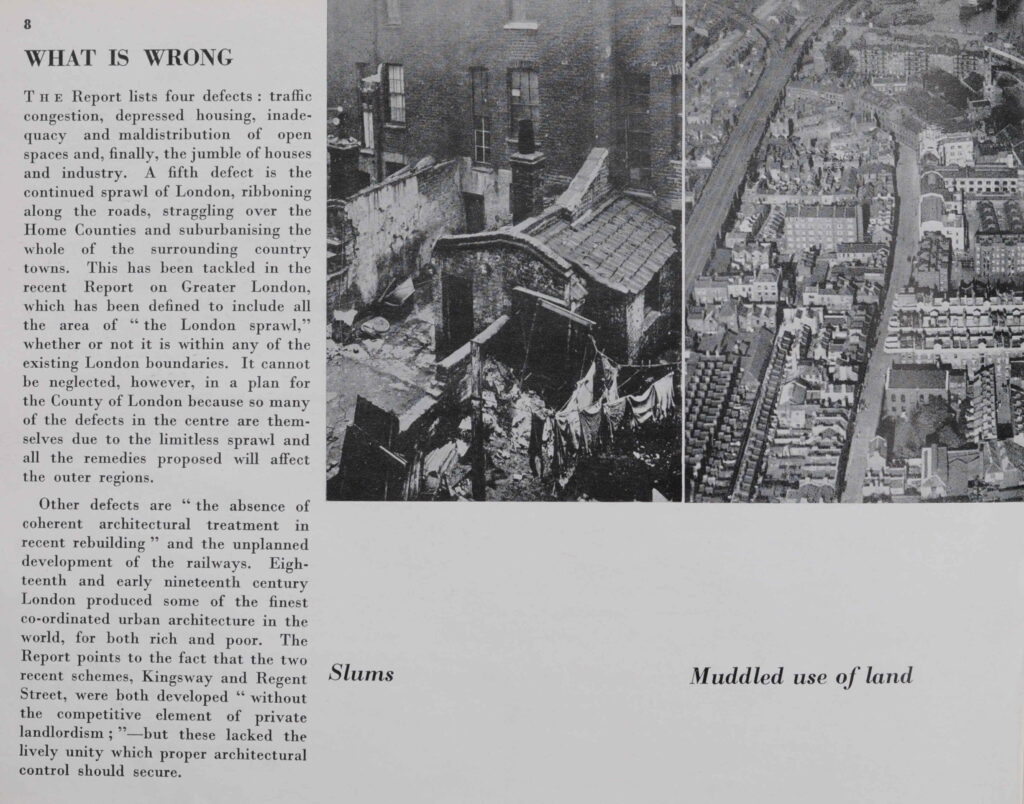
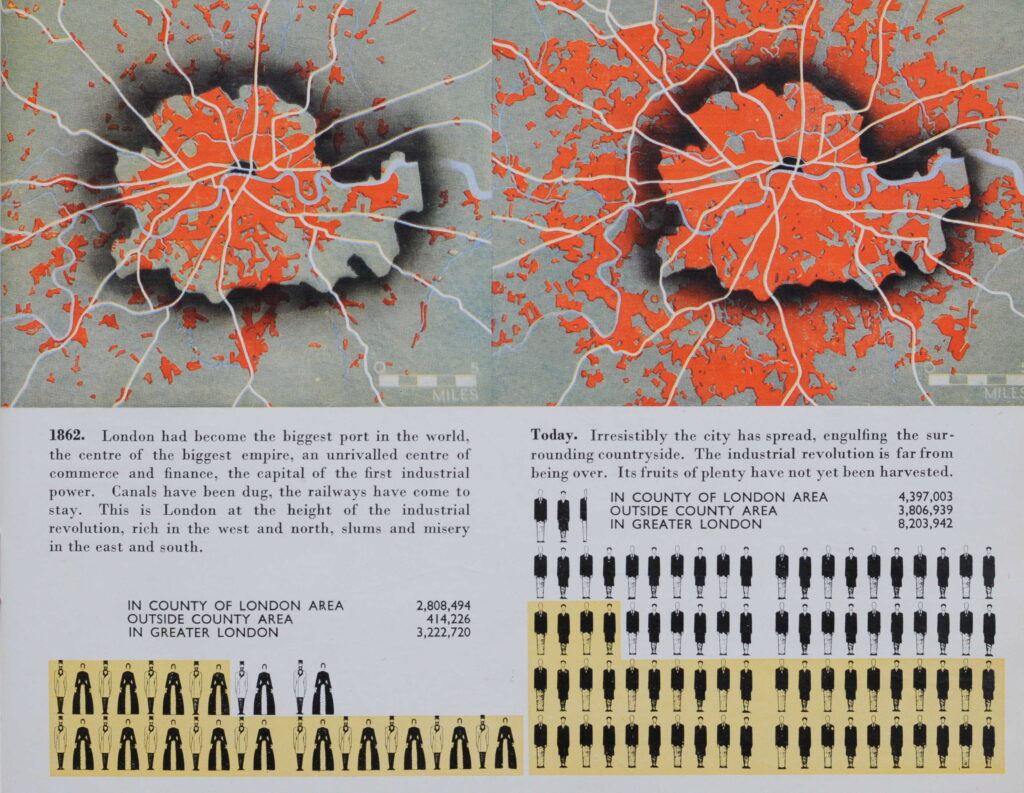
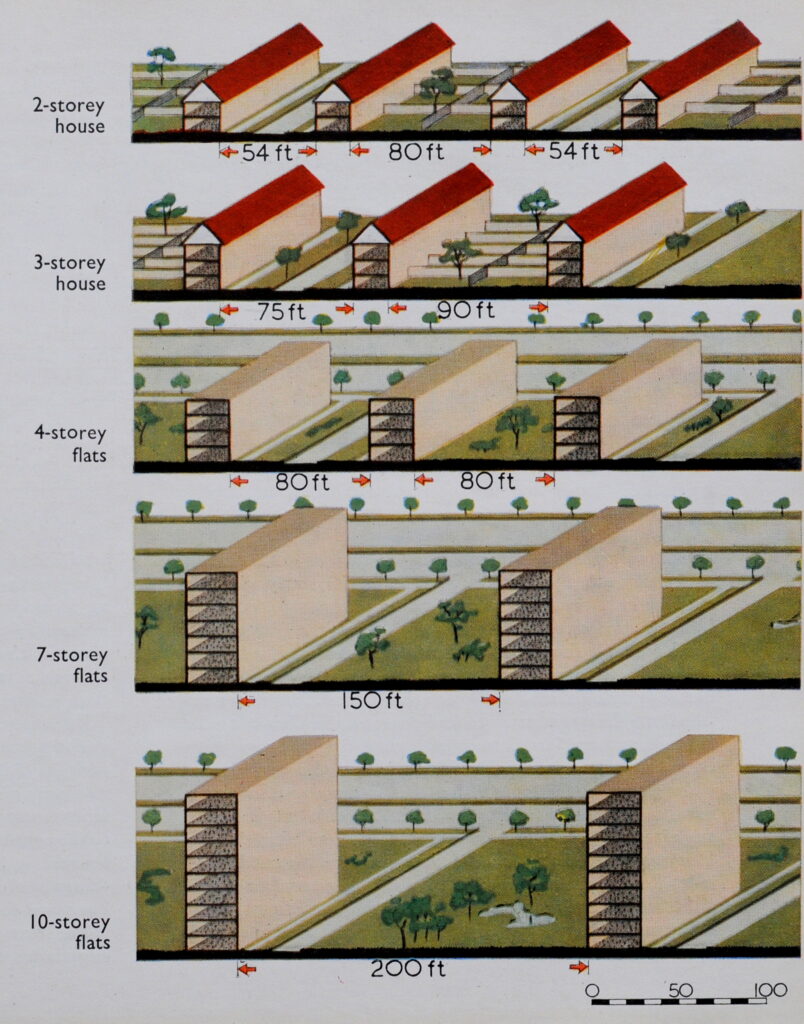
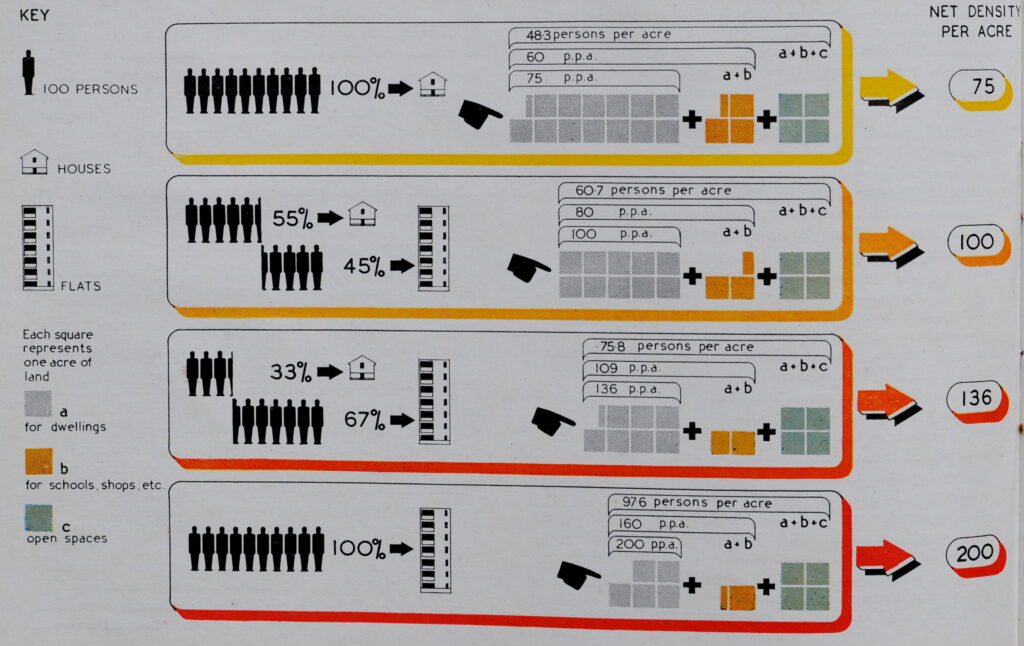
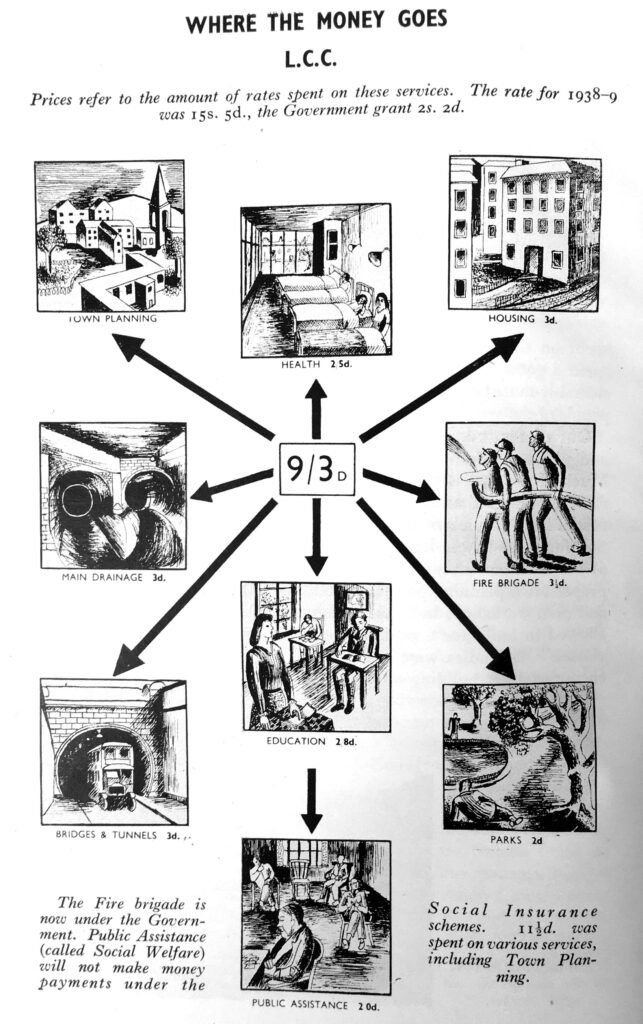
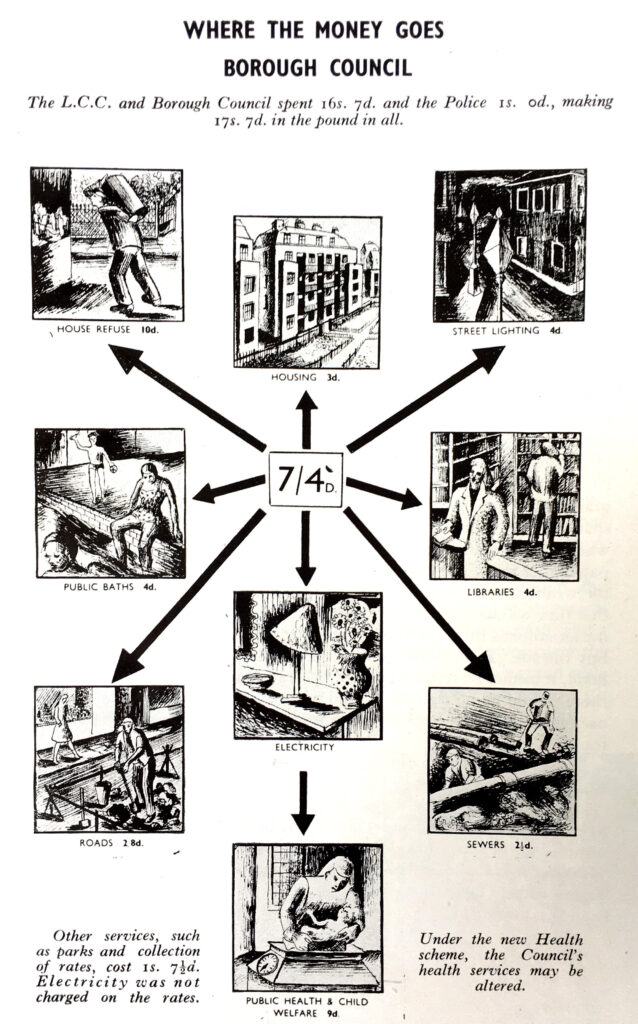
If you have walked the street of the City of London, you may possibly have noticed one of the City of London blue plaques.
The City of London Corporation have their own plaques to mark the locations of lost churches, hospitals, halls of the Guilds of the City, famous names and events etc. Whilst English Heritage are responsible for the circular blue plaque outside of the City, within the City, the rectangular blue plaque is the standard, and there are around 170 to be found.
New plaques are still occasionally installed, however the process is slow as there is approximately five years for a successful application, with many authorities being consulted regarding the subject of the proposed plaque, along with the owner of the building on which the plaque will be installed.
They display a minimal amount of information – “Site of”, “Near this spot” etc. followed by a name of a building or institution. Where an individual’s name is the subject of a plaque, there is usually a small amount of additional information, although limited by the standard dimensions of the plaque.
One of my many photographic side projects has been to photograph these over the years, so to start a very occasional series of posts on the City’s plaques, for today’s post, the story of three halls and a hospital.
Upholders’ Hall
The first plaque is not that obvious. Walk up towards St Paul’s Cathedral, along Peter’s Hill from Queen Victoria Street, and towards ground level on one of the buildings on the right, partly covered by some planting, is the plaque recording the site of Upholders’ Hall (see bottom right corner in following photo):

Site of Upholders’ Hall, destroyed in the Great Fire 1666:

My go to book on the City’s Guilds is “The Armorial Bearings of the Guilds of London”, by John Bromley and published in 1960. The book provides an overview of each Guild or Company, along with their coat of arms. The book describes an Upholder as:
“An upholder, or upholster, was originally one who dealt in soft furnishings which involved the use of stuffing to ‘uphold’ them”.
Therefore an upholder is an upholster, and the origin of the word upholster which is now generally used as a verb, is from the act of stuffing an item of furniture.
The Upholders’ formed around 1360, and as with most of the City’s Guilds at the time, their main role was to regulate their craft and ensure that goods produced met certain standards and quality, and were sold at a fair price (to both the customer and other craftsman to minimise any undercutting of members of the Guild). In 1474, the scope of the Upholders’ included “feather-beds, pillows, mattresses, cushions, quilts, curtains and spervers” (a sperver was the canopy over a bed).
The scope of the Upholders’ was enlarged in 1495 to provide them with powers of inspection and control “throughout the kingdom”, and the manufacture of clothing also came within their scope, including mourning clothes which led the Upholders to be spoken of as:
“The upholder, rueful harbinger of death, Waits with impatience for the dying breadth”
As the plaque describes, their Hall was close to Peter’s Hill and was destroyed during the Great Fire of 1666. As with a number of Guilds, their hall was not rebuilt and they were able to use the halls of other Guilds for their ceremonial events.
The Worshipful Company of Upholders, as they are now known, is still in existence. As with many of the City’s Guilds or Companies, they lost their regulatory powers during the 19th century, and are now mainly a charitable organisation, but still have strong links with those in the upholstery business and upholstery trade organisations.
The Upholders were granted their Coat of Arms in 1465, and Charles I granted a Royal Charter which was lost during the fire in 1666.
The coat of arms of the Upholders is shown below:

The book has a rather complex description of the coat of arms, which seems to reduce to three canopies (or spervers) with one covering the lamb of god and a cross (for religious significance) with the lamb sitting on a pillow of gold. Both the canopy and pillow being products of the Upholders trade.
My next plaque records the location of:
Poulters’ Hall
Just to the north of St Paul’s Cathedral is King Edward Street, next to the ruins of Christ Church Greyfriars, there is a plaque on the left column of a rather impressive arched entrance that leads to the offices of Bank of America. One of the very few places where I have had a security guard come out and ask me why I was taking photos.

The plaque records that near the location of the plaque stood the site of Poulters’ Hall, between 1630 and 1666:

The Worshipful Company of Poulters are an old company, with their origins dating back to at least 1299, when, according to “The Armorial Bearings of the Guilds of London”, “poulterers were one of the trades of the City of London, which elected men to supervise their respective trades in accordance with a proclamation for the regulation of food prices”.
The first documentation stating how the governance of the Poulters’ would work dates from 1370, and the Company was incorporated around 1503.
The company had the power to regulate the trade in poultry, swans, pigeons, rabbits and small game, along with butter and eggs.
Prices for these products were set by either Government, or the Mayor and Alderman of the City, and it was the Poulters’ responsibility to be answerable for any infringements of these prices.
The charter of incorporation dated June 1665 includes “all persons within seven miles of the City who trade of ‘meere poulters or selling poultry wares'”.
Companies such as the Poulters’ were almost an early form of Trading Standards. The type of action against an infringement that the Poulters’ would take, was recorded in newspaper reports on the 22nd June 1749: “Was tried in the Court of Kings-Bench at Westminster-Hall, a Cause wherein the Poulterers Company were the Prosecutors, against one Francis Patterson, for following the Trade of a Poulterer, having no Right or Title thereto; on which the said Patterson was convicted and fined £22. And we hear the said Company are determined to prosecute all Offenders in that Way, which will be a general benefit to the Public, there being no Trade in which Buyers are more imposed upon by Hawkers, and other Interlopers, who send bad and unwholesome Goods, at greater Prices that the Fair-Trader would good ones”.
As stated on the plaque, the Poulters’ Hall was destroyed during the Great Fire of 1666 and was not rebuilt, becoming one of the City Companies that use the facilities of other Halls. Since the end of the last war, the Poulters’ have used the Armourers’ Hall in Coleman Street.
The coat of arms of the Worshipful Company of Poulters’ is shown below:

The book “The Armorial Bearings of the Guilds of London” has a different view of the birds on the shield to the Poulters’ Company, who describe the birds as storks.
The book believes these to be Cranes and claims that the evidence of storks is meagre, with the earliest reference to storks being from around 1780.
A manuscript dated 1587 and held in the British Museum refers to the birds as cranes, and the crane as a food source was far more popular than the stork.
The two birds on either side of the shield are Pelicans, which provide the religious reference as the symbol of the pelican with blood on its breast comes from a pre-Christian legend that in times of famine, a mother pelican would pierce her breast, allowing her young to feed on her blood, thereby avoiding starvation (see my post on St Martin Ludgate for more on this).
Today, the Worshipful Company of Poulters’ run a number of charitable trusts, including one that aims to develop training and education in the poultry, egg and game industries and trades.
My next two plaques are along Aldersgate Street:
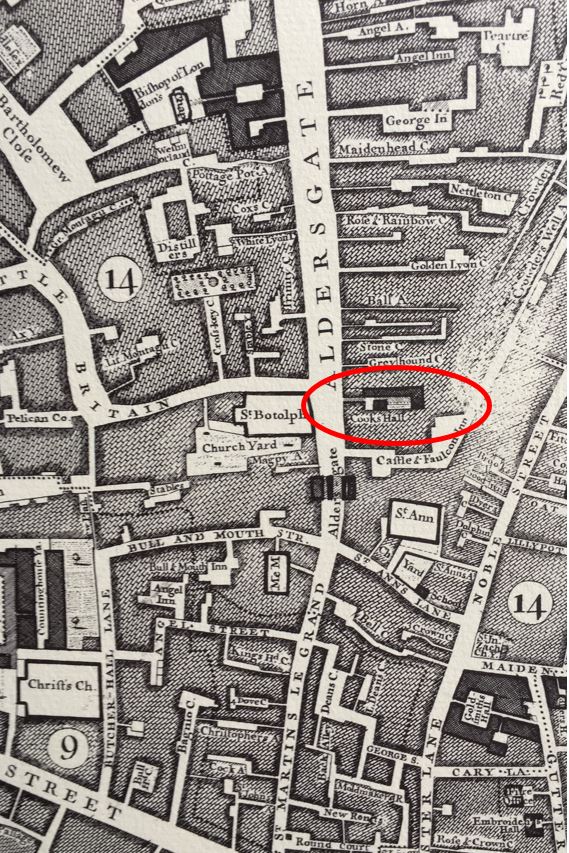
Cooks Hall
Walk up from Cheapside, along St Martin’s Le Grand to Aldersgate Street, just before the roundabout that circles part of the Museum of London, and opposite the junction with Little Britain is a building with two plaques.

The first plaque, on the right in the above photo records that this was the site of Cooks Hall, which was destroyed by fire in 1771:

The Worshipful Company of Cooks is one of the City’s old Guilds or Companies, with origins dating back possibly to the twelve century.
The Cooks received their first charter in July 1482, however in the years prior to the award of a charter, the definition of a Cook was not clear, and different groups involved in the production of food were setting up their own Guilds.
The book “The Armorial Bearings of the Guilds of London” provides some background (and uses the original word for a Guild, a Mistery):
“Some confusion exists as to the early functions of the Cooks, the Pastelers, and the Pie-Bakers, each of which appears to have existed formerly as a separate mistery with its own master and ordinances. Regulations of 1379 and 1388, forbidding pastelers to buy ‘garbage’ (probably offal) from cooks for the purpose of making pasties, indicates that the pasteleres’ trade was concerned with the manufacture of meat pies.”
It appears that if Pastelers and Pie-Bakers had existed as separate Guilds, by the time the Cooks received their charter, these separate Guilds may have simply integrated with the Cooks over time or just disappeared. A shame as I rather like the idea of a Worshipful Company of Pie-Bakers (there is still a Company of Bakers however their origins appear to be more aligned with those who baked bread).
The Cooks purchased land in Aldersgate for their hall around 1500, and remained on the site until the fire of 1771. Their hall survived the Great Fire of 1666, although was rebuilt shortly after, which implies there may have been some damage. There was another fire in 1764 before the fire which finally destroyed the hall in 1771.
Newspapers on the 16th August 1771 reported on the fire, and give an idea of the surrounding area of this part of Aldersgate Street:
“Yesterday morning, a little before One o’Clock, a Fire broke out at Cooks-Hall, in Aldersgate Street, which consumed the same, with a large Quantity of Timber in Mr. Hatton’s timber-yard adjoining; it likewise burnt the greatest Part of the Nag’s Head Alehouse, with a Stable and Outhouses belonging to it, and damaged the back part of several of the Dwelling-Houses that front the street”.
Fires were a regular occurrence across the city, and the above report gives an idea of how many buildings were clustered in a small area, and the inflammable materials that would help a fire to spread.
Companies such as the Cooks guarded their role in the setting of rules and regulation of their trade, as was typical of the City of London. On the same page as the above report of the fire, there is the following report, showing how far the City was prepared to go in protecting their privileges:
“My Lord Mayor, we are told, has declared he will spend every shilling he is worth sooner than submit to any Encroachments on the Privileges of the City, though by the King himself, to which end he is getting proper Information and is exceedingly assiduous to come to Action; and in order to enable him to go through with his design, ’tis said he will be again elected Lord Mayor for the Year ensuing”.
It may have been just electioneering, as having a Lord Mayor prepared to spend all their money in defense of the City’s privileges would have been a good message in the campaign for another term as Lord Mayor.
As the hall did not burn down until 1771, it was shown on the Roque map of 1746:

The coat of arms of the Worshipful Company of Cooks is shown below:

A pheasant is standing at the top, and to either side is a buck and a doe. Originally these were shown transfixed by an arrow – presumably to represent dead animals ready for cooking, however the arrows were removed from 1634 onwards.
The plant shown three times on the central shield is a Columbine, and there are a couple of theories as to the use of this flower as it does not have an obvious association with cooking.
It could be that the flower represents one of the three forms of ginger which apparently was known as colambyne, or it could have been down to possible medicinal properties of Columbine, and included in the arms of the Cooks to show the benefits of using a member of the Cooks Company for the cooking of food.
The Worshipful Company of Cooks are still an active City Company. After the loss of their hall, they met in the Albion Tavern in Aldersgate Street, and when this was demolished, they moved their functions to the Innholders’ Hall.
The Cooks are the only City company to have two Masters. The Cooks believe this was so that the Sovereign and Lord Mayor of the City could call upon the Master of the Cooks. with two Masters allowing this to happen at the same time.
The plaque recording the location of the Cooks Hall is interesting for those with a rather geeky love of what can be found on the City’s streets. It is one of a few that has the details of when it was made in the lower right corner of the plaque:

The details imply that the plaque was made on the 26th December 1985, by David Birch of the London Pottery at 96 Kingston Road, SW19.
The London Pottery now seems to be part of the London Design Studio which is still at 96 Kingston Road.
The second plaque, just to the left of the Cooks Hall plaque is to mark the site of:
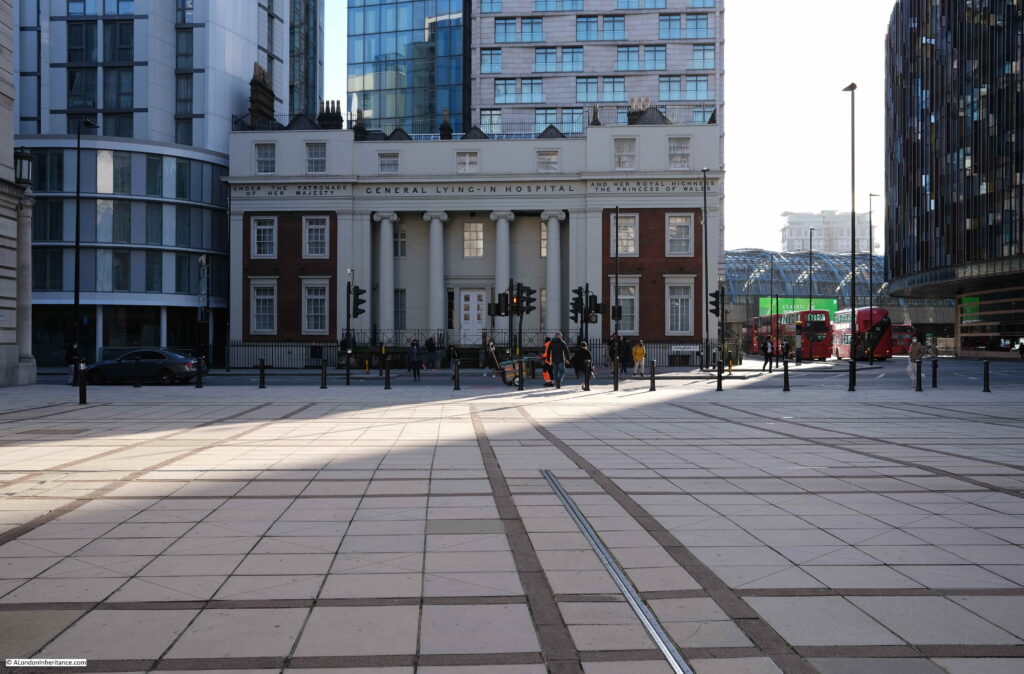
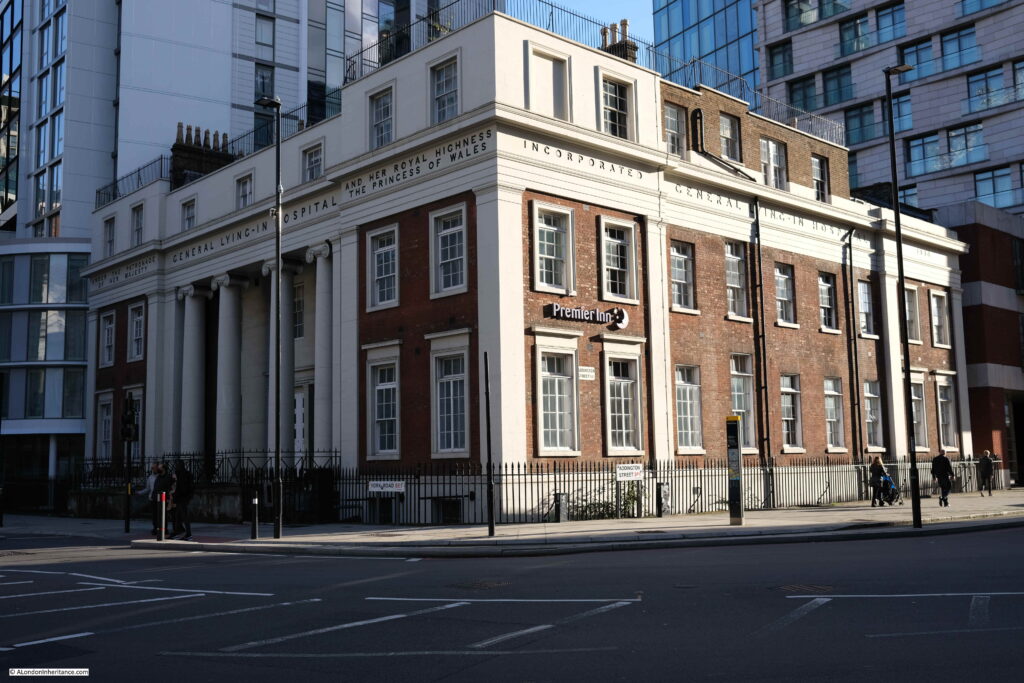
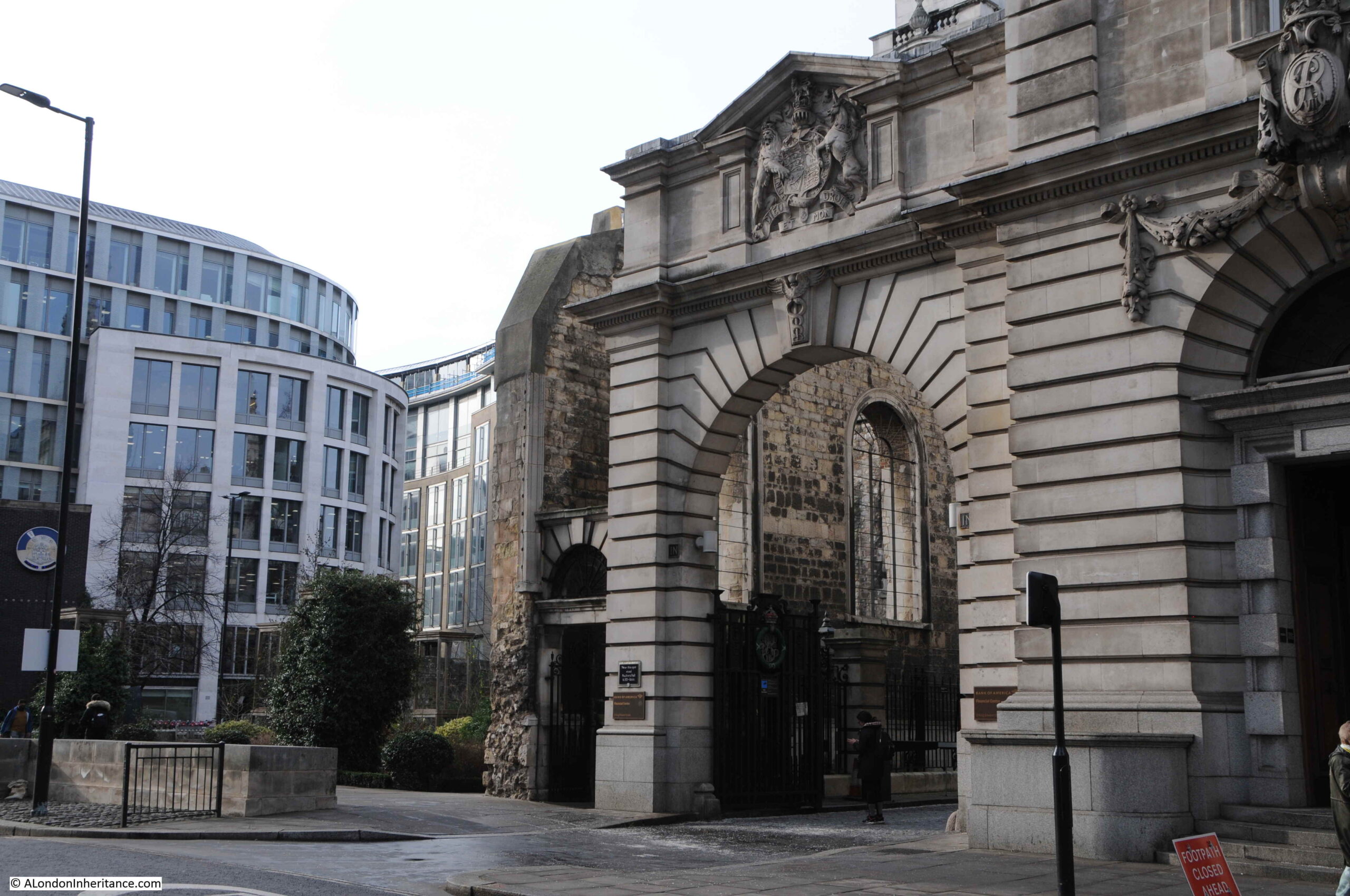
St Mark’s Hospital
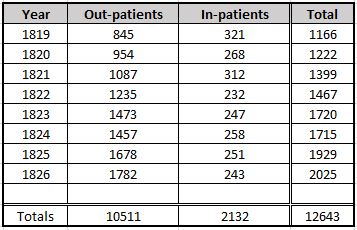
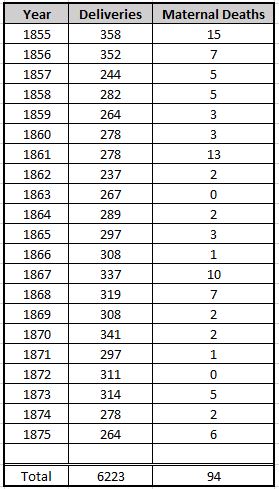
The plaque records that this was the site of St Mark’s Hospital, founded by Frederick Salmon in 1835:

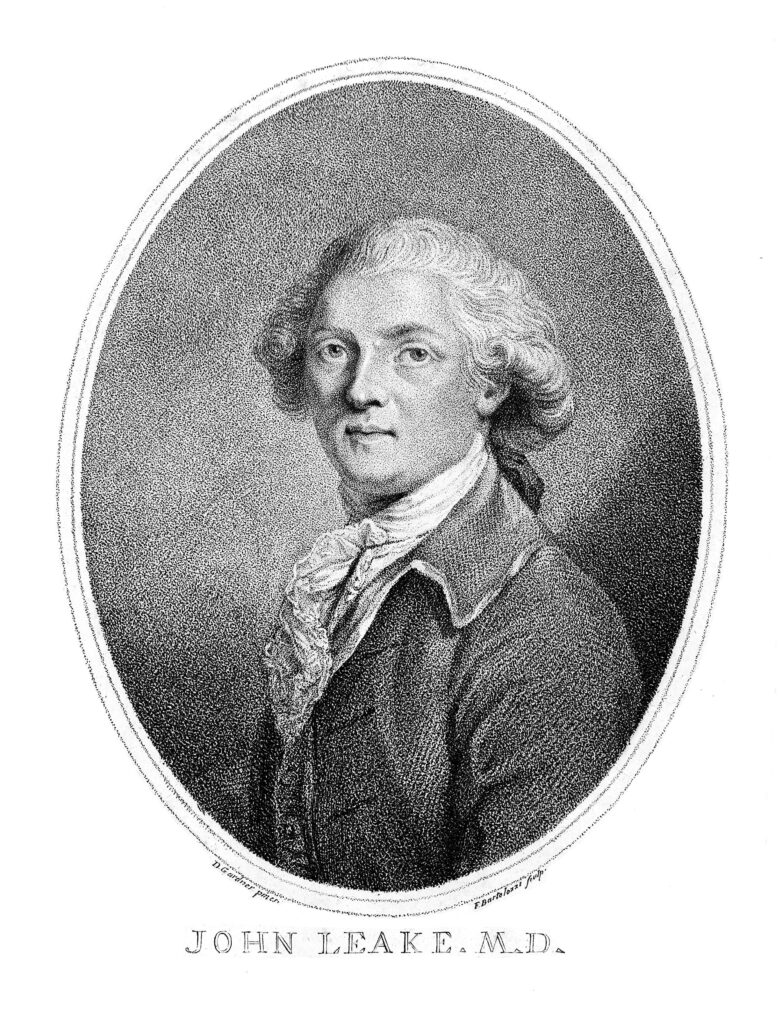
Frederick Salmon was born in Bath in 1796, and moved to London to take up a position as a medical student at St Bartholomew’s Hospital. After qualification, he set up in practice in Broad Street, where he developed a special interest in rectal diseases, which seems to have originated from his apprenticeship in Bath where patients with intestinal problems would be found as taking the Bath waters was thought to be a cure.
To further this interest, and to help the large numbers of people he was seeing with these problems at his Broad Street practice, he purchased a building at 11 Aldersgate Street in 1835 where he established the “Infirmary for the Relief of the Poor afflicted with Fistula and other Diseases of the Rectum”.
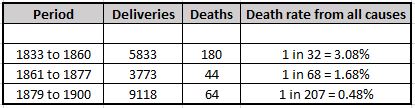
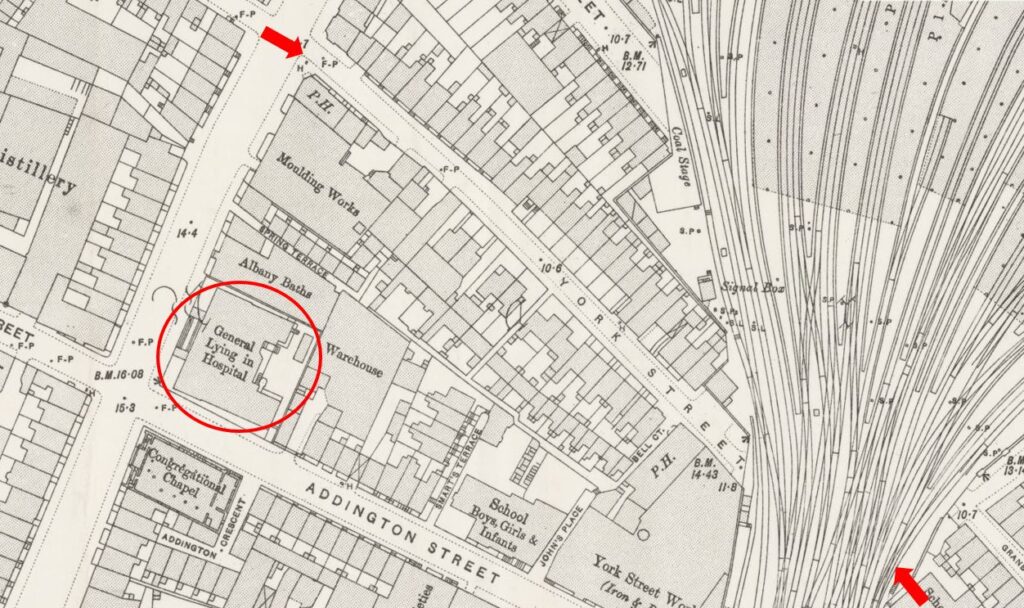
The infirmary was set up as a charity, and was small, with only seven beds available.
The infirmary was not in Aldersgate Street for long. The size of the building and the number of beds that could be accommodated was a problem, so three years after opening, the infirmary moved to a larger building at 38 Charterhouse Square, with Frederick Salmon continuing to run the infirmary almost single handed.
The infirmary would not stay for long in Charterhouse Square, and the next move would also include a name change. Although the plaque in Aldersgate Street states St Mark’s Hospital, the full name of the establishment was the “Infirmary for Fistula and Other Diseases of the Rectum”.
Despite covering serious medical conditions, this was probably not a good name to use for fund raising, or perhaps for patients to admit where they were attending for treatment, so at a meeting of the Committee of Management reported in the Morning Post on 27th April 1852: “the Chairman directed especial attention to that part of the Committee’s Report which recommended the change in the title of the Charity from that of Fistula Infirmary to St Mark’s Hospital” – the recommendation to change name was universally carried.
By 1852, Frederick Salmon had additional support as the Committee of Management stated that “the cordial thanks of the Governors be given to John Daniel, M.D. the Honorary Physician and to Frederick Salmon, the Hon Surgeon, and Founder of the Institution, for the gratuitous and effective discharge of their duties during the past year”.
The change in name also took place at the same time as the third change in location. In 1851 a site in City Road was purchased from the Worshipful Company of Dyers, and following conversion, the hospital, with the new name, opened in April 1852.
Cuthbert Dukes in a brief history of Frederick Salmon and the hospital, claimed that the source of the name was the move of the hospital to City Road on St. Mark’s Day, the 25th of April I852. (The history can be found as a PDF here)
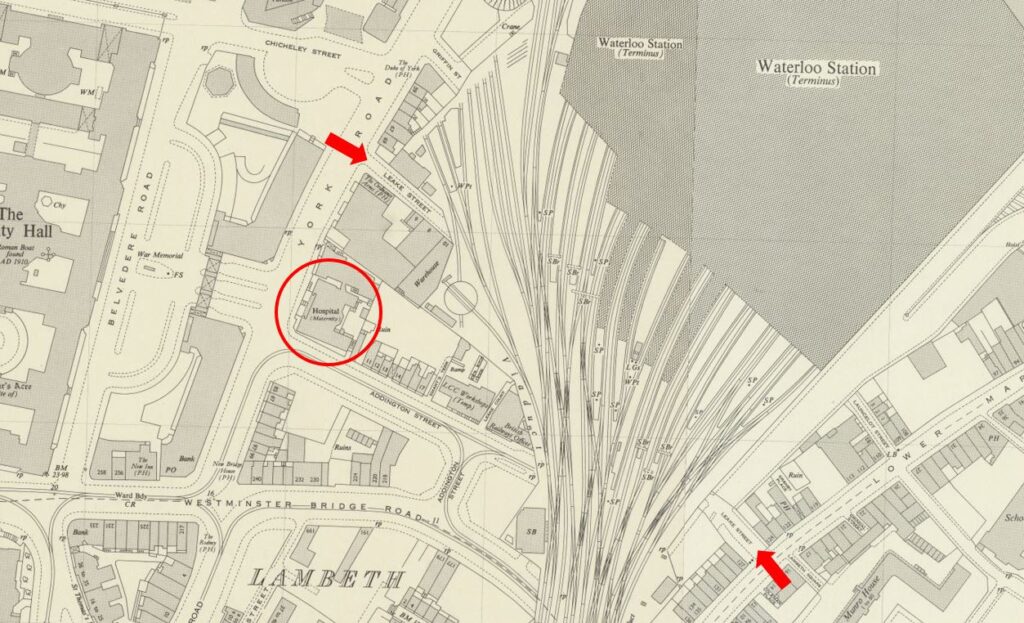
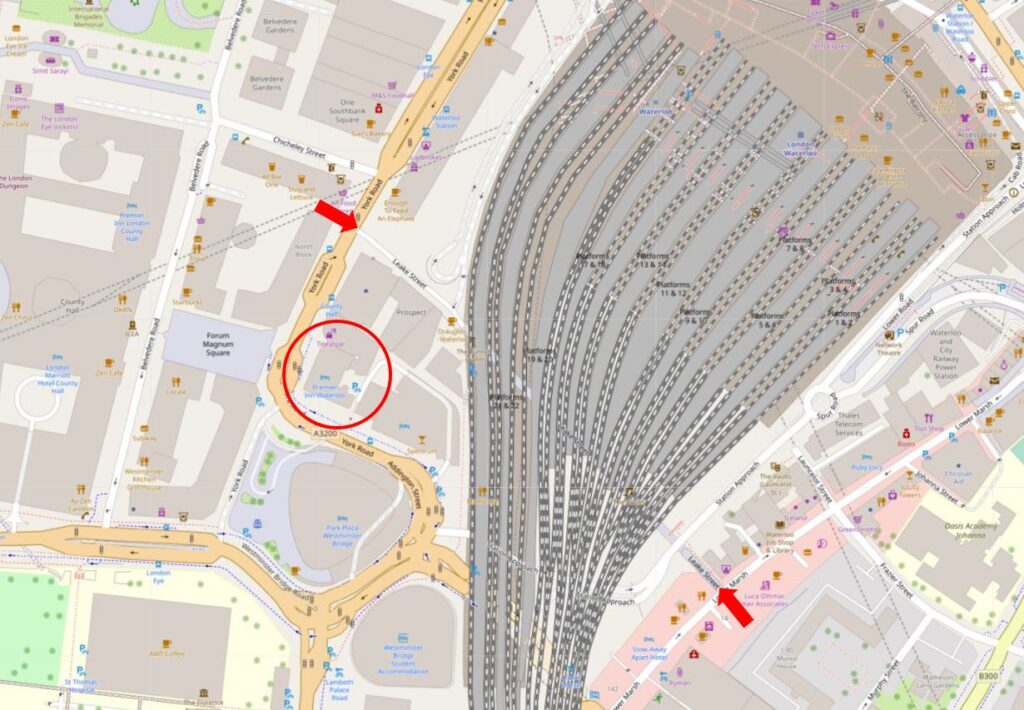
St Mark’s Hospital would stay in City Road until 1995, when it moved to Watford Road
Harrow, as part of Northwick Hospital.
St Mark’s continues to be a specialist hospital for diseases of the bowel, and with St Mark’s Academic Institute, works to develop skills and treatment for intestinal and colorectal disorders, so has stayed true to Frederick Salmon’s original specialist interest and intention for his original infirmary in Aldersgate Street.
Perhaps one of the most well known names treated by Frederick Salmon was Charles Dickens who was treated for an anal fistula in 1841, which Dickens blamed on too much sitting at his desk.
Frederick Salmon died at the age of 72 on the 3rd of January 1868 at Droitwich, which had become his home after retiring from St Mark’s Hospital in 1859.
Just four of the roughly 170 plaques that can be found across the streets of the City of London, but each hinting at a long and comprehensive history, of which I have only just scratched the surface in today’s post.
The St Mark’s Hospital plaque is historically wrong as the name would not come into use until the hospital moved to City Road, however I suspect the City of London were not too keen on the plaque recording the site of the “Infirmary for Fistula and Other Diseases of the Rectum”, but it is brilliant that Frederick Salmon, the founder of the hospital is named.