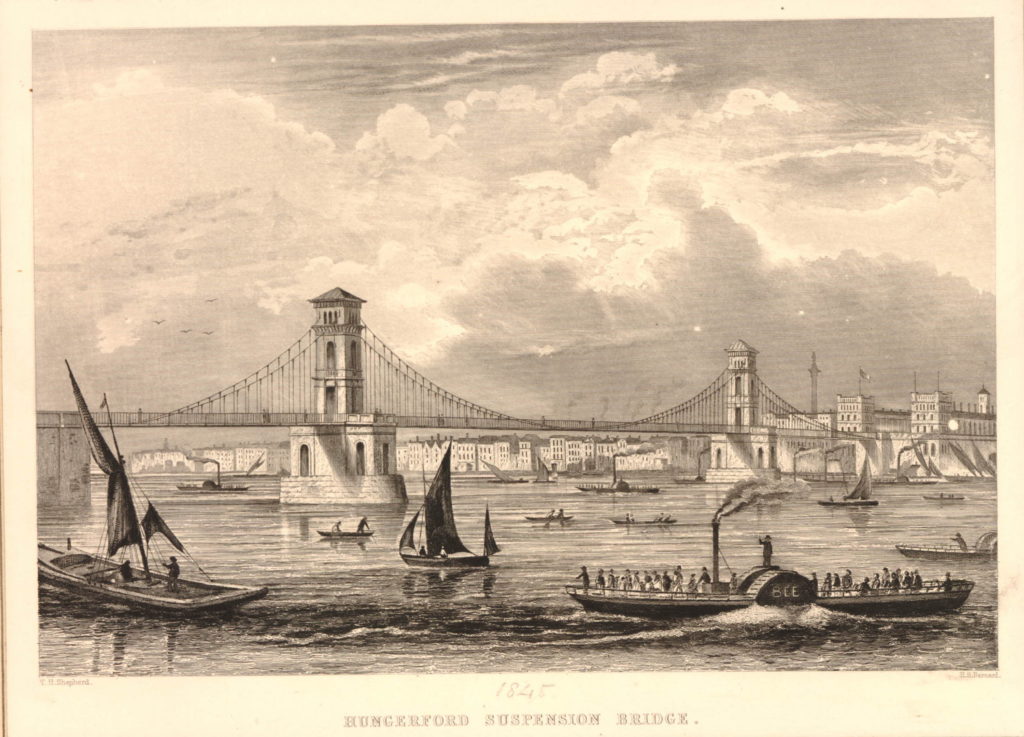
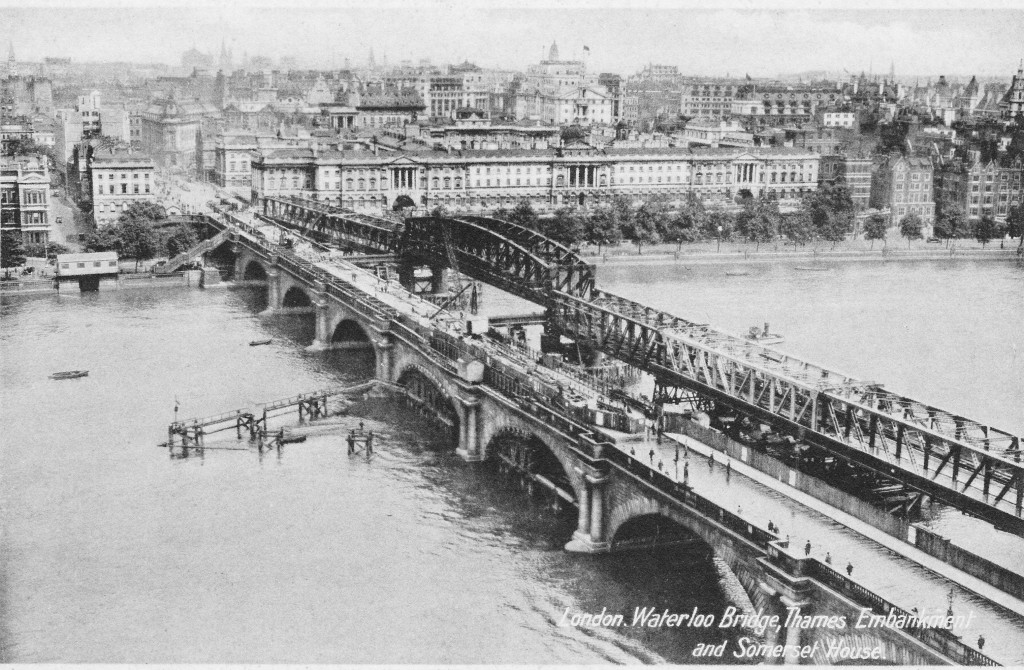
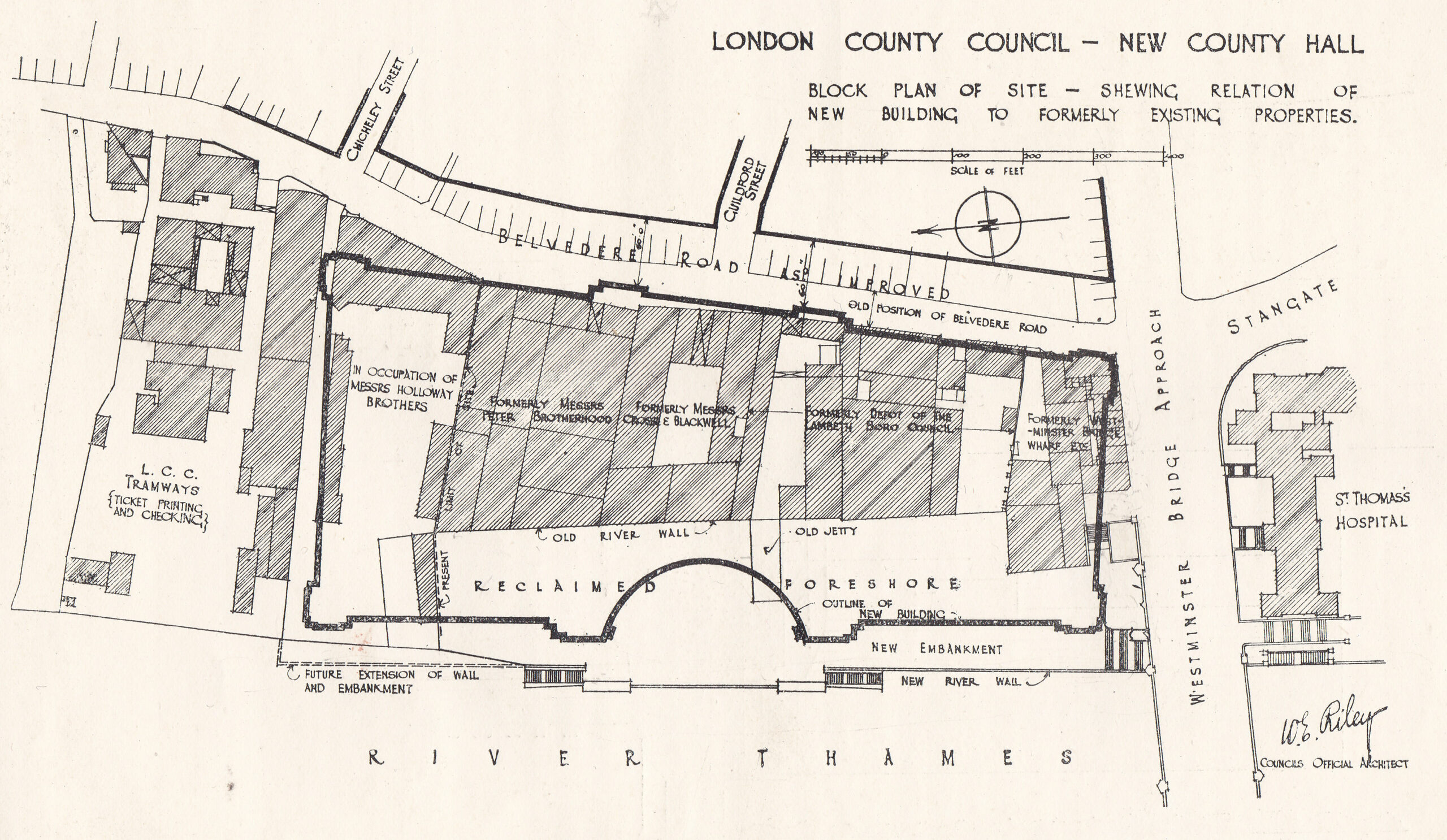
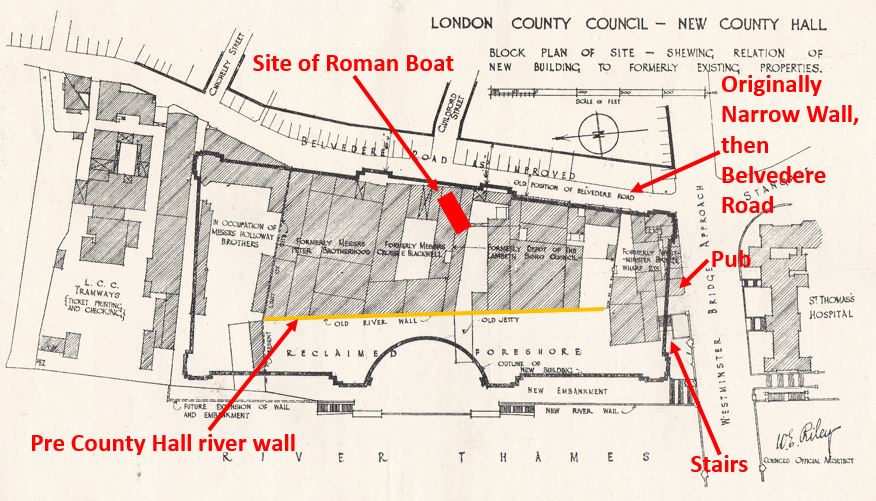
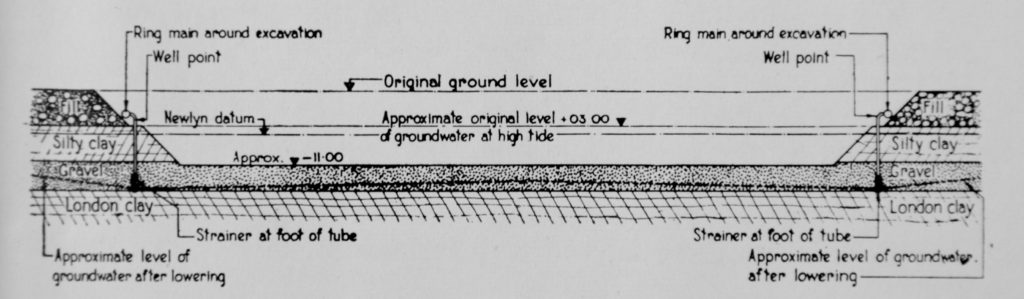
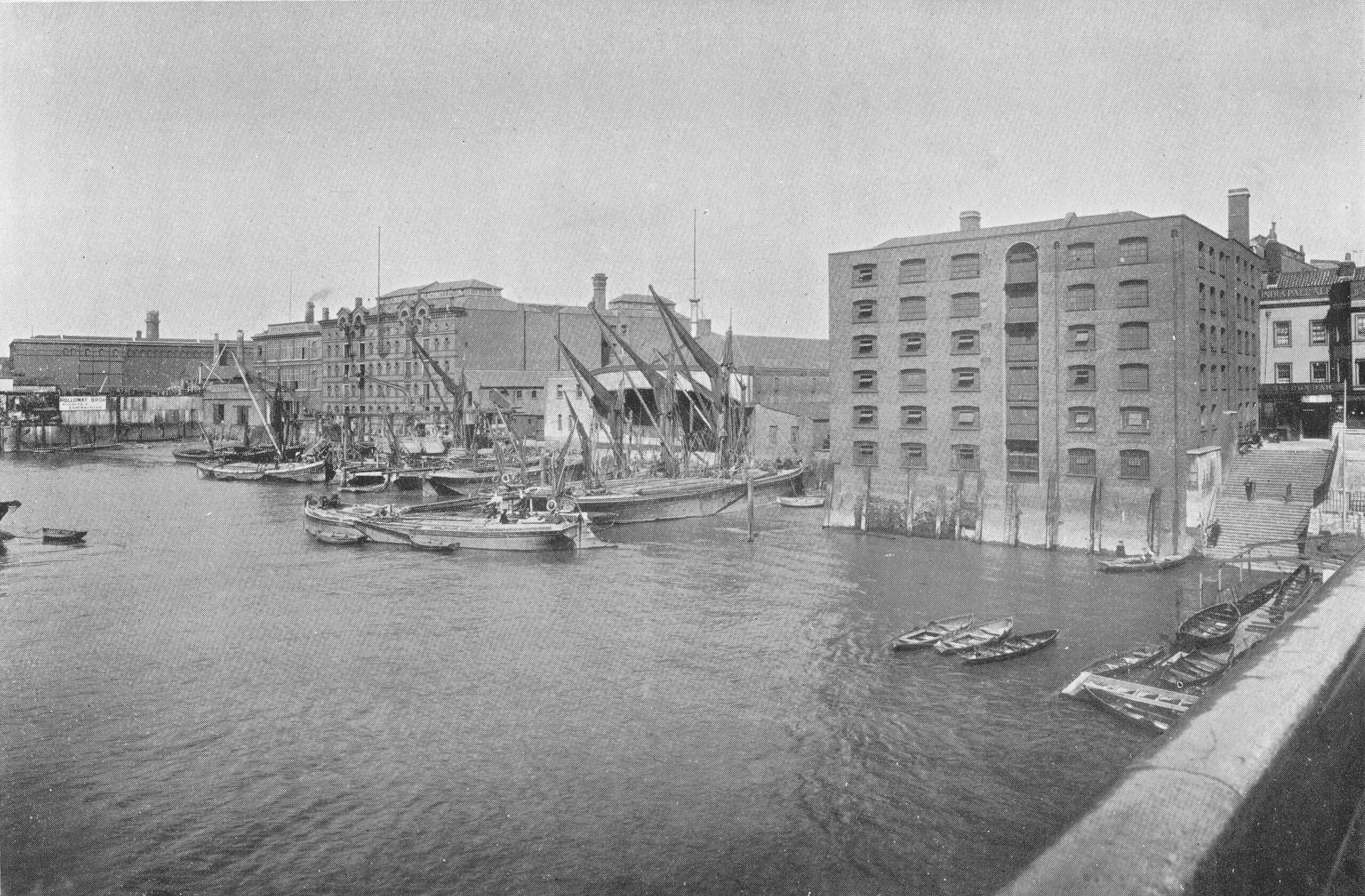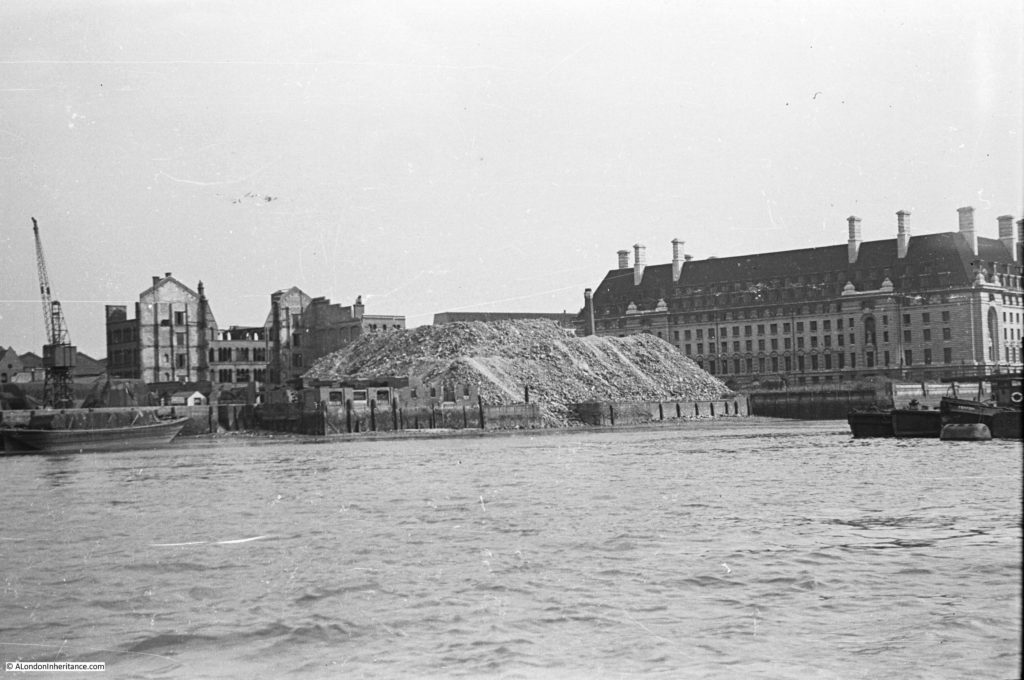I have written a number of posts about the South Bank, and the transformation of the area from industrial and terrace housing, via the Festival of Britain, to the place we see today with the Jubilee Gardens and Royal Festival Hall. The majority of my father’s photos of the area were taken in the streets of the South Bank, however there is one that was taken from across the river featuring the Shot Tower, and part of the Thames foreshore between Waterloo Bridge and the site of the Festival Hall.
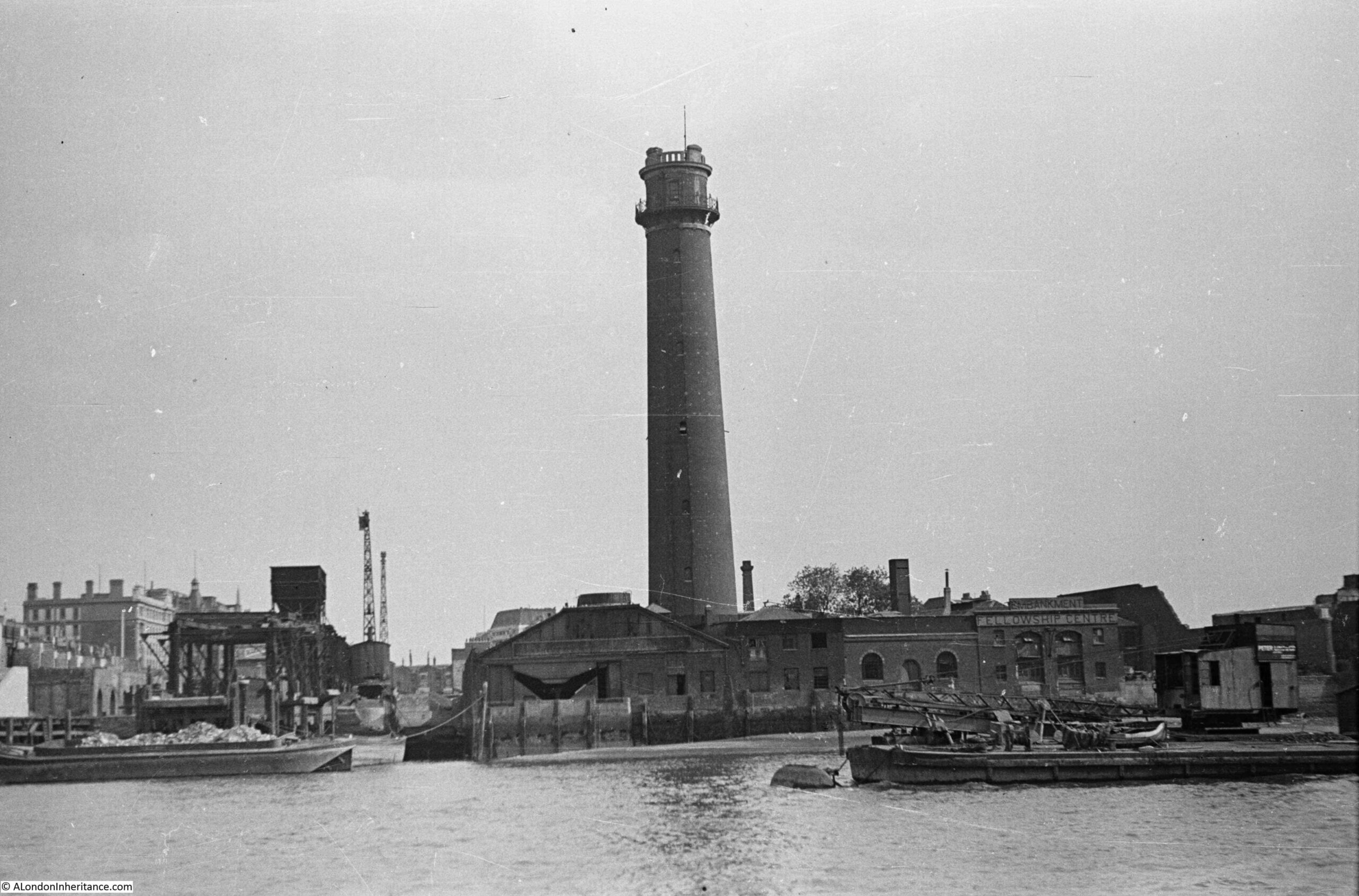

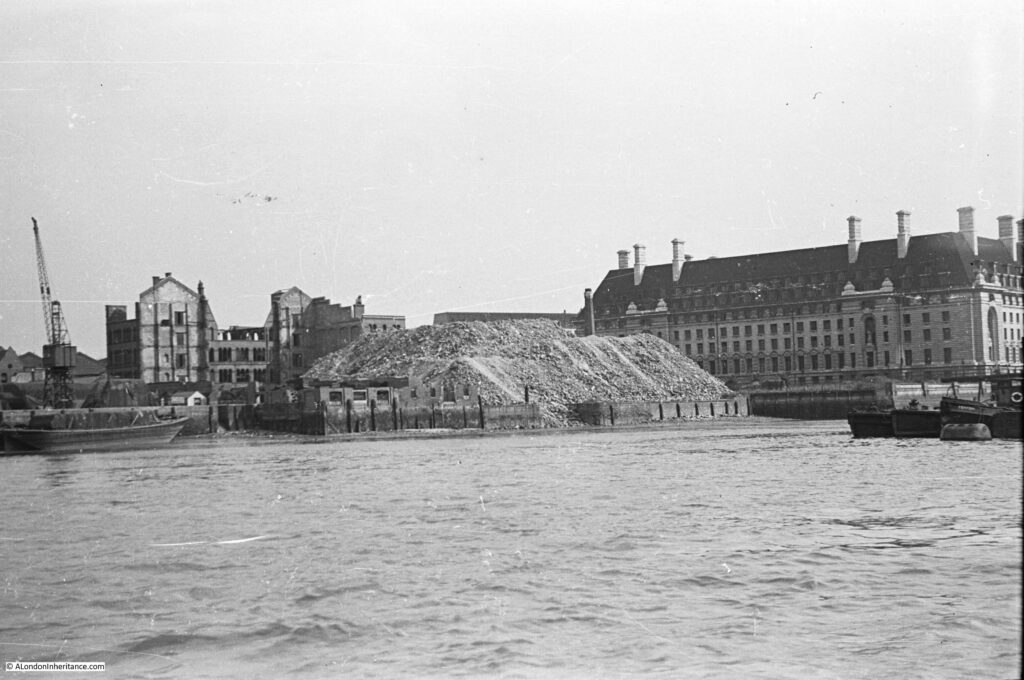
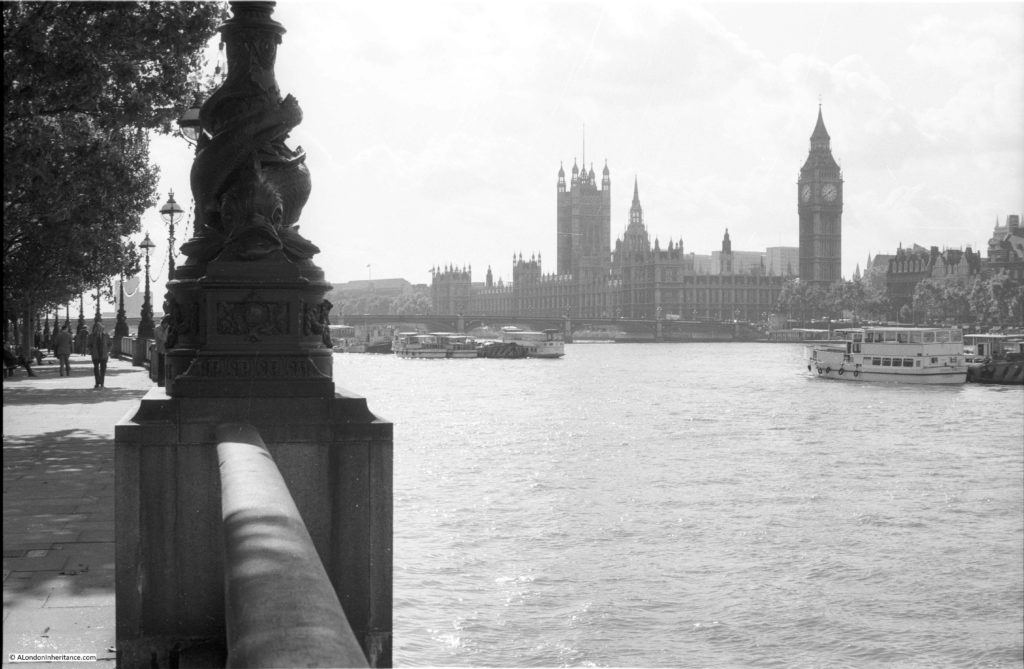
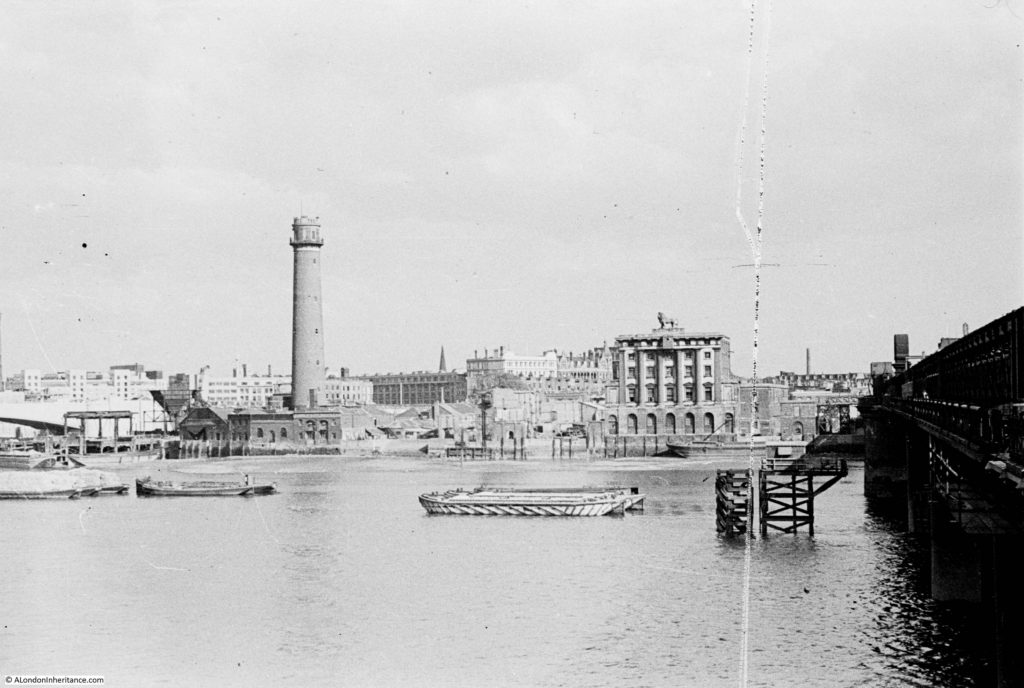
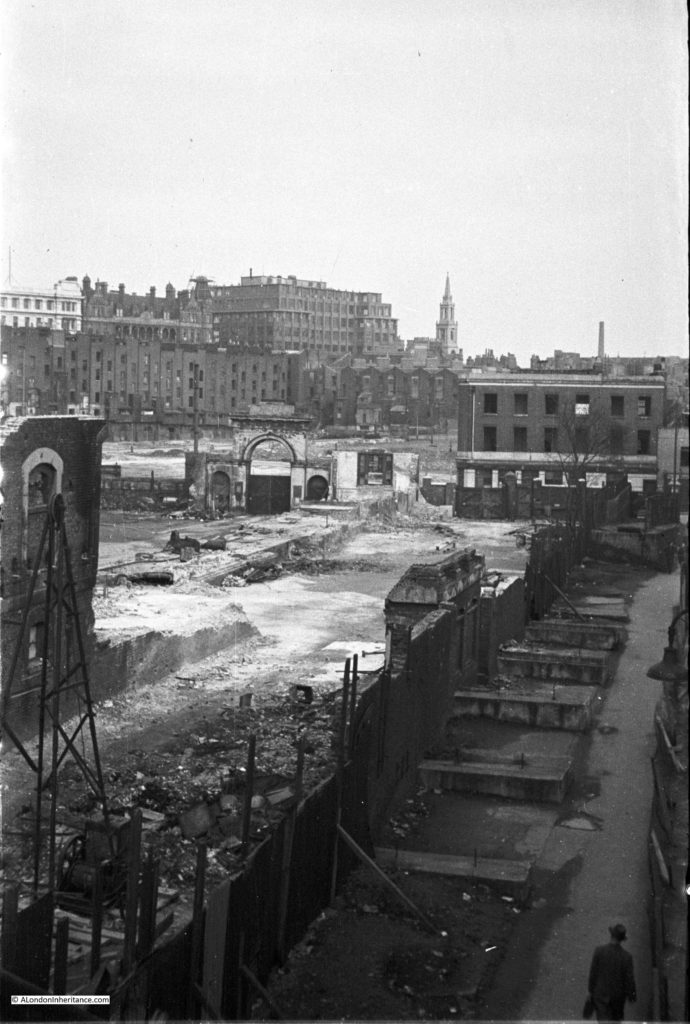
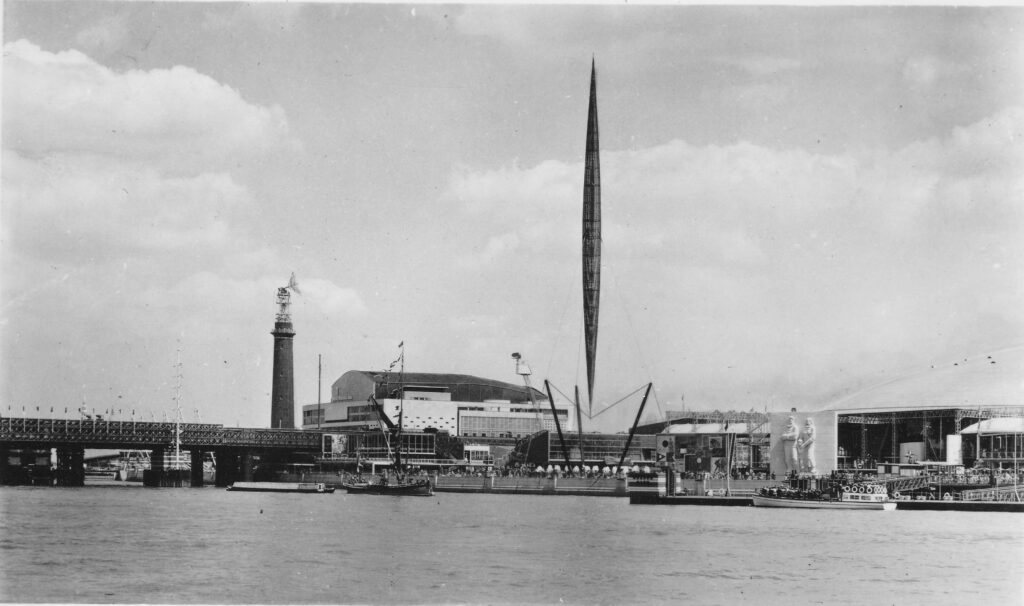
The above photo was taken on Saturday 23rd August 1947, and shows the Shot Tower, and the buildings along the river. The approach to Waterloo Bridge can just be seen on the left of the photo, and on the right would today be part of the Royal Festival Hall.
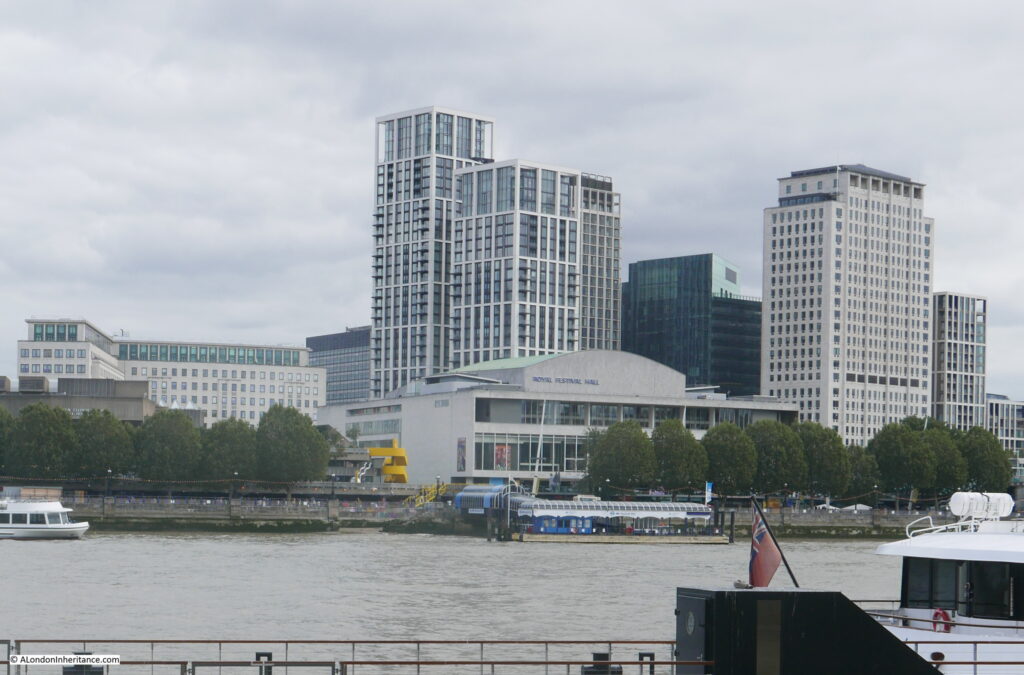
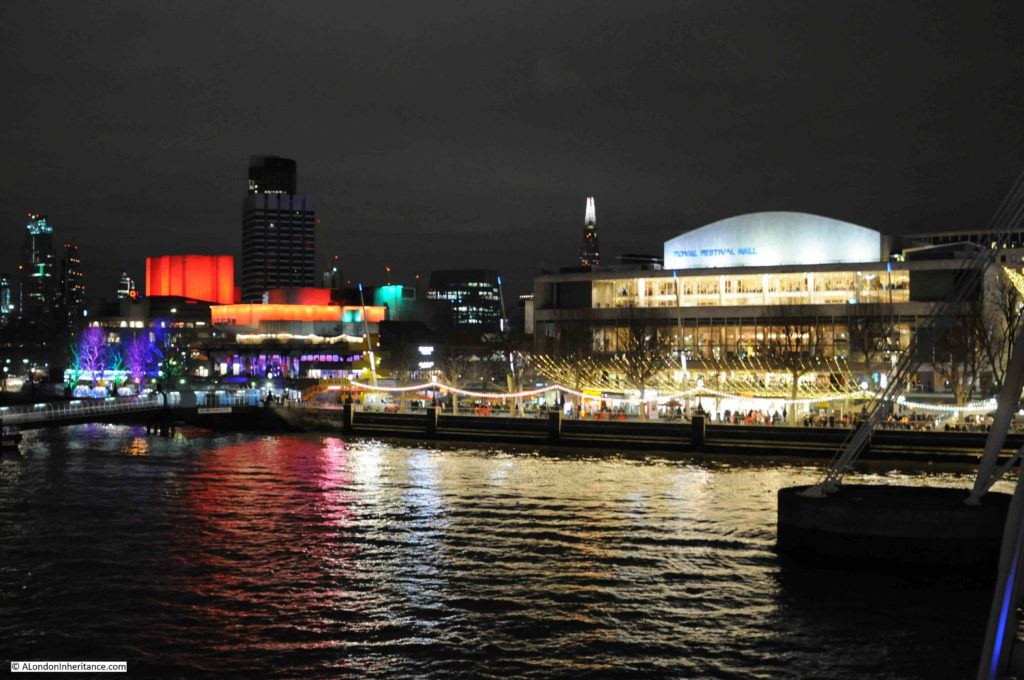
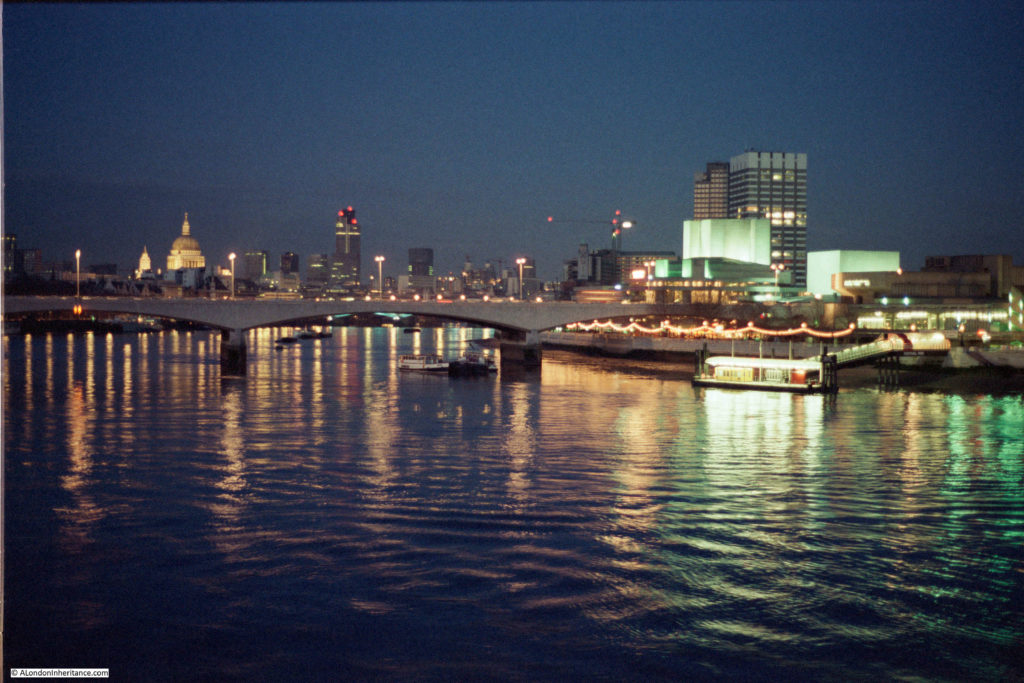
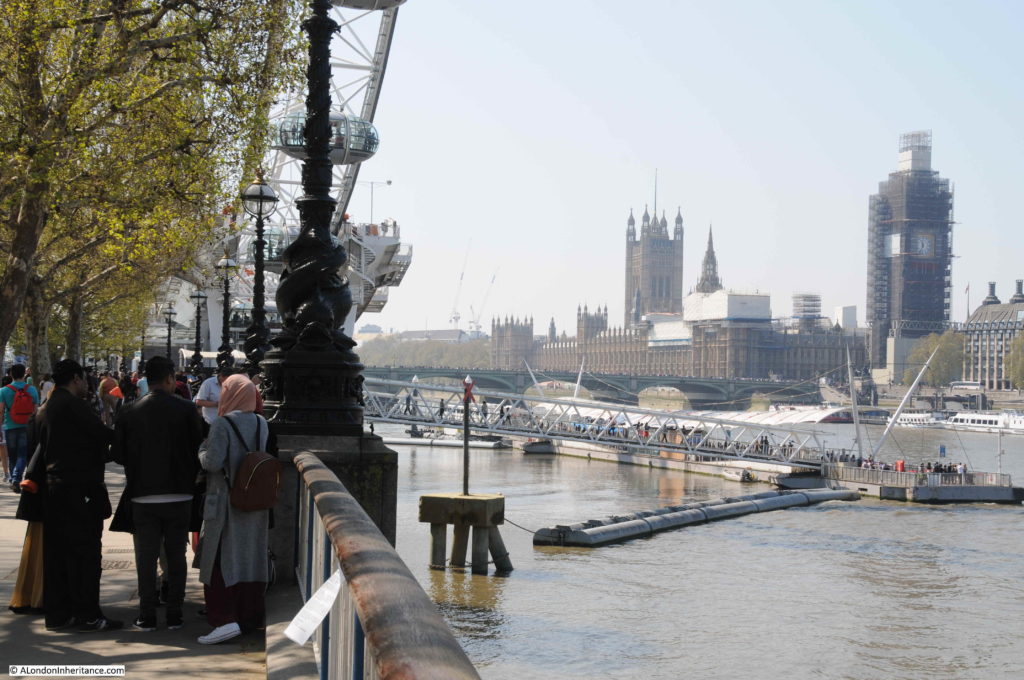
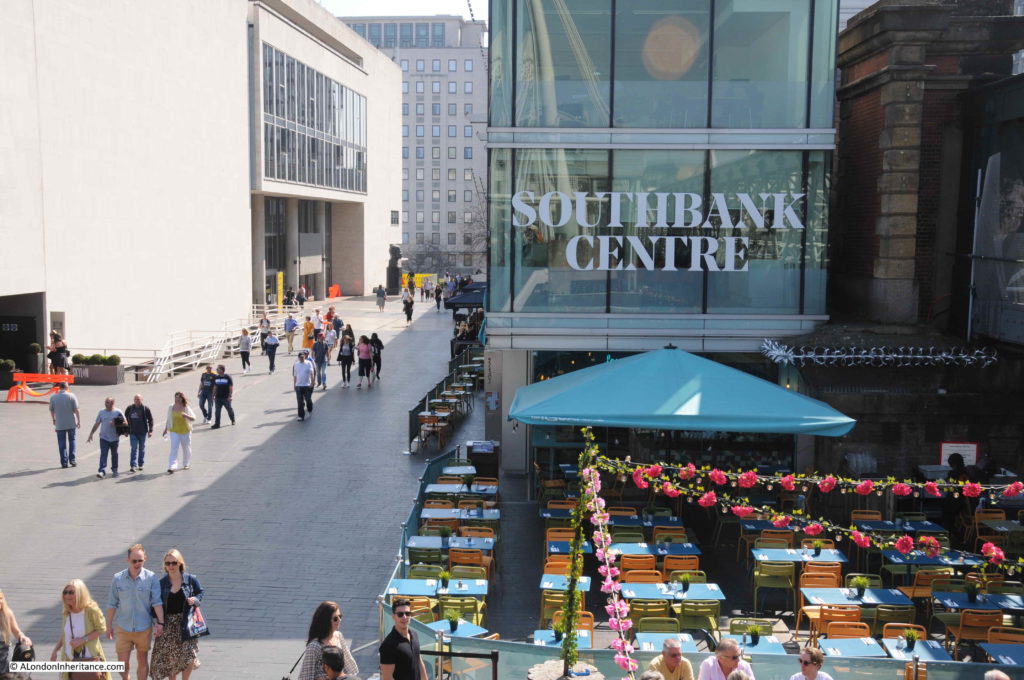
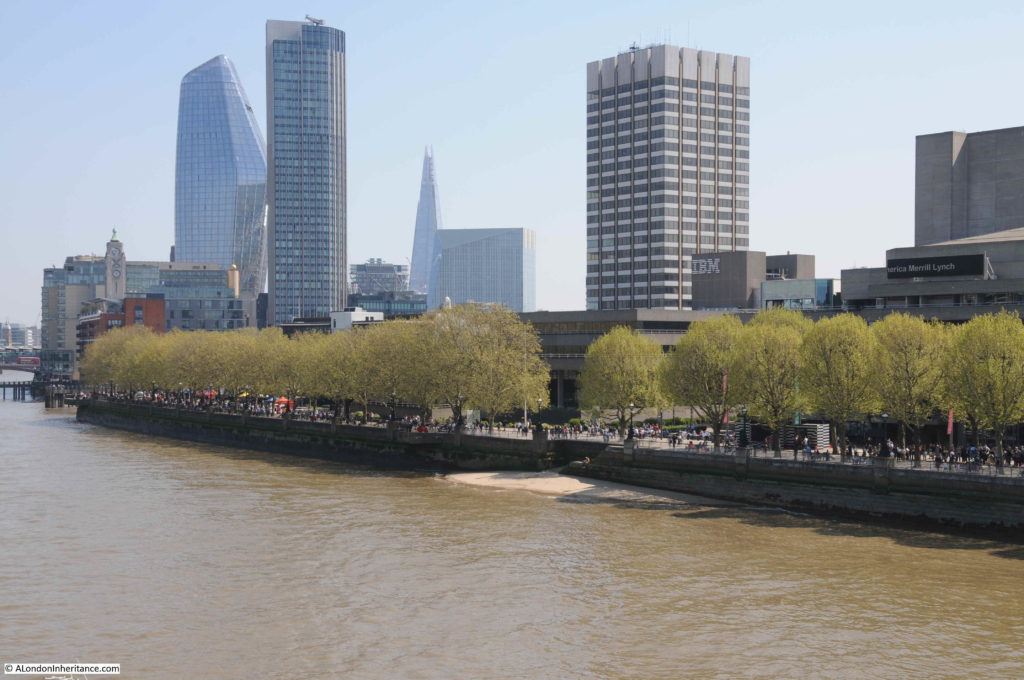
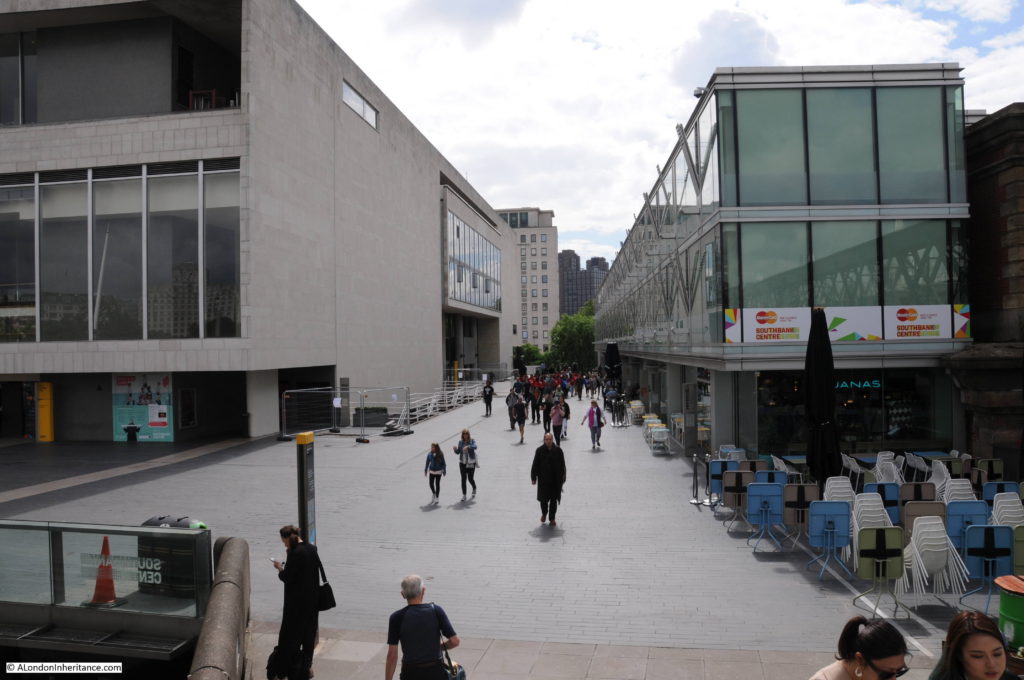
The same view in 2022 (although a bit too much of the Royal Festival Hall):
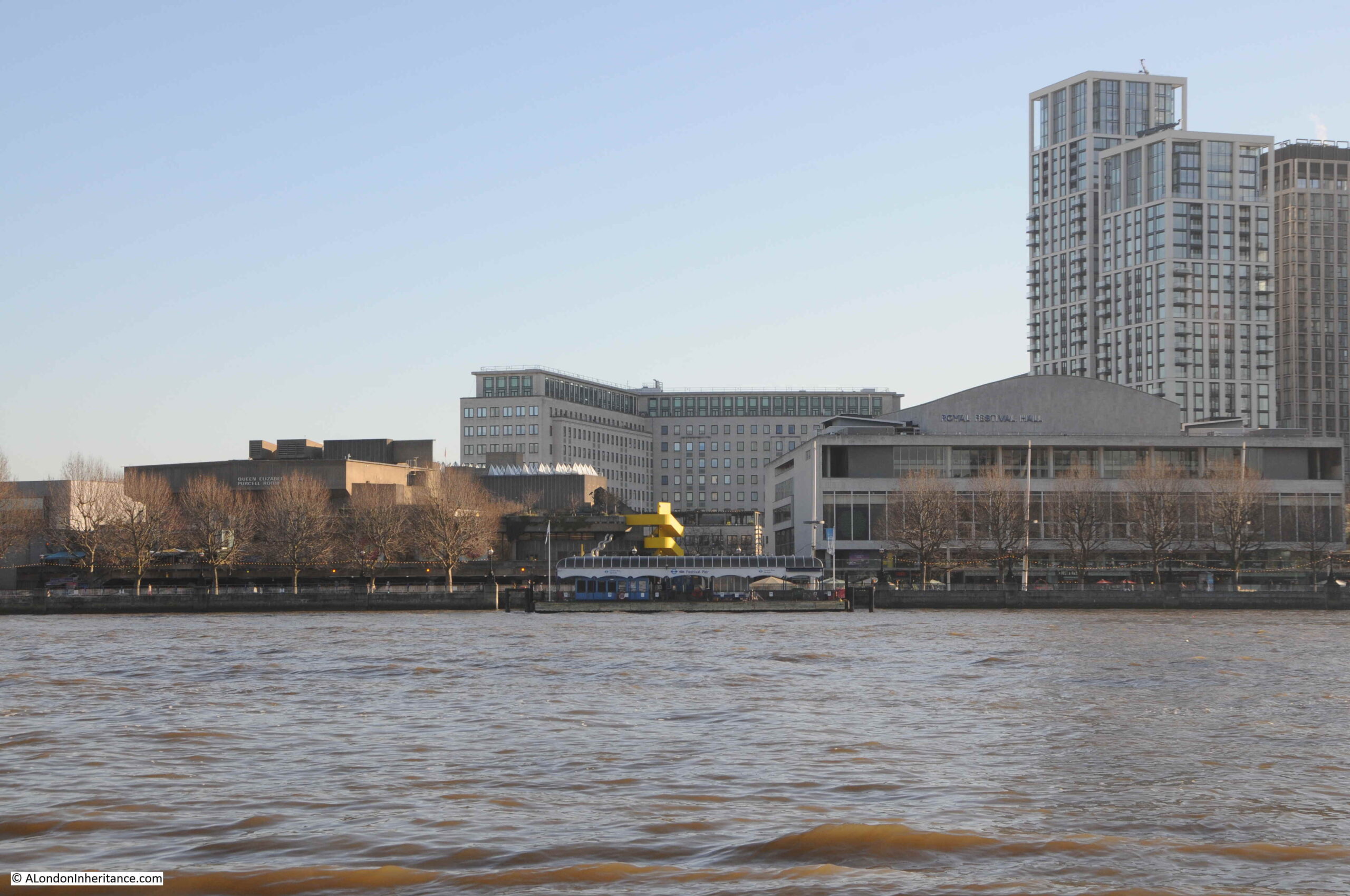

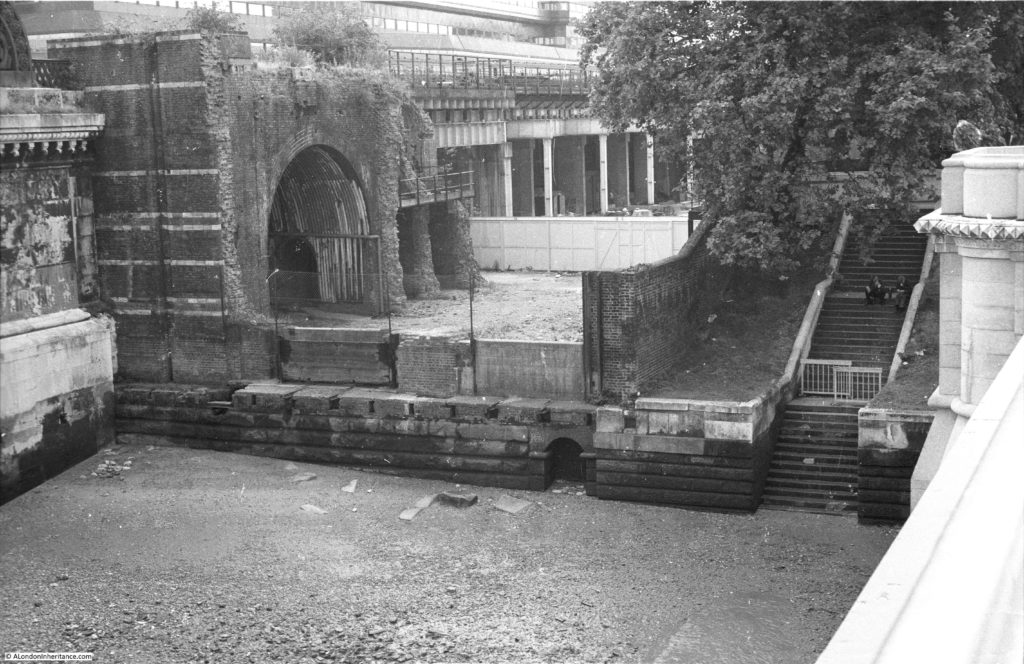
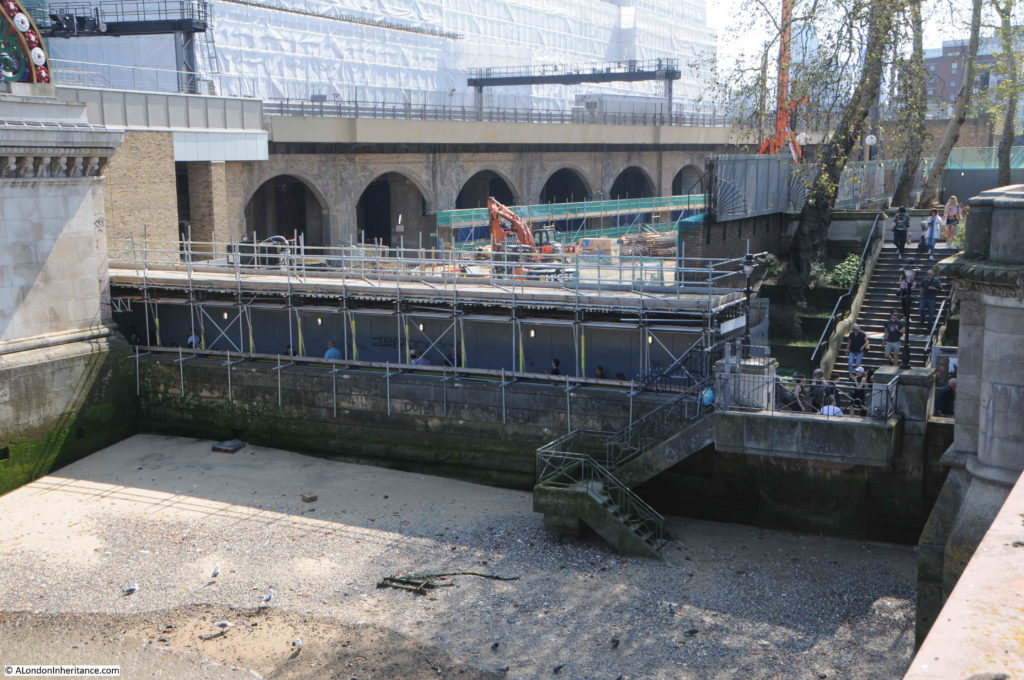
The Shot Tower was just behind and to the left of the yellow stairs seen in the centre of the above photo.
The South Bank today, and the Shot Tower would have been just to the right and further back from the yellow concrete stairs, and the edge of the Queen Elizabeth Hall:
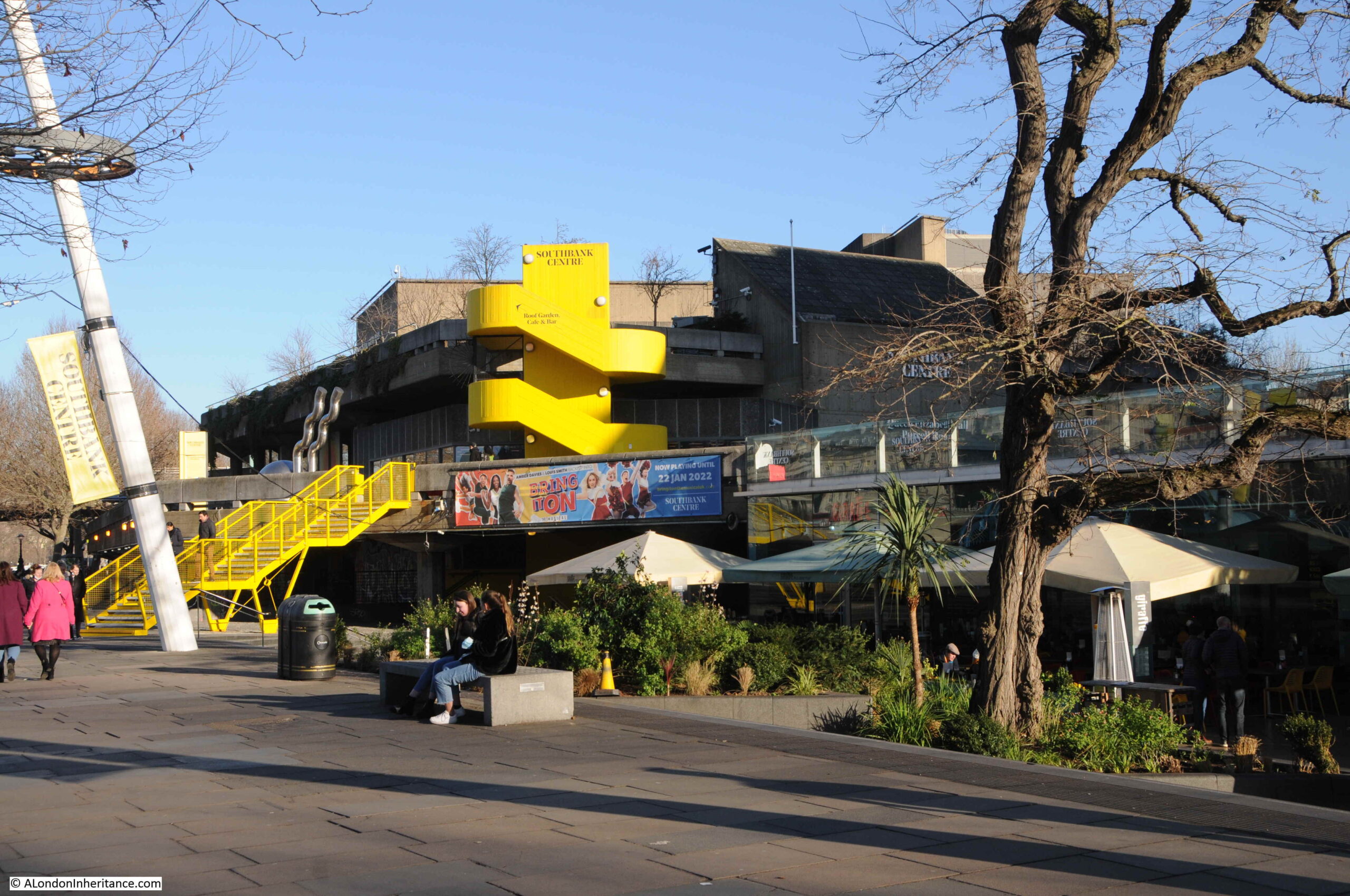

The purpose of the Shot Tower, and the process which gave its name to the tower, was the manufacture of lead shot for shotguns.
The Shot Tower was built in 1826 for Thomas Maltby & Company, and in 1839 was taken over by Walker, Parker & Company, who would continue to operate at the site until closure in 1949.
The Shot Tower was designed by David Riddal Roper and stands 163 feet from ground level to the top gallery. A spiral staircase within the tower provided access to two galleries, one half way up from where molten lead was dropped to produce small lead shot, and a gallery at the top of the tower which was used for large lead shot.
It was a considerable brick construction, with 3 foot thick walls at the base of the tower, tapering to 18 inches at the top.
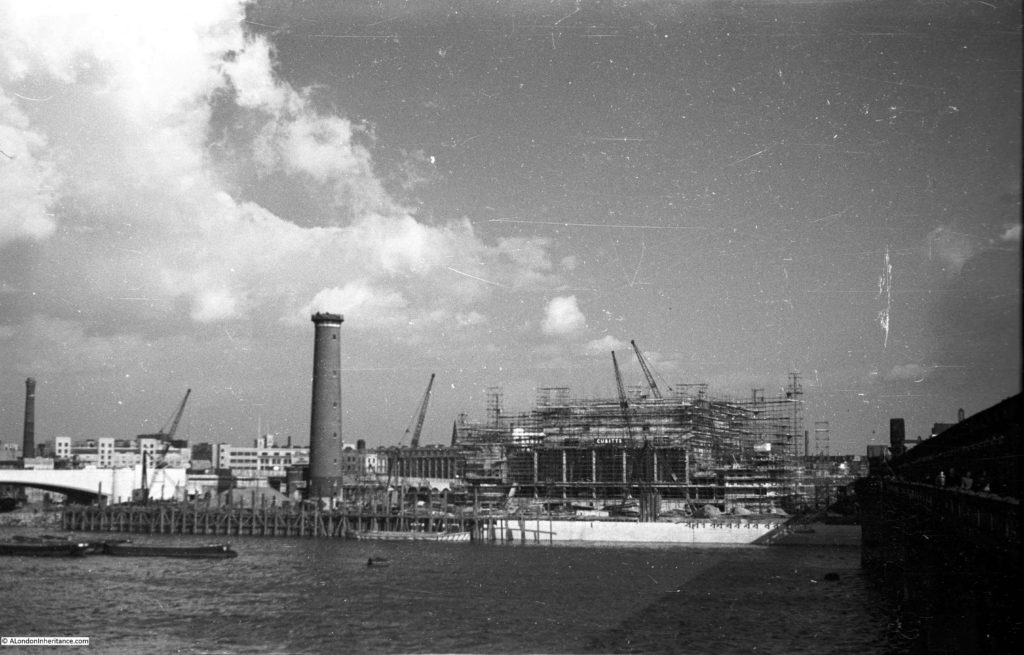
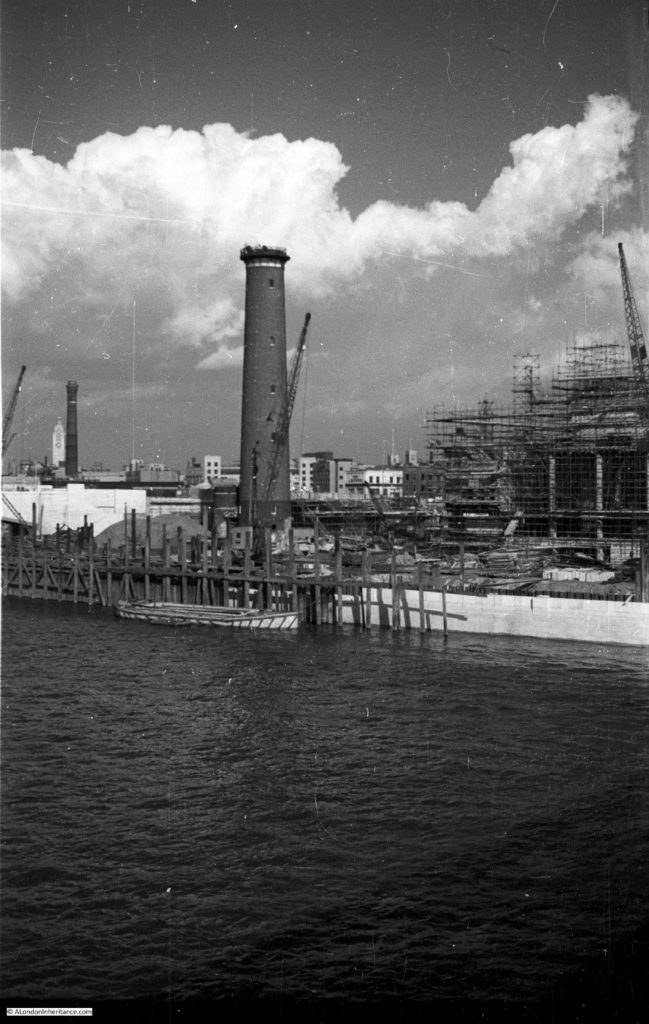
There were a number of shot towers across London, including one on the other side of Waterloo Bridge which I will show later in the post. There was also one in Edmonton and a film was made using the Edmonton tower to show how lead shot was made within the tower.
The Shot Tower survived the demolition of all the other buildings on the South Bank as part of the clearance for the Festival of Britain, and was included as part of the festival.
It was finally demolished in 1962, clearing the site for the construction of the Queen Elizabeth Hall. A real shame that it was not preserved and space made for it in the design of the new hall. It would have been a fitting reminder of the industrial history of the South Bank.
The Shot Tower survived and was included in the Festival of Britain as it was considered a well known landmark, and as with the lion on the top of the Lion Brewery, there was public concern that such a landmark would be demolished.
The festival organising committee wanted vertical features on the South Bank to draw attention to the site (the Skylon was the primary feature, designed specifically for the festival) and they also wanted the festival to demonstrate Britain’s scientific and technical achievements and advanced British manufacturing, as the country faced the economically difficult post war years and was in desperate need of foreign trade and currency.
The answer was to save the tower, and include it as part of the displays. The very top of the tower was removed and a new structure installed that consisted of a large lamp, emulating a light house, and a large radio dish antenna mounted on an anti-aircraft gun carriage.
The following photo shows the Shot Tower with the additions to the top of the tower for the Festival of Britain:
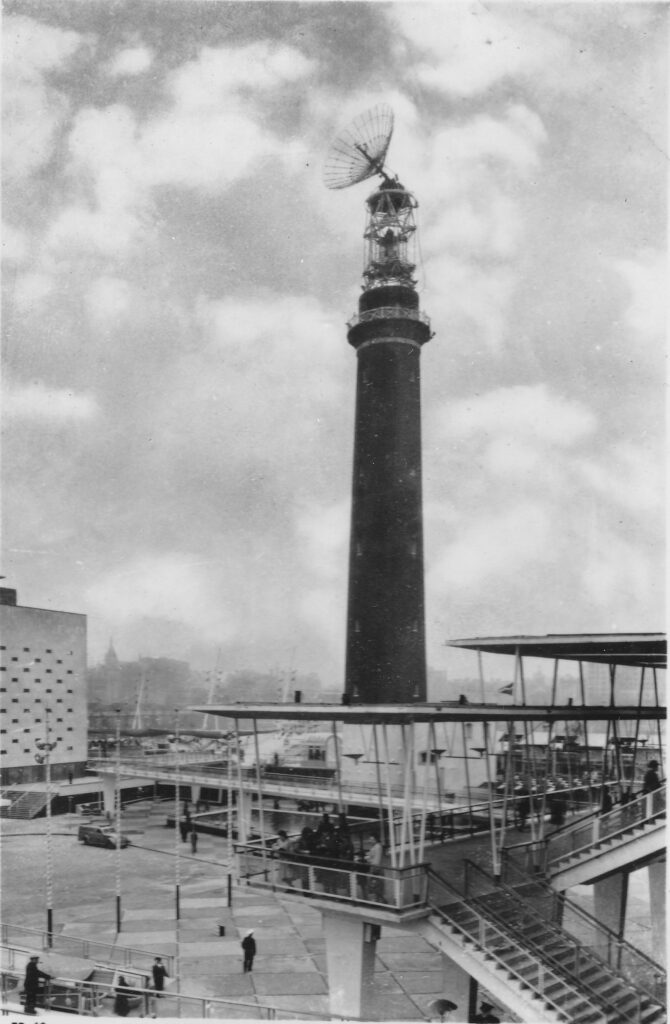

The intention with the radio dish at the top of the tower was described in the Festival of Britain Guide Book, as: “The radio beacon is above the lighthouse optic. The most obvious part of it is a large reflector which beams a signal to the moon. This is part of the radio telescope and is connected with the display in the Dome of Discovery by underground cable. In the Dome visitors can transmit signals to the moon and actually see them reflected back to the earth after about two and a half seconds”.
The display was in the Outer Space section of the Dome of Discovery, and the use of an anti-aircraft gun carriage at the top of the tower on which the radio dish was mounted, was to enable the dish to move to follow the moon in the sky.
The above description of the intended use of the radio dish is from the official festival guide, and the majority of books on the Festival of Britain repeat this planned use, however it seems that a different use for the dish had to be found after the technically advanced parts for such as radio transmitter / receiver were not available in time.
The Illustrated London News on the 21st April 1951 (not long before the opening of the festival on the 3rd of May 1951) records the new use of the radio dish: “There is to be no moon radar telescope on the top of the 200-ft shot tower on the South Bank: instead , visitors will see radio ‘noises’ or atmospherics from outer space on a television screen.” I assume the guide book had already been printed when the change was made.
The display on a TV of radio noise from sources such as the sun was probably far less visibly dramatic than the radio dish on the top of the old Shot Tower, but it did follow one of the Festival’s aims of showing scientific and technical advancements, just not in such a dramatic way as bouncing a radio signal off the moon.
Mounting an anti-aircraft gun carriage at the top of the tower was not without its dangers as this report from the Evening Telegraph on the 26th of October 1950 describes: “GUN CRASHES INSIDE SHOT TOWER – The gun mounting of a 3.7 A.A. gun being hoisted to the top of the Shot Tower at the Festival of Britain site fell 120 feet inside the tower to-day.
A 20-year-old soldier, Edward Bradley, was taken to St Thomas’s Hospital with slight bruises.
The mounting which weighs about five tons was being placed at the top of the Shot Tower. The gun is to carry a radar set which will send pulsations to the moon during the Festival.
Mr. Morrison told the Commons yesterday the equipment would cost £25,000 and would help in the development of radar astronomy.
Gunner Bradley was half-way up the staircase inside the tower, guiding the load, when he was struck by a falling plank. The gun mounting landed squarely in the centre of the tower and broke through the concrete floor to a depth of a foot.
Also inside the tower at the time were Captain Elliott, in charge of the operation, and a sergeant. The sergeant said ‘We heard a noise as if there was something amiss and we baled out of the tower as quickly as possible'”.
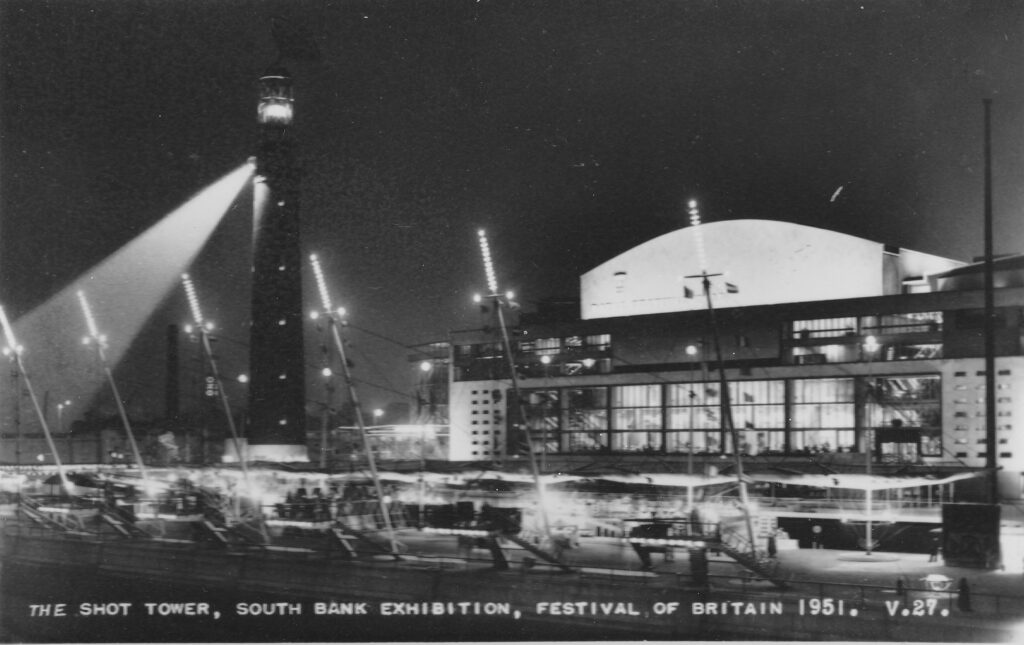
Underneath the radio dish was the “lighthouse” which was in operation from dusk until the evening closure of the festival. It was an electrically operated light (described as “of the most modern all-electric design”) with a lamp of three thousand watts, with a second lamp available should the main fail. The glass of the lighthouse optics which focused the light was made by Chance Brothers, the company that had made the glass for the original Crystal Palace in 1851.
The beam from the lighthouse could be seen up to 45 miles away from the South Bank site.
The following postcard showed the Shot Tower at Night. The lighthouse is the lit section at the very top of the tower, not the beam of light shining down from the tower.

There were discussions on how to decorate the brick tower. Aluminum was suggested (the material was used for the Dome of Discovery and the Skylon), but was deemed too expensive. Cellophane was also suggested but considered a very poor choice. In the end, it was left as the original brick
The two vertical features of the South Bank, Festival of Britain – the Shot Tower, and much taller (300 feet from ground to tip) Skylon:

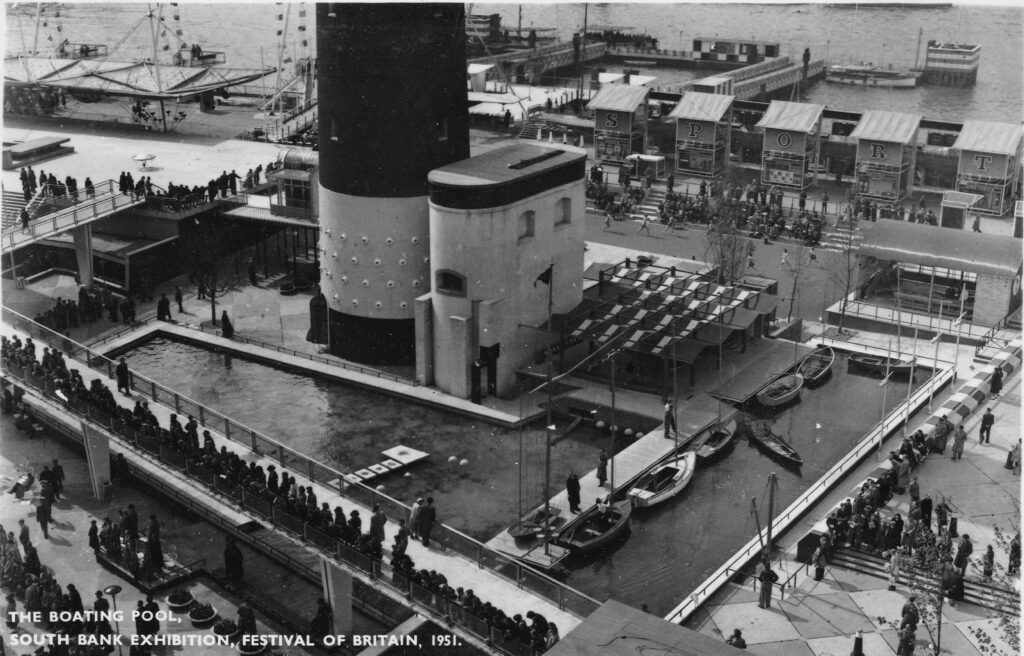
As well as the Shot Tower, a brick building at the base of the tower was retained and used for a small exhibit showing the development of the South Bank site, as well as some control equipment for the radio system at the top of the tower.
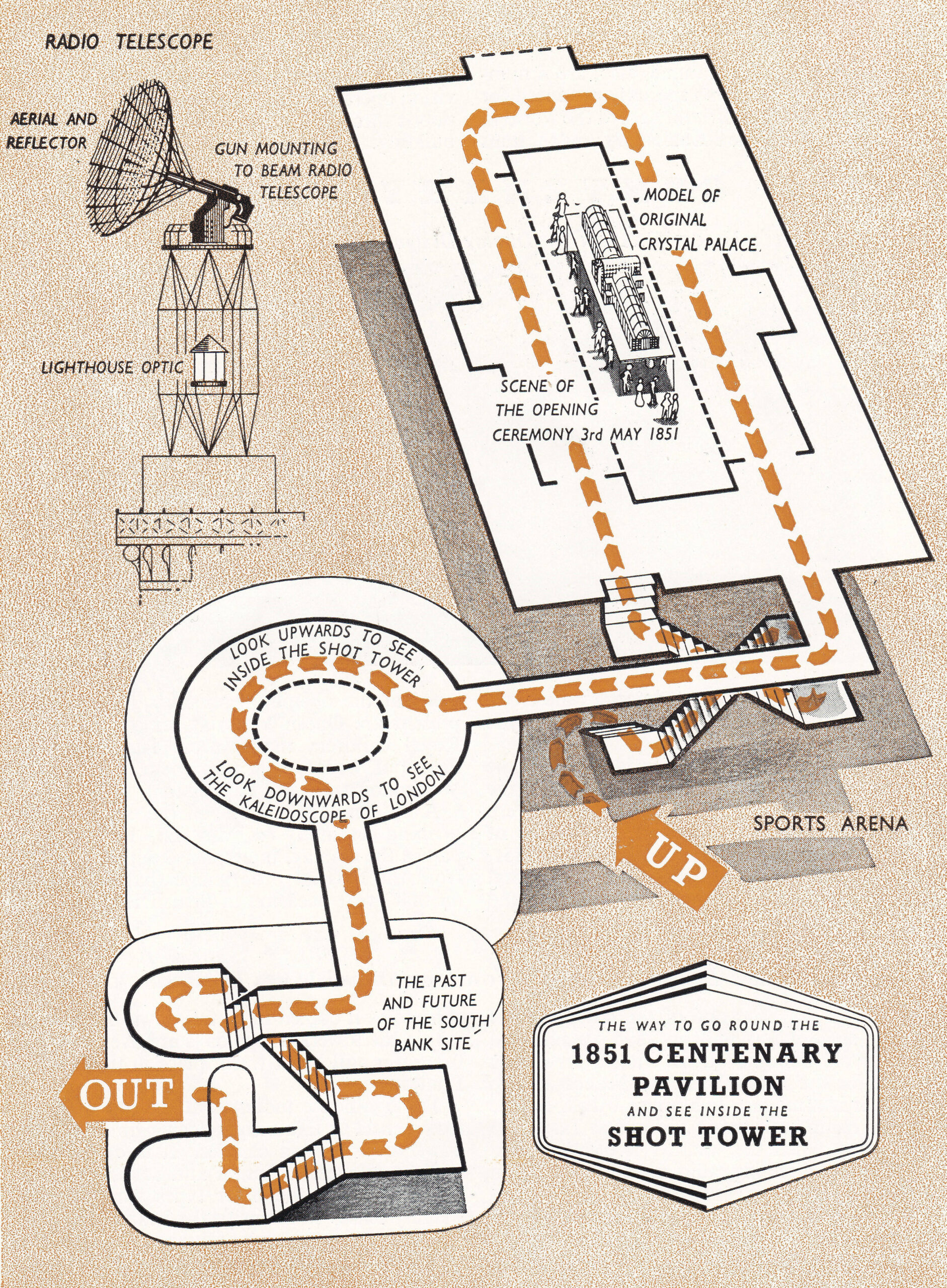
A walkway from this building led into the Shot Tower where visitors could look up and see the top of tower, and below a kaleidoscope of changing London scenes was shown.
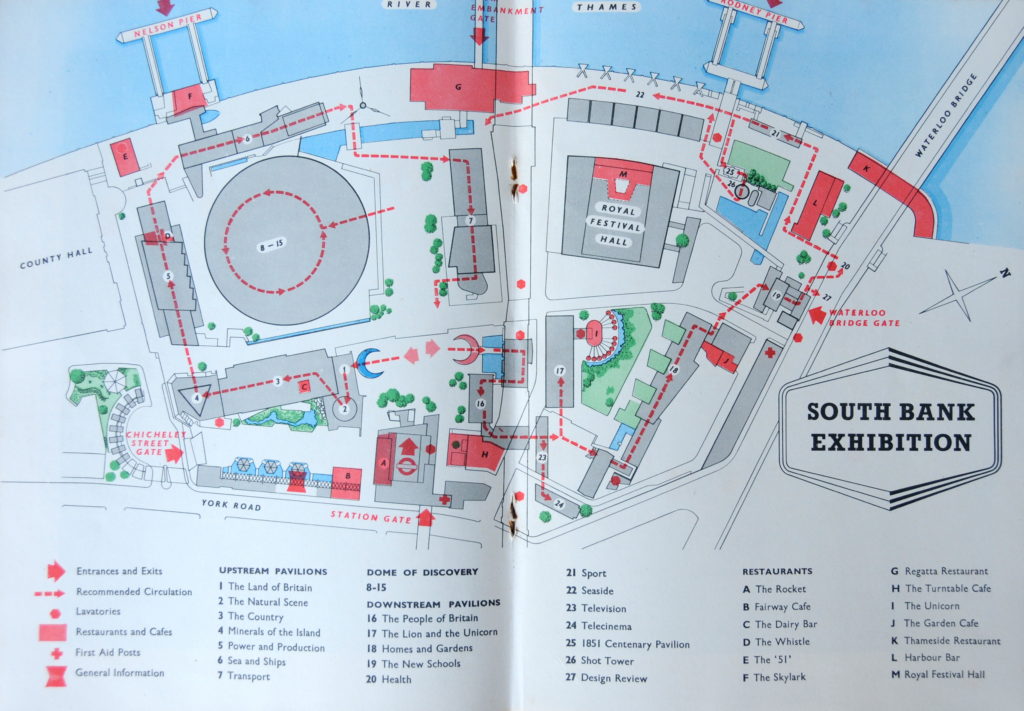
The following page from the Festival of Britain, South Bank Guide Book shows the Shot Tower and the recommended route:
The Guide Book also included a rather good colour advert from the construction engineers who had completed the work to extend the steelwork at the top of the Shot Tower for the lantern and for supporting the anti-aircraft gun and radio dish:

The following postcard shows the base of the Shot Tower and the adjacent brick building which provided the access route to the tower during the festival:

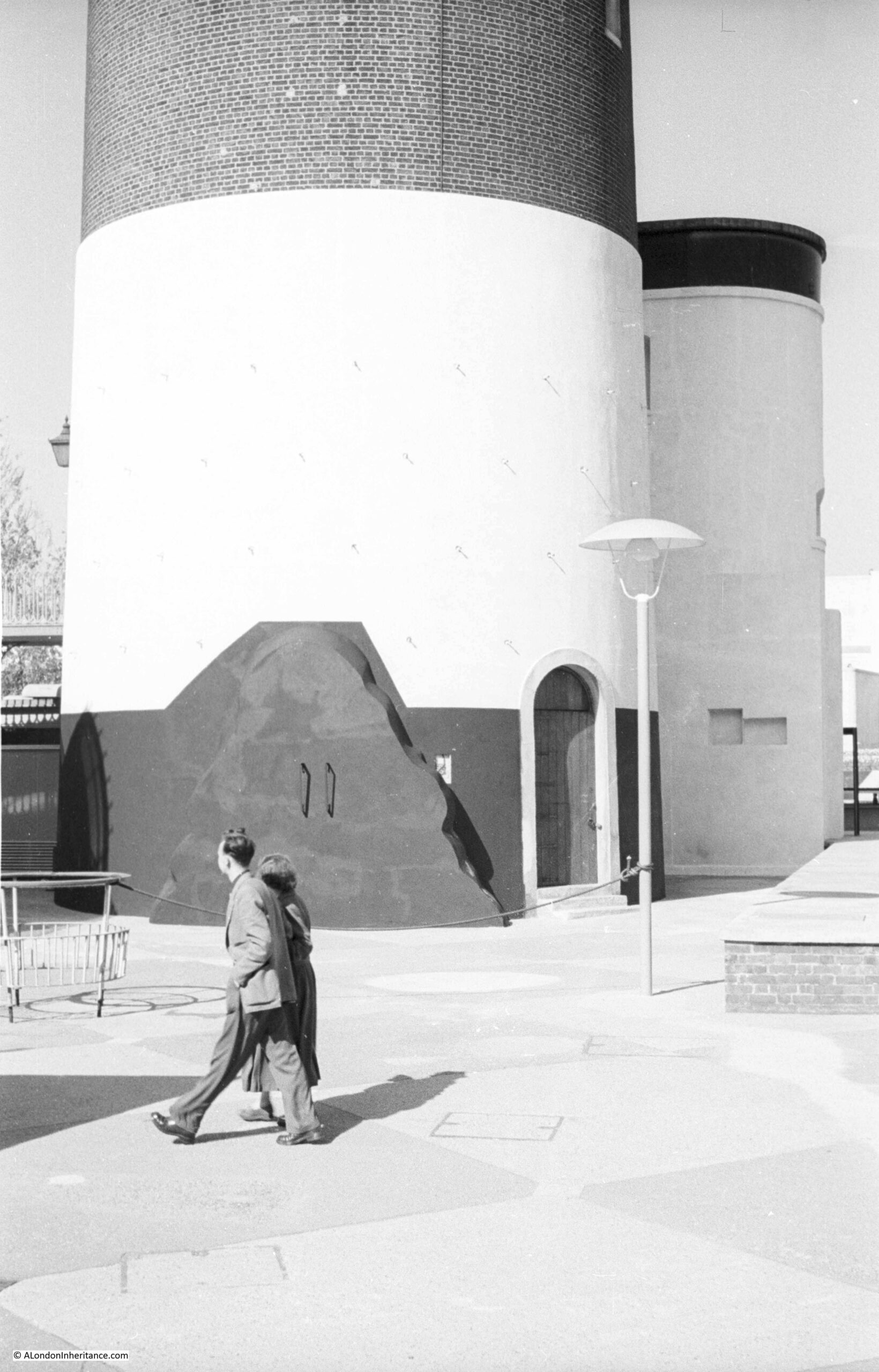
My father took the following photo at the base of the Shot Tower:

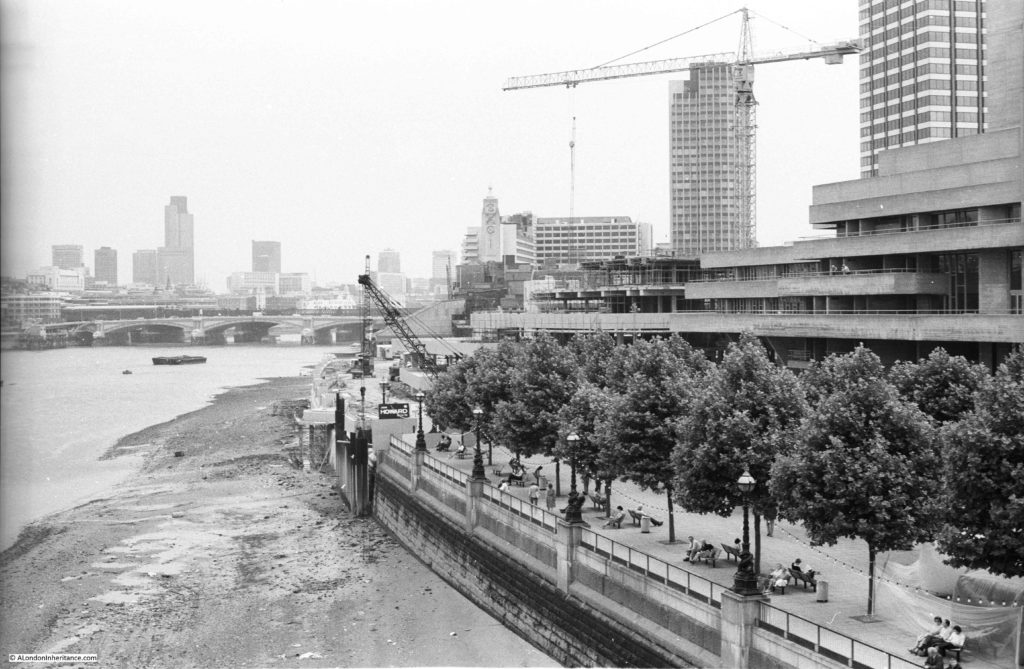
Time to return to my father’s original photo and look at the other buildings facing onto the river:
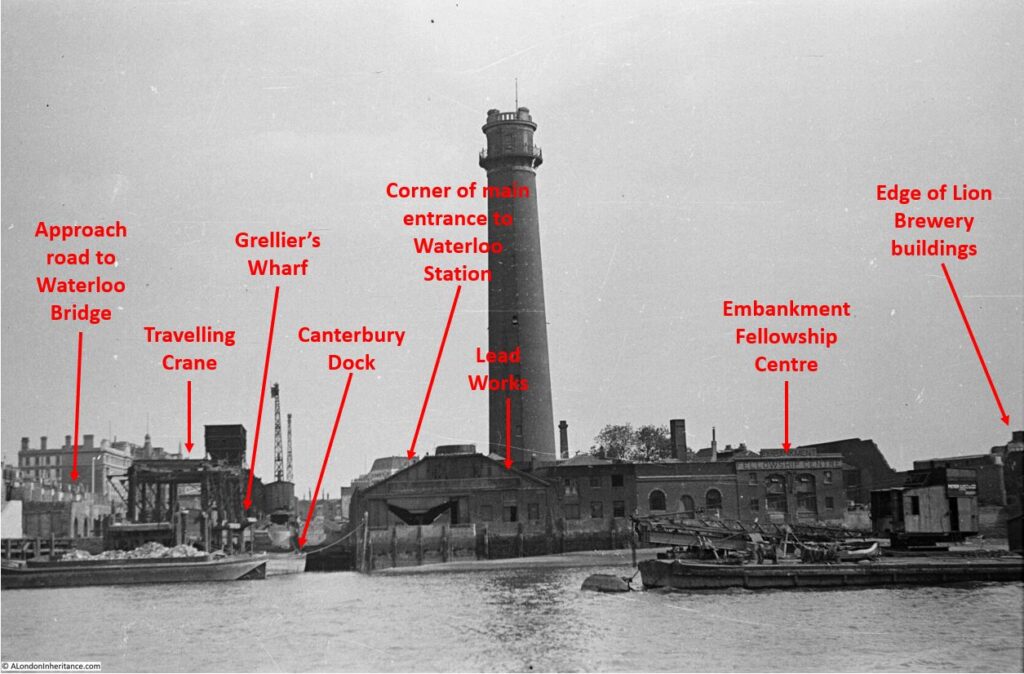
From left to right:
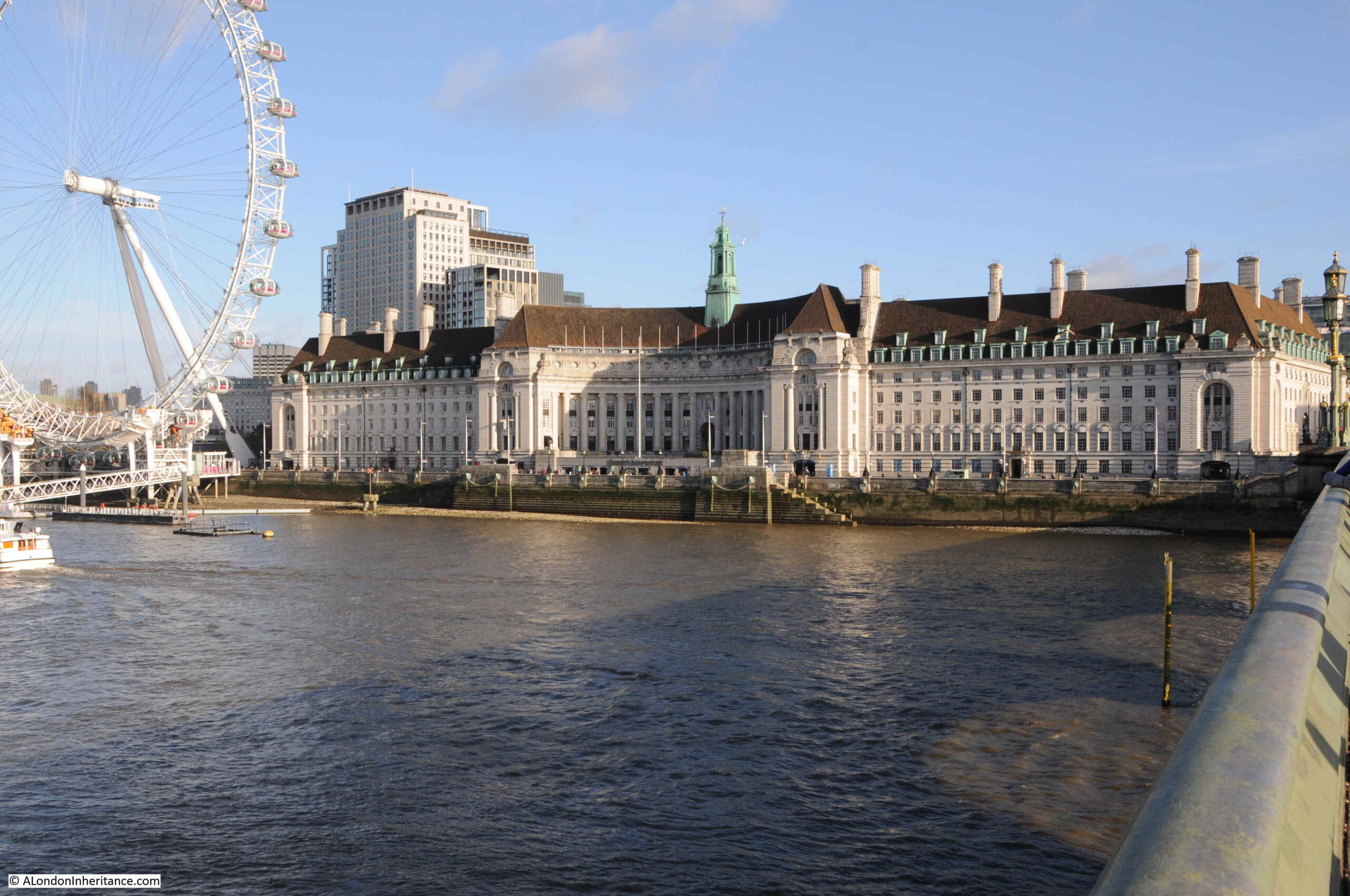
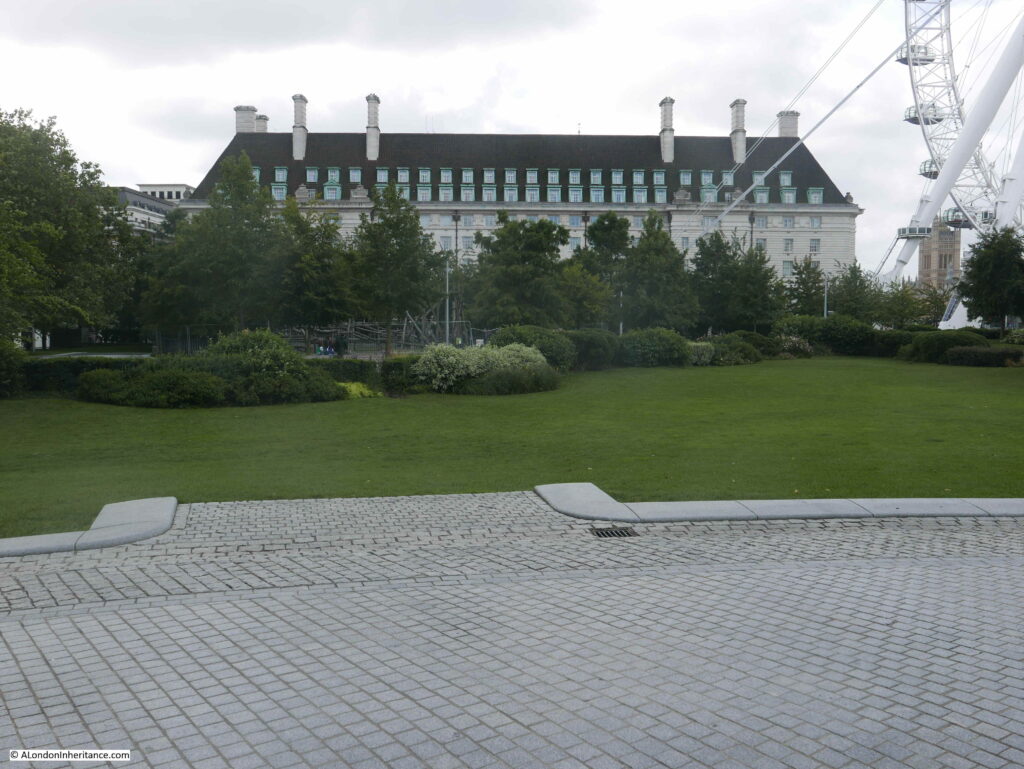
On the far left edge of the photo is the approach road to Waterloo Bridge. Behind the red arrow pointing to the approach road is one of only two buildings that have survived from the photo, the building is now part of King’s College, London.
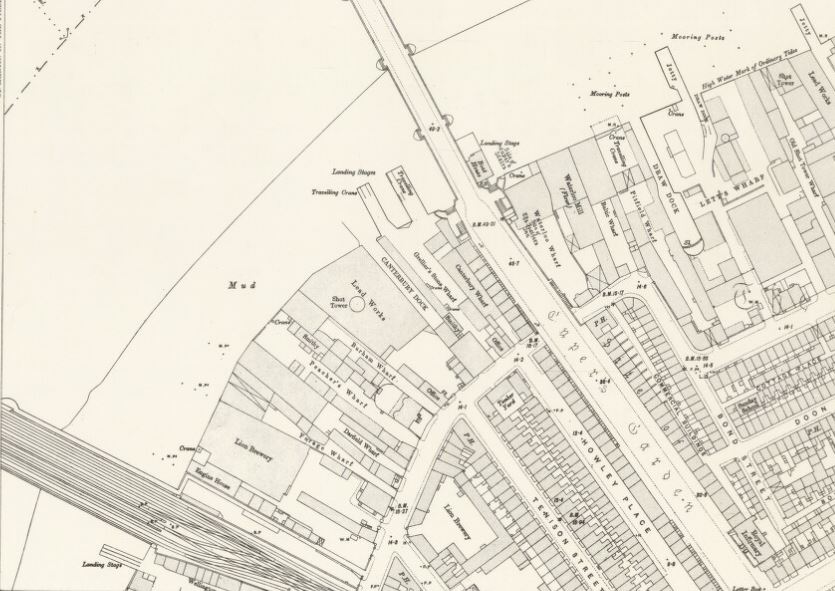
To the right is a travelling crane and Canterbury Dock that were part of Grellier’s Wharf.
The name Grellier’s Wharf came from Peter Paul Grellier, who opened a stone and marble business at the site between Belvedere Road and the Thames. Auctions were held at the site of imported stone and marble, for example, on the 20th July 1843, there was an auction of “a very large importation of very fine marble, consisting of statuary, black, black and gold, vein, dove and bardilla. This importation is recommended to the attention of the trade, as being of a very superior description”.
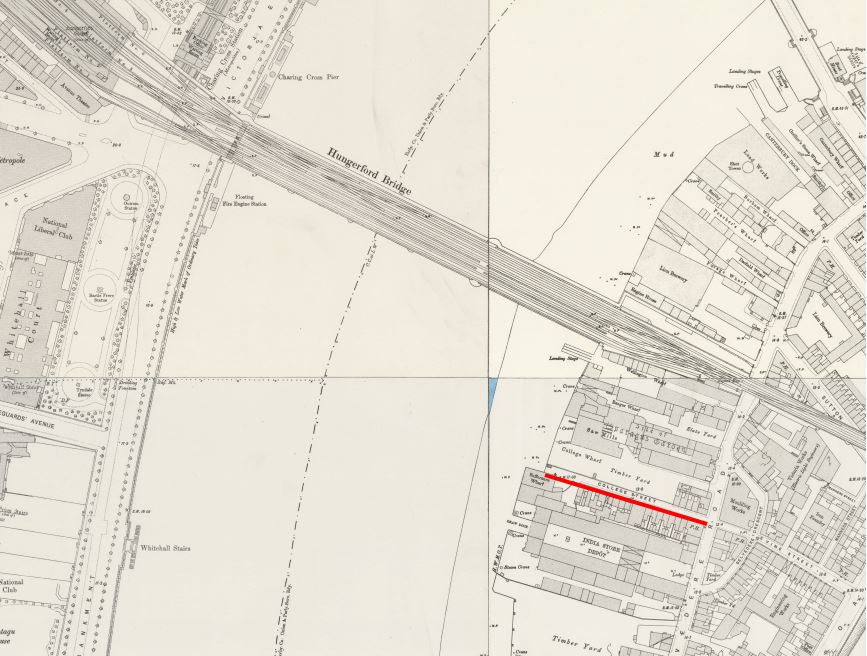
Canterbury Dock was a small inlet of the river into the site. The name Canterbury came from the Archbishop of Canterbury who was a major landowner in the area (and is also why many of the streets with housing developed in the area between Belvedere Road and Waterloo Station in the 19th century were named after Archbishops of Canterbury).
Slightly to the right, in the background can be seen a small part of the main entrance to Waterloo Station, the second building that remains from the 1947 photo.
The buildings of the lead works are next with the Shot Tower behind.
To the right of the Shot Tower, along the buildings facing the river, there is one with the name “Embankment Fellowship Centre” along the top of the building. An enlargement from the original photo is below:

The Embankment Fellowship Centre was a charitable organisation with an aim of helping unemployed ex-servicemen who had fallen into poverty. Established in 1932 by Mrs. Gwen Huggins the wife of the Adjutant of Chelsea Hospital. She decided to do something to help the ex-servicemen she saw sleeping rough in London, and along the Thames Embankment.
Originally known as H10, and changing name to Embankment Fellowship Centre in 1933, the following article from The Sketch on the 30th of August, 1939 provides a good summary of the organisation’s approach and what took place on the south bank:
“The EMBANKMENT FELLOWSHIP CENTRE provides a constructive solution to the unemployment problem where it affects its most difficult victim, the middle-aged ex-Service man from the Navy, Army, R.A.F., or Mercantile Marine. The Centre does not cater for the vagrant, the work-shy, or the waster, but can claim that every man helped has been reduced by sheer misfortune and no fault of his own to the lowest ebb of poverty.
Painters, doctors, miners, schoolmasters, chauffer’s, stockbrokers, plasterers, mechanics and clerks are all among those who have been assisted. The credentials of all applicants who must be over forty-five, are carefully examined before admission to the Centre, where they are housed, fed and re-clothed and maintained for a period averaging 47 days per case. When a man reaches the Centre he has usually been through a bad period of stress, so the first task is to ‘recondition’ him. To that end he is surrounded by an atmousphere of cheerfulness, comfort and companionship. In the daytime he has occupational work, and every evening he has something to look forward to – a lecture, a show by an amateur dramatic society, a game of darts or billiards, or a film.
Meanwhile officials endeavour to find suitable employment for him; and since many applicants belong to overcrowded or depressed trades, the Fellowship Centre undertakes free training in its own workshops for employment in which middle-age is only a slight handicap, such as valeting, housework, cookery, carpentry, boot and shoe repairs, and so on.
Last year employment was found for 549 men, at an average age of 53 years. The total could have been larger had the premises been capable of accommodating more men. During the past four years some 2000 men have been found employment at an average age exceeding 50 years. Included in the Centre is the Ward of Hope, where a period of free convalescence is provided, following discharge from hospital for homeless and friendless men.
The Council are trying to solve the problem of expansion. They are also trying to raise capital for maintaining a country home, to be modelled on Chelsea Hospital, where veterans of good record with no pension and past the working age can be housed.
Subscriptions to this excellent cause to be sent to Major R.M. Lloyd, Appeal Director, the Embankment Fellowship Centre, 59 Belvedere Road, S.E.1.”
The Embankment Fellowship Centre made a film in 1939 telling the story of a middle aged man named Smith, who lost his job, and could not get another because of his age. Things went downhill quickly with the family possessions being repossessed until he was recommended to the centre. With the centre’s help, he found a new job, and the last scene of the film is Smith and his wife agreeing to donate his recent pay rise to the Embankment Fellowship Centre.
The film “Smith” can be watched here.
The centre on the South Bank was closed not long after my father took the photo, and Hansard records a question in Parliament about the closure, when on the 23rd September 1948, Commander Noble “asked the Minister of Health why the Embankment Fellowship Centre, Lambeth, which provides accommodation for ex-Service men, has just been given notice to quit by 1st December”
Mr. Bevan answered “I understand that this and other notices are occasioned by a London County Council scheme for the redevelopment of the area of the South Bank in which this centre lies.”
The redevelopment of the South Bank would lead to the Royal Festival Hall and the Festival of Britain.
The Embankment Fellowship Centre relocated, and in 2007 changed name to ‘Veterans Aid’, and is still in operation.
Veterans Aid have their main London centre at ” New Belvedere House”, which is rather nice as hopefully the intention was to name the building after the original location at 59 Belvedere Road on the South Bank.
On the right edge of the 1947 photo is part of the Lion brewery. It would be demolished to make way for the Royal Festival Hall which would be built on the land to the right of the Shot Tower.
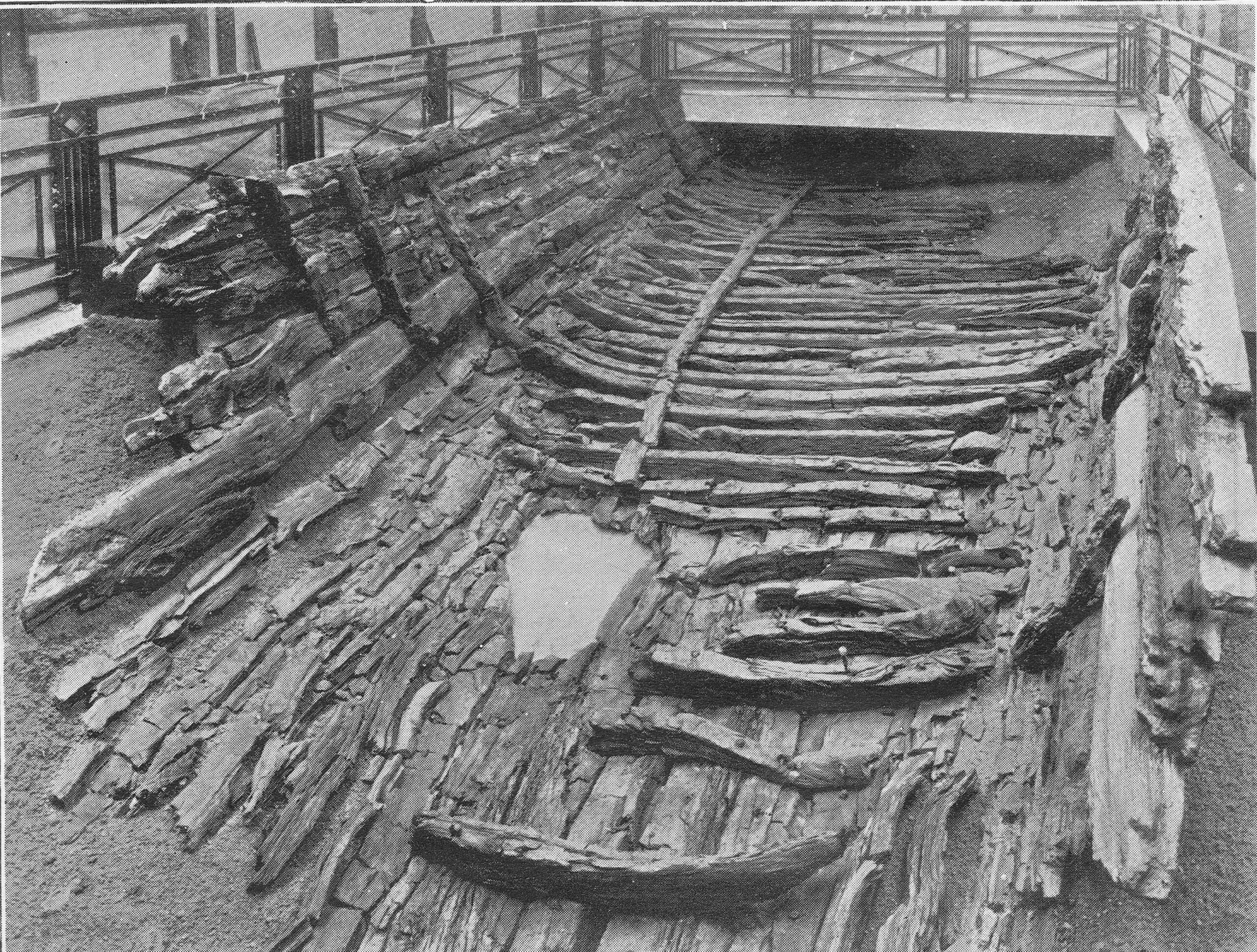
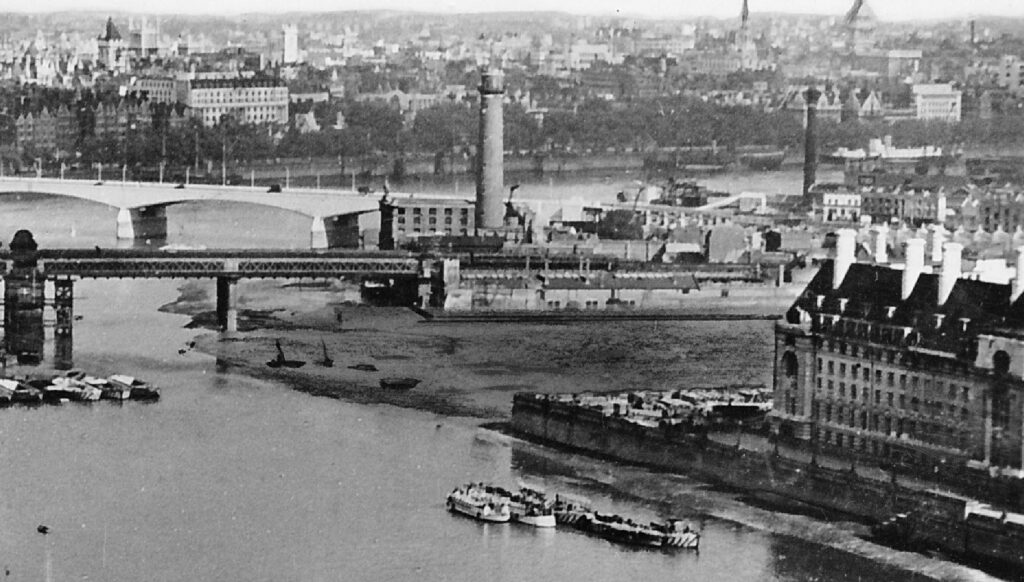
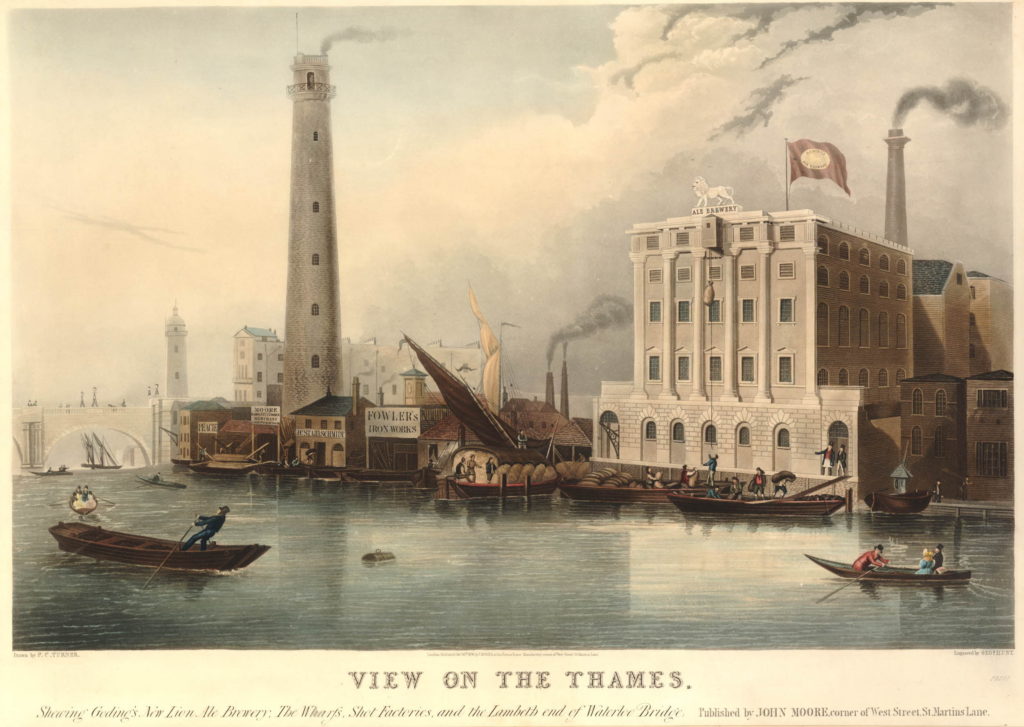
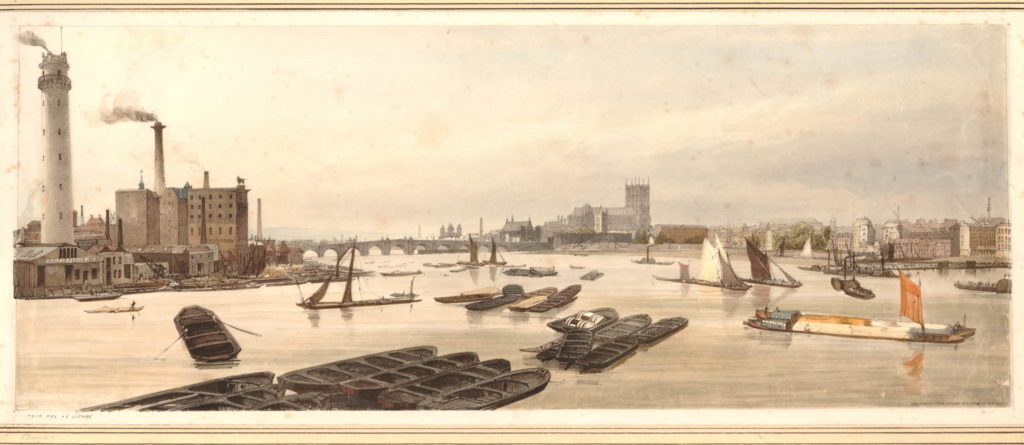
The South Bank Shot Tower was not the only shot tower along the south bank of the river. The following postcard is a view from the top of the Shot Tower, looking towards the City of London:
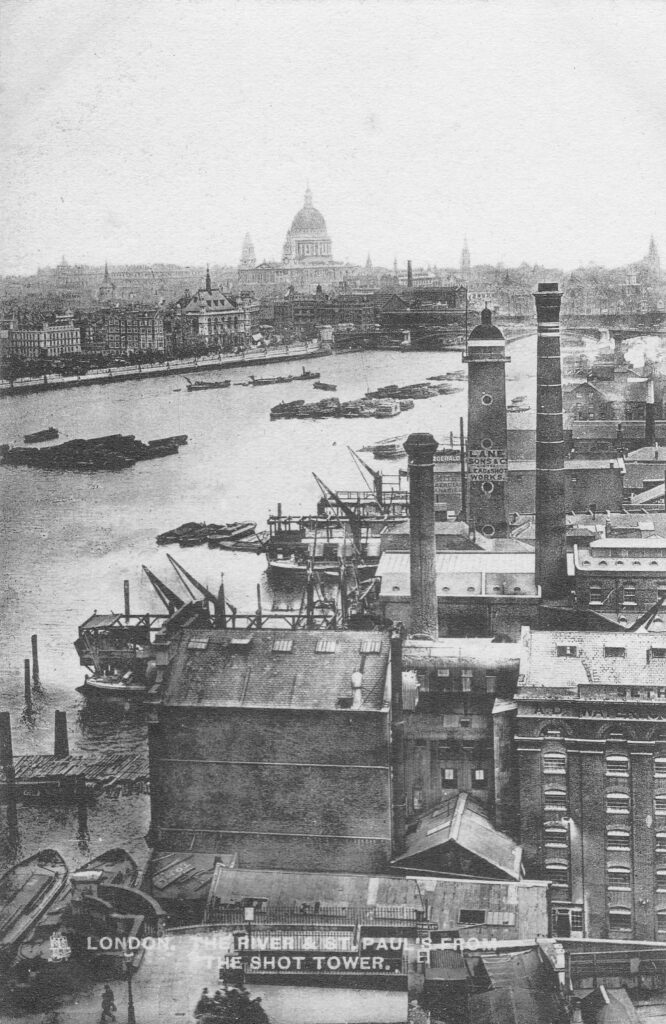

Between the two chimneys is a much wider tower, with a dome shaped top. This was also a shot tower, and was older than the one on the South Bank.
Built around 1789, it was described as “a new structure, which cost near six thousand pounds, but cannot be considered as an object ornamental to the River Thames”. It was 150 feet high, and in 1826 the top part was destroyed by fire, which was not surprising given the activity carried out within the tower.
The lead works which included this second shot tower were also owned for a period by Walker, Parker & Company, the same company that owned the South Bank Shot Tower. They left the works in 1845 to concentrate on their South Bank site. The site was advertised in the Morning Chronicle on the 9th October 1845 as: “EXTENSIVE LEAD WORKS, Shot Tower, Wharf, Dwelling-house, and Buildings, Commercial-road, Waterloo-bridge. To be LET on LEASE for twenty one years, from Michaelmas next, when possession will be given in one or two lettings, all those capital and spacious PREMISES, with Wharf, extending about 120 feet next the river Thames, with the lead works, shot tower, and buildings lately occupied by Messrs.’ Walker and Co. Also a counting house, extensive stabling and premises, lately occupied by Mr. Sherwood”.
By the time of the above photo, the large advertising sign on the side of the shot tower was advertising that the works were “Lane, Sons & Co Limited. Lead and Shot Works”.
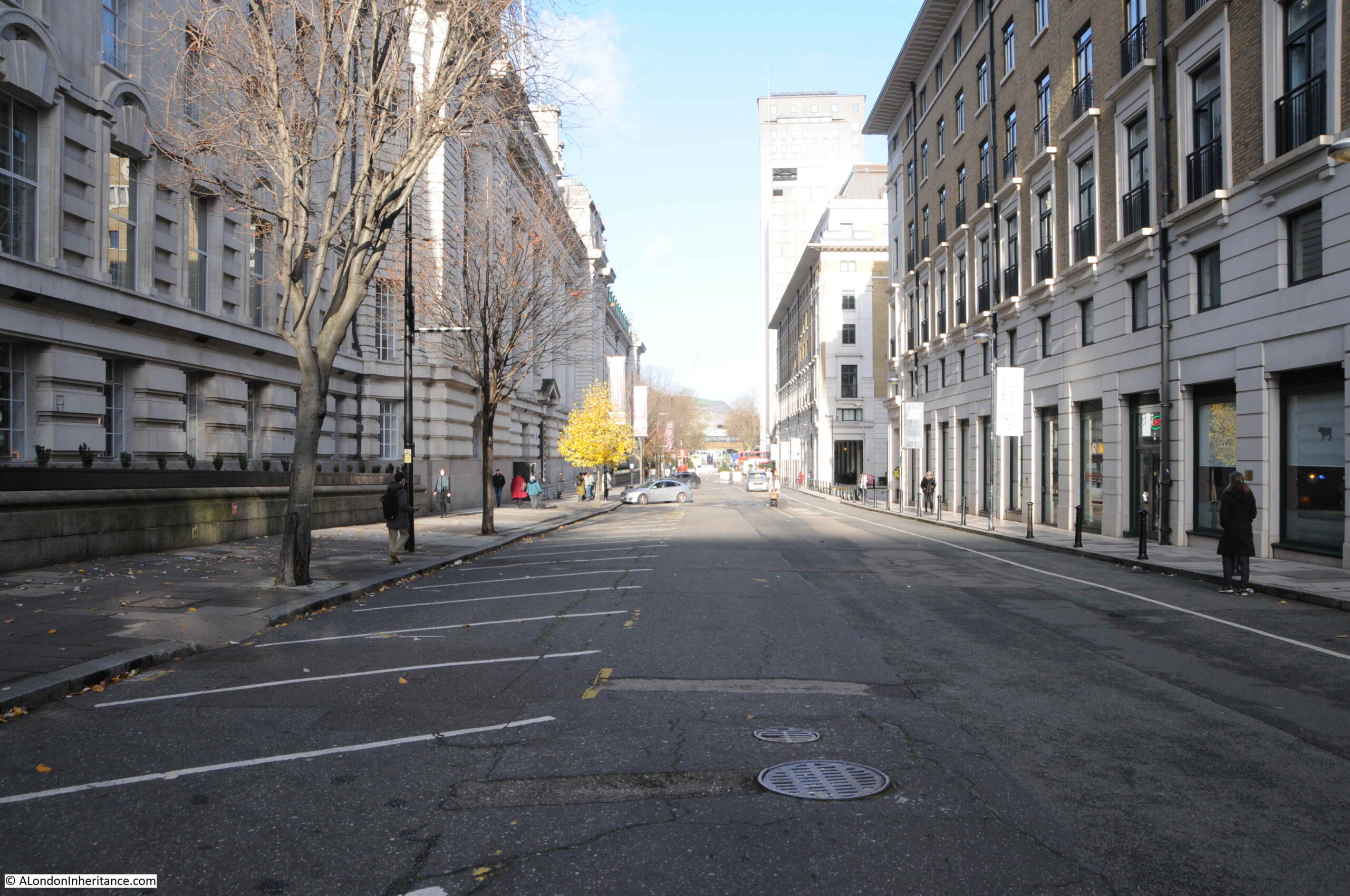
The street name in the advert is given as Commercial Road. This was a short lived name for the street which is now Upper Ground.
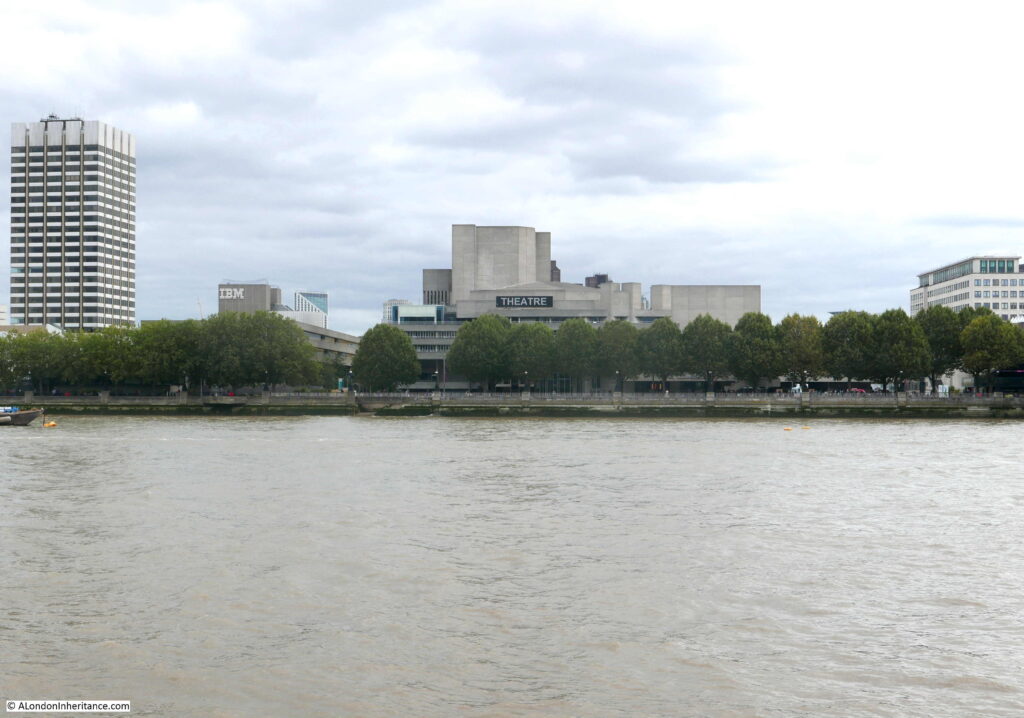
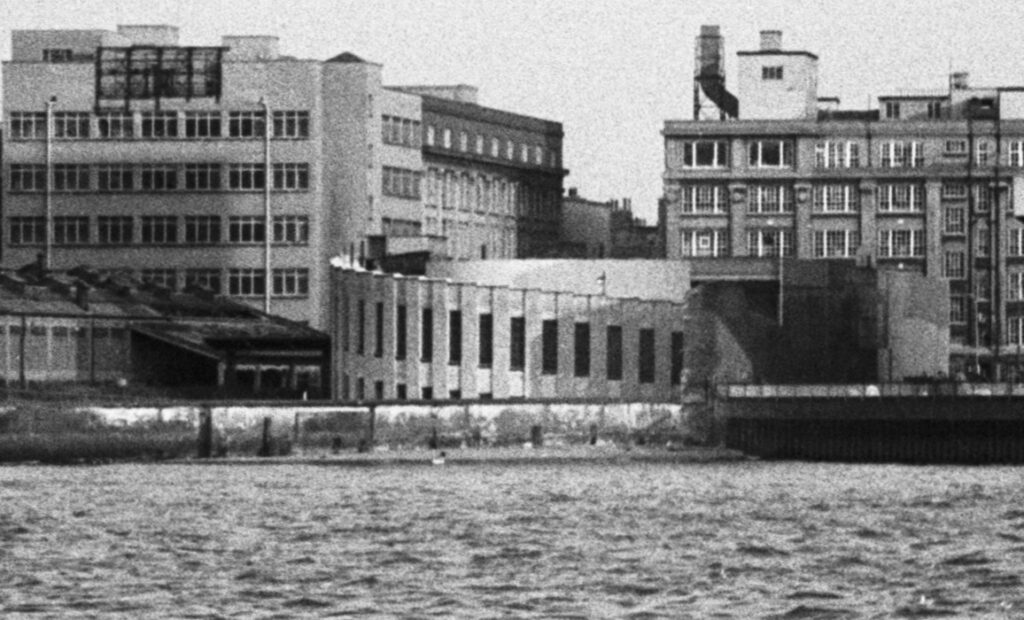
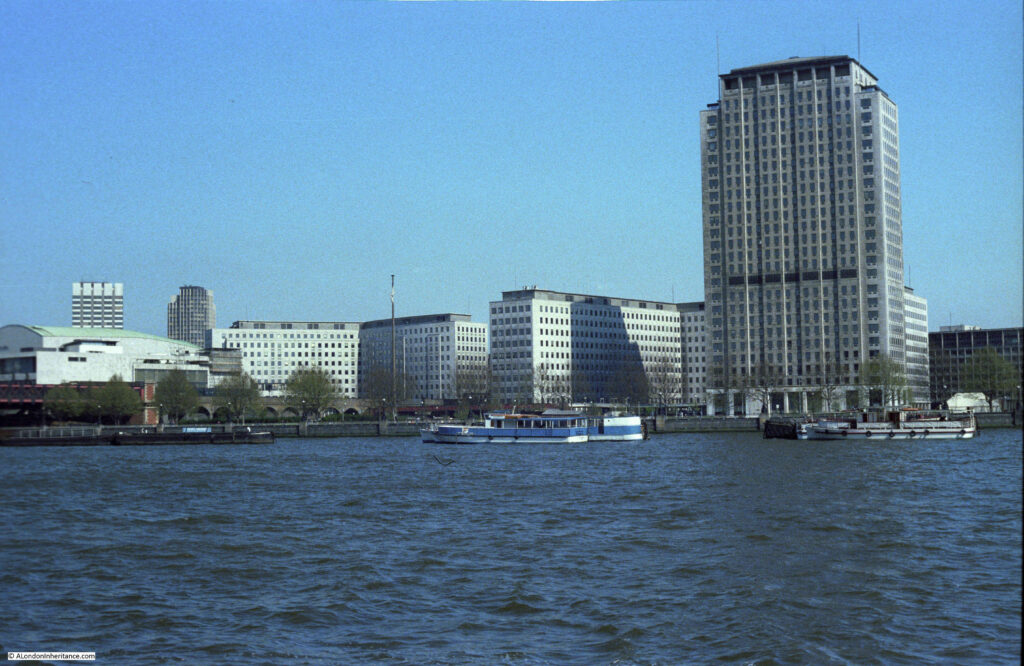
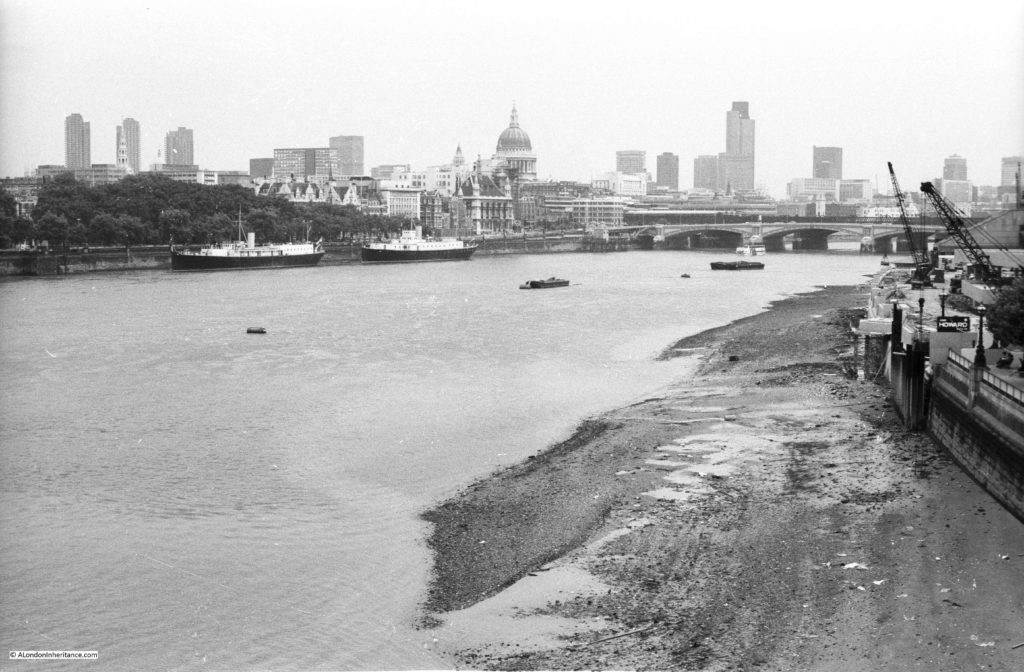
The shot tower was demolished in 1937 after having been out of use for several years. Today, the IBM offices (in the photo below) occupy the site of this second shot tower and lead works:

It is such a shame that the South Bank Shot Tower could not have been included in revised plans for the Queen Elizabeth Hall, and could today be seen between the Queen Elizabeth and Royal Festival Halls.
A reminder of the industrial history of the area, and adding some historical complexity to the buildings we see today, lining the side of the river.